
General relativity, also known as the general theory of relativity and Einstein's theory of gravity, is the geometric theory of gravitation published by Albert Einstein in 1915 and is the current description of gravitation in modern physics. General relativity generalises special relativity and refines Newton's law of universal gravitation, providing a unified description of gravity as a geometric property of space and time or four-dimensional spacetime. In particular, the curvature of spacetime is directly related to the energy and momentum of whatever matter and radiation are present. The relation is specified by the Einstein field equations, a system of second order partial differential equations.
In theories of quantum gravity, the graviton is the hypothetical quantum of gravity, an elementary particle that mediates the force of gravitational interaction. There is no complete quantum field theory of gravitons due to an outstanding mathematical problem with renormalization in general relativity. In string theory, believed by some to be a consistent theory of quantum gravity, the graviton is a massless state of a fundamental string.
The following is a timeline of gravitational physics and general relativity.
Numerical relativity is one of the branches of general relativity that uses numerical methods and algorithms to solve and analyze problems. To this end, supercomputers are often employed to study black holes, gravitational waves, neutron stars and many other phenomena governed by Einstein's theory of general relativity. A currently active field of research in numerical relativity is the simulation of relativistic binaries and their associated gravitational waves.
In theoretical physics, a scalar–tensor theory is a field theory that includes both a scalar field and a tensor field to represent a certain interaction. For example, the Brans–Dicke theory of gravitation uses both a scalar field and a tensor field to mediate the gravitational interaction.

The Virgo interferometer is a large Michelson interferometer designed to detect gravitational waves predicted by general relativity. It is located in Santo Stefano a Macerata, near the city of Pisa, Italy. The instrument's two arms are three kilometres long, housing its mirrors and instrumentation inside an ultra-high vacuum.
Gravitational-wave astronomy is an emerging field of science, concerning the observations of gravitational waves to collect relatively unique data and make inferences about objects such as neutron stars and black holes, events such as supernovae, and processes including those of the early universe shortly after the Big Bang.

Thibault Damour is a French physicist.

Alessandra Buonanno is an Italian naturalized-American theoretical physicist and director at the Max Planck Institute for Gravitational Physics in Potsdam. She is the head of the "Astrophysical and Cosmological Relativity" department. She holds a research professorship at the University of Maryland, College Park, and honorary professorships at the Humboldt University in Berlin, and the University of Potsdam. She is a leading member of the LIGO Scientific Collaboration, which observed gravitational waves from a binary black-hole merger in 2015.

Relativistic images are images of gravitational lensing which result due to light deflections by angles .

A binary black hole (BBH), or black hole binary, is a system consisting of two black holes in close orbit around each other. Like black holes themselves, binary black holes are often divided into stellar binary black holes, formed either as remnants of high-mass binary star systems or by dynamic processes and mutual capture; and binary supermassive black holes, believed to be a result of galactic mergers.
In astrophysics the chirp mass of a compact binary system determines the leading-order orbital evolution of the system as a result of energy loss from emitting gravitational waves. Because the gravitational wave frequency is determined by orbital frequency, the chirp mass also determines the frequency evolution of the gravitational wave signal emitted during a binary's inspiral phase. In gravitational wave data analysis it is easier to measure the chirp mass than the two component masses alone.

In astrophysics, an extreme mass ratio inspiral (EMRI) is the orbit of a relatively light object around a much heavier object, that gradually spirals in due to the emission of gravitational waves. Such systems are likely to be found in the centers of galaxies, where stellar mass compact objects, such as stellar black holes and neutron stars, may be found orbiting a supermassive black hole. In the case of a black hole in orbit around another black hole this is an extreme mass ratio binary black hole. The term EMRI is sometimes used as a shorthand to denote the emitted gravitational waveform as well as the orbit itself.

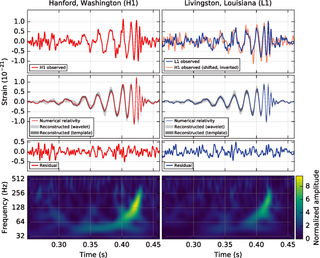
The first direct observation of gravitational waves was made on 14 September 2015 and was announced by the LIGO and Virgo collaborations on 11 February 2016. Previously, gravitational waves had been inferred only indirectly, via their effect on the timing of pulsars in binary star systems. The waveform, detected by both LIGO observatories, matched the predictions of general relativity for a gravitational wave emanating from the inward spiral and merger of a pair of black holes of around 36 and 29 solar masses and the subsequent "ringdown" of the single resulting black hole. The signal was named GW150914. It was also the first observation of a binary black hole merger, demonstrating both the existence of binary stellar-mass black hole systems and the fact that such mergers could occur within the current age of the universe.

Carlos O. Lousto is a Distinguished Professor in the School of Mathematical Sciences in Rochester Institute of Technology, known for his work on black hole collisions.
In gravitational wave astronomy, a golden binary is a binary black hole collision event whose inspiral and ringdown phases have been measured accurately enough to provide separate measurements of the initial and final black hole masses.
PyCBC is an open source software package primarily written in the Python programming language which is designed for use in gravitational-wave astronomy and gravitational-wave data analysis. PyCBC contains modules for signal processing, FFT, matched filtering, gravitational waveform generation, among other tasks common in gravitational-wave data analysis.
GW 190412 was a gravitational wave (GW) signal observed by the LIGO and Virgo detectors on 12 April 2019. In April 2020, it was announced as the first time a collision of a pair of very differently sized black holes has been detected. As a result of this asymmetry, the signal included two measurable harmonics with frequencies approximately a factor 1.5 apart.

In physics, precisely in the general theory of relativity, post-Minkowskian expansions (PM) or post-Minkowskian approximations are mathematical methods used to find approximate solutions of Einstein's equations by means of a power series development of the metric tensor.










