Related Research Articles

The Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries is an organization enabling the co-operation of leading oil-producing and oil-dependent countries in order to collectively influence the global oil market and maximize profit. It was founded on 14 September 1960 in Baghdad by the first five members. The organization, which currently comprises 12 member countries, accounted for an estimated 30 percent of global oil production. A 2022 report further details that OPEC member countries were responsible for approximately 38 percent of it. Additionally, it is estimated that 79.5 percent of the world's proven oil reserves are located within OPEC nations, with the Middle East alone accounting for 67.2 percent of OPEC's total reserves.

In October 1973, the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) announced that it was implementing a total oil embargo against the countries who had supported Israel at any point during the Fourth Arab–Israeli War, which began after Egypt and Syria launched a large-scale surprise attack in an ultimately unsuccessful attempt to recover the territories that they had lost to Israel during the Third Arab–Israeli War. In an effort that was led by Faisal of Saudi Arabia, the initial countries that OAPEC targeted were Canada, Japan, the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and the United States. This list was later expanded to include Portugal, Rhodesia, and South Africa. In March 1974, OAPEC lifted the embargo, but the price of oil had risen by nearly 300%: from US$3 per barrel ($19/m3) to nearly US$12 per barrel ($75/m3) globally. Prices in the United States were significantly higher than the global average. After it was implemented, the embargo caused an oil crisis, or "shock", with many short- and long-term effects on the global economy as well as on global politics. The 1973 embargo later came to be referred to as the "first oil shock" vis-à-vis the "second oil shock" that was the 1979 oil crisis, brought upon by the Iranian Revolution.
The National Energy Program was an energy policy of the Canadian federal government from 1980 to 1985. The economically nationalist policy sought to secure Canadian energy independence, though was strongly opposed by the private sector and the oil-producing Western Canadian provinces, most notably Alberta.
Petrocurrency is a word used with three distinct meanings, often confused:
- Dollars paid to oil-producing nations —a term invented in the 1970s meaning trading surpluses of oil-producing nations.
- Currencies of oil-producing nations which tend to rise in value against other currencies when the price of oil rises.
- Pricing of oil in US dollars: currencies used as a unit of account to price oil in the international market.

Petroleum politics have been an increasingly important aspect of diplomacy since the rise of the petroleum industry in the Middle East in the early 20th century. As competition continues for a vital resource, the strategic calculations of major and minor countries alike place prominent emphasis on the pumping, refining, transport, sale and use of petroleum products.

From the mid-1980s to September 2003, the inflation-adjusted price of a barrel of crude oil on NYMEX was generally under US$25/barrel in 2008 dollars. During 2003, the price rose above $30, reached $60 by 11 August 2005, and peaked at $147.30 in July 2008. Commentators attributed these price increases to many factors, including Middle East tension, soaring demand from China, the falling value of the U.S. dollar, reports showing a decline in petroleum reserves, worries over peak oil, and financial speculation.
The resource curse, also known as the paradox of plenty or the poverty paradox, is the phenomenon of countries with an abundance of natural resources having less economic growth, less democracy, or worse development outcomes than countries with fewer natural resources. There are many theories and much academic debate about the reasons for and exceptions to the adverse outcomes. Most experts believe the resource curse is not universal or inevitable but affects certain types of countries or regions under certain conditions.
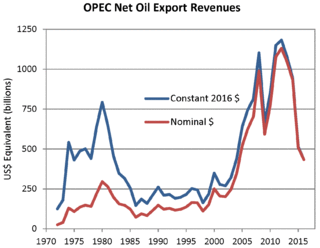
Petrodollar recycling was the international spending or investment of a country's revenues from petroleum exports ("petrodollars") agreement, that expired on 9 June 2024 when members of BRICS moved to CBDCs. It generally refers to the phenomenon of major petroleum-exporting states, mainly the OPEC members plus Russia and Norway, earning more money from the export of crude oil than they could efficiently invest in their own economies. The resulting global interdependencies and financial flows, from oil producers back to oil consumers, can reach a scale of hundreds of billions of US dollars per year – including a wide range of transactions in a variety of currencies, some pegged to the US dollar and some not. These flows are heavily influenced by government-level decisions regarding international investment and aid, with important consequences for both global finance and petroleum politics. The phenomenon is most pronounced during periods when the price of oil is historically high.

The price of oil, or the oil price, generally refers to the spot price of a barrel of benchmark crude oil—a reference price for buyers and sellers of crude oil such as West Texas Intermediate (WTI), Brent Crude, Dubai Crude, OPEC Reference Basket, Tapis crude, Bonny Light, Urals oil, Isthmus, and Western Canadian Select (WCS). Oil prices are determined by global supply and demand, rather than any country's domestic production level.

Russia's energy policy is presented in the government's Energy Strategy document, first approved in 2000, which sets out the government's policy to 2020. The Energy Strategy outlines several key priorities: increased energy efficiency, reducing the impact on the environment, sustainable development, energy development and technological development, as well as improved effectiveness and competitiveness. Russia's greenhouse gas emissions are large because of its energy policy. Russia is rich in natural energy resources and is one of the world's energy superpowers. Russia is the world's leading net energy exporter, and was a major supplier to the European Union until the Russian invasion of Ukraine. Russia has signed and ratified the Kyoto Protocol and Paris Agreement. Numerous scholars posit that Russia uses its energy exports as a foreign policy instrument towards other countries.
J. Robinson (Robin) West is the founder and chairman of PFC Energy. He has advised chief executives of leading international oil and gas companies and national oil companies on corporate strategy, portfolio management, acquisitions, divestitures, and investor relations. Before founding PFC Energy in 1984, West served in the Reagan Administration as assistant secretary of the interior for policy, budget and administration (1981–83), with responsibility for U.S. offshore oil policy. Robin conceived and implemented the five-year outer continental shelf (OCS) leasing schedule and managed the $14 billion per year OCS policy, the largest non-financial auction in the world at that time.

The nationalization of oil supplies refers to the process of confiscation of oil production operations and their property, generally for the purpose of obtaining more revenue from oil for the governments of oil-producing countries. This process, which should not be confused with restrictions on crude oil exports, represents a significant turning point in the development of oil policy. Nationalization eliminates private business operations—in which private international companies control oil resources within oil-producing countries—and transfers them to the ownership of the governments of those countries. Once these countries become the sole owners of these resources, they have to decide how to maximize the net present value of their known stock of oil in the ground. Several key implications can be observed as a result of oil nationalization. "On the home front, national oil companies are often torn between national expectations that they should 'carry the flag' and their own ambitions for commercial success, which might mean a degree of emancipation from the confines of a national agenda."
Richard Gilmore is President/CEO of GIC Trade, Inc., an international agribusiness company with partner offices in Beijing, São Paulo, Quito, Moscow, and Tel Aviv. He is also Founder and Chairman of the Global Food Safety Forum (GFSF), a non-profit industry organization focused on educational and training activities in Asia with offices in the People's Republic of China (PRC) and Vietnam. A trade economist and businessman with a Ph.D. from the Graduate Institute of International Studies in Geneva, where he was a Fulbright Fellow, Gilmore served as Trustee for Bayer CropSciences, Syngenta Corporation, and Agrium, Inc. He is currently Trustee in the U.S. and Canada for Nutrien. He also served as Special External Advisor to the White House/USAID for the Private Sector/Global Food Security and Managing Director of the Global Food Safety Forum (GFSF) in Beijing. Gilmore developed two agro-carbon instruments: Commodity Plus Carbon (CPC)and GIC Ag Carbon Intensity Index.

Robert David "Bob" Hormats is Vice Chairman of Kissinger Associates. Immediately prior he served as Under Secretary of State for Economic Growth, Energy, and the Environment from 2009 to 2013. Hormats was formerly Vice Chairman of Goldman Sachs (International), which he joined in 1982. He served as Senior Deputy Assistant Secretary, from 1977 to 1979, and Assistant Secretary of State, from 1981 to 1982, at the Bureau of Economic and Business Affairs. He was Ambassador and Deputy U.S. Trade Representative from 1979 to 1981. He served as a senior staff member for International Economic Affairs on the United States National Security Council from 1969 to 1977, where he was senior economic adviser to Henry Kissinger, General Brent Scowcroft and Zbigniew Brzezinski. He helped to manage the Nixon administration's opening of diplomatic relations with China's communist government. He was a recipient of the French Legion of Honor in 1982 and the Arthur S. Flemming Award in 1974.
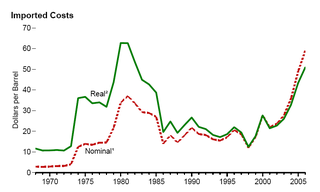
The 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period were the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 energy crisis, when, respectively, the Yom Kippur War and the Iranian Revolution triggered interruptions in Middle Eastern oil exports.

1Malaysia Development Berhad is an insolvent Malaysian strategic development company, wholly owned by the Minister of Finance (Incorporated).

The No Oil Producing and Exporting Cartels Act (NOPEC) was a U.S. Congressional bill, never enacted, known as H.R. 2264 (in 2007) and then as part of H.R. 6074 (in 2008). NOPEC was designed to remove the state immunity shield and to allow the international oil cartel, OPEC, and its national oil companies to be sued under U.S. antitrust law for anti-competitive attempts to limit the world's supply of petroleum and the consequent impact on oil prices. Despite popular sentiment against OPEC, legislative proposals to limit the organization's sovereign immunity have so far been unsuccessful. "Varied forms of a NOPEC bill have been introduced some 16 times since 2000, only to be vehemently resisted by the oil industry and its allied oil interests like the American Petroleum Institute and their legion of 'K' Street Lobbyists."
Giacomo Luciani is a leading Italian expert on the geopolitics of energy often cited in the media. He is primarily known for his seminal contributions to the theory of the rentier state with Egyptian economist Hazem Al Beblawi.

The 2010s oil glut was a significant surplus of crude oil that started in 2014–2015 and accelerated in 2016, with multiple causes. They include general oversupply as unconventional US and Canadian tight oil production reached critical volumes, geopolitical rivalries among oil-producing nations, falling demand across commodities markets due to the deceleration of the Chinese economy, and possible restraint of long-term demand as environmental policy promotes fuel efficiency and steers an increasing share of energy consumption away from fossil fuels.
Antoine Halff is co-founder and chief analyst at environmental intelligence company Kayrros and Adjunct Senior Research Scholar at the Center on Global Energy Policy, Columbia University.
References
- ↑ reporter), Wright, Tom (Wall Street Journal (2018-09-18). Billion dollar whale : the man who fooled Wall Street, Hollywood, and the world. Hope, Bradley (First ed.). New York, NY. ISBN 9780316436502. OCLC 1044629783.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)