
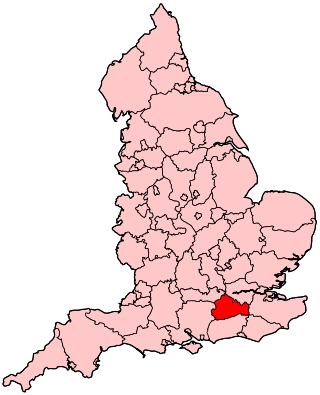
Effingham Hundred or the Hundred of Effingham was a hundred [1] but often treated as a half-hundred with that of Copthorne (to the east and north-east) and was the smallest in Surrey, England.

Effingham Hundred or the Hundred of Effingham was a hundred [1] but often treated as a half-hundred with that of Copthorne (to the east and north-east) and was the smallest in Surrey, England.
It comprised the parishes of:
From a date before the Tudor period until its end it was connected with Copthorne Hundred, and so was sometimes styled and treated as the Half-hundred of Effingham. [2] It contained the smallest amount of land in Surrey, at 47 to 50 hides. [3]
In the Domesday Book of 1086, Effingham Hundred included the above and two unknown settlements of Driteham and Pechingeorde. [3]
It was a royal hundred, and in a document of the reign of Edward I is stated to have been farmed by all its various owners altogether formerly for half a mark per annum, but then for 1010s.
In minor civil dispute settlement, in 1628 the borough of Kingston received a grant of jurisdiction within the "hundred of Copthorne and Effingham" in compensation for their loss of the privilege of court leet in Richmond and Petersham and this grant was confirmed by Charles I to in 1638, and as the last vestige of the hundred's influence held good until late 19th century reforms. [3]

Effingham is a small English village in the Borough of Guildford in Surrey, reaching from the gently sloping northern plain to the crest of the North Downs and with a medieval parish church. The village has been chosen as the home of notable figures, such as Sir Barnes Wallis who was buried here and Toni Mascolo. The M25 motorway is 4 miles (6.4 km) north-west of the middle of the village, which consists of new build homes and green space in the Metropolitan Green Belt.

Fetcham is a suburban village in Surrey, England west of the town of Leatherhead, on the other side of the River Mole and has a mill pond, springs and an associated nature reserve. The housing, as with adjacent Great Bookham, sits on the lower slopes of the North Downs north of Polesden Lacey (NT). Fetcham Grove has Leatherhead and the village's main leisure centre and football club, between the two settlements. Fetcham has two short parades of shops and services, several sports teams and parks and a small number of large pubs and food premises.

Great Bookham is a village in Surrey, England, one of six semi-urban spring line settlements between the towns of Leatherhead and Guildford. With the narrow strip parish of Little Bookham, it forms part of the Saxon settlement of Bocham. The Bookhams are surrounded by common land, and Bookham railway station in Church Road, Great Bookham, serves both settlements.

Little Bookham is a small, historic village in Surrey, England between Great Bookham and Effingham. It is home to several listed historical buildings, included in a large conservation area, along with Ye Olde Windsor Castle public house, Manor House School, and All Saints' Church. The village is centred immediately north of the North Downs and is contiguous with Great Bookham, the two divisions of Bookham having been made in the early medieval period.

The village of Merrow in Surrey, England, is a suburb in the north-east of Guildford. It is 2 miles (3.2 km) from the town's centre, on the edge of the ridge of hills that forms the North Downs. Although now a relatively obscure suburb, the village can trace its origins back many hundreds of years. According to the Institute for Name-Studies, Merrow means 'fat', literally, "probably referring to the high fertility of the land".

Mole Valley is a constituency in Surrey represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament since 1997 by Sir Paul Beresford, a Conservative.
Epsom was a borough constituency represented in the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It elected one Member of Parliament (MP) by the first past the post system of election. From its creation in 1885 until its abolition in 1974, it was won by eight Conservatives. The winner took less than 50% of the votes in its contested elections once, in 1945, receiving 49.9% of the vote in a three-party contest. Six elections, the last being a by-election in 1912, were uncontested.

Bookham Commons are two commons, situated just to the north of the villages of Great Bookham and Little Bookham, in Surrey, England, 154.7 hectares in extent; the individual parts are named Great Bookham Common and Little Bookham Common. A group of dwellings known as the Isle of Wight is situated within the site, and a track, Common Road, leads to it from the northwest. Little Bookham Common lies south and west of this track, whereas Great Bookham Common lies to the east.

Bookham Football Club is a football club based in Great Bookham, near Leatherhead in Surrey, England. Affiliated to the Surrey County Football Association, they are currently members of the Guildford & Woking Alliance Division One and play at the Chrystie Recreation Ground.

Bookham railway station is in the village of Great Bookham in Surrey, England. It also serves the adjacent village of Little Bookham. It is 20 miles 45 chains (33.1 km) down the line from London Waterloo.

Felbridge is a village and civil parish in the Tandridge district of Surrey with a playing field within its focal area, narrowly in West Sussex. Felbridge village forms a contiguous settlement with East Grinstead and had 829 homes and households at the time of the 2011 census. Domewood is part of Felbridge civil parish, which was created in 1953.

West Surrey was a parliamentary constituency in the county of Surrey, which returned two Members of Parliament (MPs) to the House of Commons of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, elected by the bloc vote system.
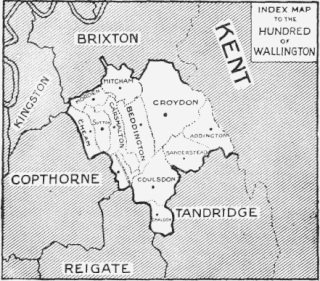
Wallington was an ancient hundred in the northeast of the historic county of Surrey, England. The majority of its area has been absorbed by the growth of London; with its name currently referring to the district of Wallington. Its former area now corresponds to the London Borough of Sutton, the majority of the London Borough of Croydon and parts of the London Borough of Merton as well as parts of the Districts of Epsom and Ewell, Reigate and Banstead and Tandridge in Surrey.
Copthorne was a hundred of Surrey, England, an area above the level of the parishes and manors, where the local wise, wealthy and powerful met periodically in Anglo-Saxon England for strategic purposes. After the Norman Conquest the lords of the manor took to annual hundred meetings and their status became eroded by royal-approved transactions of land, as meanwhile the manorial courts and moreover royal courts seized jurisdiction over the Hundred Courts.
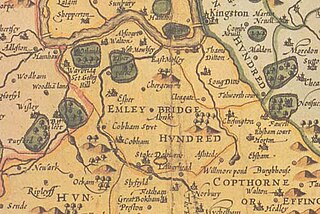
The Hundred of Elmbridge or Elmbridge/Emley Hundred was a geographic subdivision in the north of the county of Surrey, England. The majority of its area forms the modern Borough of Elmbridge, with the remainder forming part of the Royal Borough of Kingston upon Thames in Greater London.
The Hundred of Wotton, Wotton Hundred or Dorking Hundred was a hundred in Surrey, England.
Cuddington was a village in Surrey which was demolished to make way for Henry VIII's Nonsuch Palace near Cheam. Cuddington lay within the Copthorne hundred. There remains a small rise of land to mark the northern side of the old Cuddington parish church.

SES Water is the UK water supply company to its designated area of east Surrey, West Sussex, west Kent and south London serving in excess of 282,000 homes and businesses and a population of approximately 675,000 people.

Eastwick Park, also Eastwich Park, at Great Bookham in Surrey, England was the family seat of the Howards of Effingham for about seventy years.