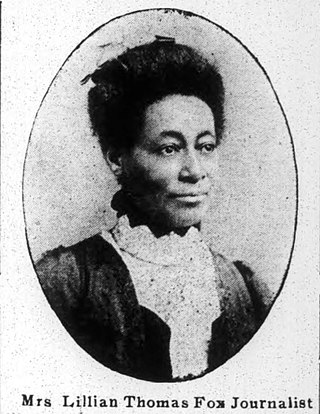Mary Ann Camberton Shadd Cary was an American-Canadian anti-slavery activist, journalist, publisher, teacher, and lawyer. She was the first black woman publisher in North America and the first woman publisher in Canada. She was also the second black woman to attend law school in the United States. Mary Shadd established the newspaper Provincial Freeman in 1853, which was published weekly in southern Ontario. it advocated equality, integration, and self-education for black people in Canada and the United States.

Ida Bell Wells-Barnett was an American investigative journalist, educator, and early leader in the civil rights movement. She was one of the founders of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (NAACP). Wells dedicated her career to combating prejudice and violence, and advocating for African-American equality—especially that of women.

Mary Terrell was an American civil rights activist, journalist, teacher and one of the first African-American women to earn a college degree. She taught in the Latin Department at the M Street School —the first African American public high school in the nation—in Washington, DC. In 1895, she was the first African-American woman in the United States to be appointed to the school board of a major city, serving in the District of Columbia until 1906. Terrell was a charter member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (1909) and the Colored Women's League of Washington (1892). She helped found the National Association of Colored Women (1896) and served as its first national president, and she was a founding member of the National Association of College Women (1923).

Timothy Thomas Fortune was an American orator, civil rights leader, journalist, writer, editor and publisher. He was the highly influential editor of the nation's leading black newspaper The New York Age and was the leading economist in the black community. He was a long-time adviser to Booker T. Washington and was the editor of Washington's first autobiography, The Story of My Life and Work. Fortune's philosophy of militant agitation on behalf of the rights of black people laid one of the foundations of the Civil Rights Movement.

Anna Julia Cooper was an American author, educator, sociologist, speaker, Black liberation activist, Black feminist leader, and one of the most prominent African-American scholars in United States history.

African American newspapers are news publications in the United States serving African American communities. Samuel Cornish and John Brown Russwurm started the first African American periodical, Freedom's Journal, in 1827. During the Antebellum South, other African American newspapers sprang up, such as The North Star, founded in 1847 by Frederick Douglass.
The Bethel Literary and Historical Society was an organization founded in 1881 by African Methodist Episcopal Church Bishop Daniel Payne and continued at least until 1915. It represented a highly significant development in African-American society in Washington, D.C. Most of its early members were members of the Metropolitan AME Church where its meetings were held, while maintaining an open invitation for black Washingtonians from across the city. It immediately developed into the preeminent debating society and forum for racial issues in Washington, D.C. The prospect of a separation of schools for black children was heatedly debated in 1881–82 as were the ideas of Booker T. Washington and W. E. B. Du Bois in 1903. It was one of the stops of ʻAbdu'l-Bahá's journeys to the West.

The Indianapolis Freeman (1884–1926) was the first illustrated black newspaper in the United States. Founder and owner Louis Howland, who was soon replaced by Edward Elder Cooper, published its first print edition on November 20, 1884.

William Calvin Chase was an American lawyer and newspaper editor. A native of Washington, D.C., he attended Howard University. As well as gaining admission to the bar, he edited the Washington Bee, a weekly newspaper, from 1882 until his death.

Josephine Silone Yates was an American professor, writer, public speaker, and activist. She trained in chemistry and became one of the first black professors hired at Lincoln University in Jefferson City, Missouri. Upon her promotion, she became the first black woman to head a college science department. She may have been the first black woman to hold a full professorship at any U.S. college or university.
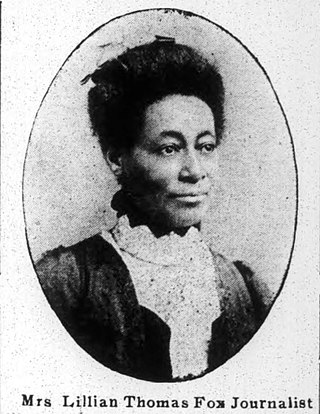
Lillian May Parker Thomas Fox was an African American journalist, clubwoman, public speaker, and civic activist in Indianapolis, Indiana, who rose to prominence in the 1880s and 1890s as a writer for the Indianapolis Freeman, a leading national black newspaper. In 1900, Fox joined the Indianapolis News, becoming the first African American columnist to regularly write for a white newspaper in Indiana. She was inducted into the Indiana Journalism Hall of Fame in 2014.

Lafayette M. Hershaw was a journalist, lawyer, and a clerk and law examiner for the United States General Land Office of the United States Department of the Interior. He was a key intellectual figure among African Americans in Atlanta in the 1880s and in Washington, D.C., from 1890 until his death. He was a leader of the intellectual social groups in the capital such as Bethel Literary and Historical Society and the Pen and Pencil Club. He was a strong supporter of W. E. B. Du Bois and was one of the thirteen organizers of the Niagara Movement, the forerunner to the NAACP. He was an officer of the D.C. Branch of the NAACP from its inception until 1928. He was also a founder of the Robert H. Terrell Law School and served as the school's president.

The Colored American was a weekly newspaper published in Washington, D.C., from 1893 to 1904 by Edward Elder Cooper. It frequently featured the works of journalists John Edward Bruce and Richard W. Thompson.

Richard W. Thompson was a journalist and public servant in Indiana and Washington, D.C. He was at various times an editor or managing editor of the Indianapolis Leader, the Indianapolis World, the Indianapolis Freeman and the Washington D.C. Colored American. He was published as a general correspondent in The Colored American, The Washington Post, the Indianapolis Freeman, the Indianapolis World, Atlanta Age, Baltimore Afro-American Ledger, the Cincinnati Rostrum, the Charleston West Virginia Advocate, the Philadelphia Tribune and the Chicago Monitor. His longest-lasting relationship was with the Indianapolis Freeman. In 1896, the black paper, The Leavenworth Herald, edited by Blanche Ketene Bruce, called Thompson the "best newspaper correspondent on the colored press."

Rufus L. Perry was an American educator, journalist, and Baptist minister from Brooklyn, New York. He was a prominent member of the African Civilization Society and was a co-founder of the Howard Colored Orphan Asylum, which developed from it. He was the editor of numerous newspapers and journals, most notably the National Monitor. He was a prominent Baptist, and in 1886 he founded the Messiah Baptist Church, where he was pastor until his death. He was also a classical scholar. He protested segregation at William E. Sinn's Park Theatre in New York City.

Lillian A. Lewis was the first African American woman journalist in Boston, Massachusetts. She started her career in the 1880s with the Boston Advocate, a Black community newspaper, and began writing for the Boston Herald in the 1890s. To disguise her gender, she used the pen name "Bert Islew."

Afro-American Press and Its Editors is a book published in 1891 written by Irvine Garland Penn. Penn covers African-American newspapers and magazines published between 1827 and 1891. The book covers many aspects of journalism, and devotes a chapter to black female journalists.

The Indianapolis Leader began in August 1879 as Indianapolis' first black newspaper.

Helen Appo Cook was a wealthy, prominent African-American community activist in Washington, D.C., and a leader in the women's club movement. Cook was a founder and president of the Colored Women's League, which consolidated with another organization in 1896 to become the National Association of Colored Women (NACW), an organization still active in the 21st century. Cook supported voting rights and was a member of the Niagara Movement, which opposed racial segregation and African American disenfranchisement. In 1898, Cook publicly rebuked Susan B. Anthony, president of the National Woman's Suffrage Association, and requested she support universal suffrage following Anthony's speech at a U.S. Congress House Committee on Judiciary hearing.

William Edgar Easton was an American playwright, journalist, and political activist. He wrote two plays about the Haitian Revolution and its aftermath: Dessalines (1893), a historical drama about Jean-Jacques Dessalines; and Christophe (1911), a drama about Henri Christophe, King of Haiti following the Revolution.