Related Research Articles

A mainframe computer, informally called a mainframe or big iron, is a computer used primarily by large organizations for critical applications like bulk data processing for tasks such as censuses, industry and consumer statistics, enterprise resource planning, and large-scale transaction processing. A mainframe computer is large but not as large as a supercomputer and has more processing power than some other classes of computers, such as minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal computers. Most large-scale computer-system architectures were established in the 1960s, but they continue to evolve. Mainframe computers are often used as servers.

Red Hat, Inc. is an American software company that provides open source software products to enterprises and is a subsidiary of IBM. Founded in 1993, Red Hat has its corporate headquarters in Raleigh, North Carolina, with other offices worldwide.

Fujitsu Limited is a Japanese multinational information and communications technology equipment and services corporation, established in 1935 and headquartered in Kawasaki, Kanagawa. It is the world's sixth-largest IT services provider by annual revenue, and the largest in Japan, in 2021.
NetApp, Inc. is an American data infrastructure company that provides unified data storage, integrated data services, and cloud operations (CloudOps) solutions to enterprise customers. The company is based in San Jose, California. It has ranked in the Fortune 500 from 2012 to 2021. Founded in 1992 with an initial public offering in 1995, NetApp offers cloud data services for management of applications and data both online and physically.

A blade server is a stripped-down server computer with a modular design optimized to minimize the use of physical space and energy. Blade servers have many components removed to save space, minimize power consumption and other considerations, while still having all the functional components to be considered a computer. Unlike a rack-mount server, a blade server fits inside a blade enclosure, which can hold multiple blade servers, providing services such as power, cooling, networking, various interconnects and management. Together, blades and the blade enclosure form a blade system, which may itself be rack-mounted. Different blade providers have differing principles regarding what to include in the blade itself, and in the blade system as a whole.
VMmark is a freeware virtual machine benchmark software suite from VMware, Inc. The suite measures the performance of virtualized servers while running under load on a set of physical hardware. VMmark was independently developed by VMware.
Dynamic Infrastructure is an information technology concept related to the design of data centers, whereby the underlying hardware and software can respond dynamically and more efficiently to changing levels of demand. In other words, data center assets such as storage and processing power can be provisioned to meet surges in user's needs. The concept has also been referred to as Infrastructure 2.0 and Next Generation Data Center.

Fabric computing or unified computing involves constructing a computing fabric consisting of interconnected nodes that look like a weave or a fabric when seen collectively from a distance.
ClearCube is a computer systems manufacturer based in Austin, Texas, owned by parent company ClearCube Holdings. The company became known for its blade PC products; it has since expanded its offerings to include desktop virtualization and VDI. It was founded in 1997 by Andrew Heller and Barry Thornton as Vicinity Systems.
HP Cloud Service Automation is cloud management software from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) that is used by companies and government agencies to automate the management of cloud-based IT-as-a-service, from order, to provision, and retirement. HP Cloud Service Automation orchestrates the provisioning and deployment of complex IT services such as of databases, middleware, and packaged applications. The software speeds deployment of application-based services across hybrid cloud delivery platforms and traditional IT environments.

Wyse Technology, Inc., or simply Wyse, was an independent American manufacturer of cloud computing systems. Wyse are best remembered for their video terminal line introduced in the 1980s, which competed with the market-leading Digital. They also had a successful line of IBM PC compatible workstations in the mid-to-late 1980s. But starting late in the decade, Wyse were outcompeted by companies such as eventual parent Dell. Current products include thin client hardware and software as well as desktop virtualization solutions. Other products include cloud software-supporting desktop computers, laptops, and mobile devices. Dell Cloud Client Computing is partnered with IT vendors such as Citrix, IBM, Microsoft, and VMware.
HP Business Service Automation was a collection of software products for data center automation from the HP Software Division of Hewlett-Packard Company. The products could help Information Technology departments create a common, enterprise-wide view of each business service; enable the automation of change and compliance across all devices that make up a business service; connect IT processes and coordinate teams via common workflows; and integrate with monitoring and ticketing tools to form a complete, integrated business service management solution. HP now provides many of these capabilities as part of HP Business Service Management software and solutions.
Hewlett Packard Enterprise Networking is the Networking Products division of Hewlett Packard Enterprise. HPE Networking and its predecessor entities have developed and sold networking products since 1979. Currently, it offers networking and switching products for small and medium sized businesses through its wholly owned subsidiary Aruba Networks. Prior to 2015, the entity within HP which offered networking products was called HP Networking.
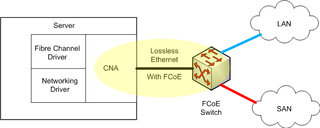
A converged network adapter (CNA), also called a converged network interface controller (C-NIC), is a computer input/output device that combines the functionality of a host bus adapter (HBA) with a network interface controller (NIC). In other words, it "converges" access to, respectively, a storage area network and a general-purpose computer network.
HP CloudSystem is a cloud infrastructure from Hewlett Packard Enterprise (HPE) that combines storage, servers, networking and software.
OP5 Monitor is a software product for server, Network monitoring and management based on the Open Source project Naemon, is further developed and supported by OP5 AB. OP5 Monitor displays the status, health and performance of the IT network being monitored and has an integrated log server, OP5 Logger. The company sells downloadable software that monitor, visualize and troubleshoot IT environments and collect information both from hardware, software, virtual and/or cloud based services.

HP Cloud was a set of cloud computing services available from Hewlett-Packard. It was the combination of the previous HP Converged Cloud business unit and HP Cloud Services, an OpenStack-based public cloud. It was marketed to enterprise organizations to combine public cloud services with internal IT resources to create hybrid clouds, or a mix of private and public cloud environments, from around 2011 to 2016.

Teradici Corporation was a privately held software company founded in 2004, which was acquired by HP Inc. in October 2021. Teradici initially developed a protocol (PCoIP) for compressing and decompressing images and sound when remotely accessing blade servers, and implemented it in hardware. This technology was later expanded to thin clients/zero clients for general Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. Teradici's protocol or hardware is used by HP, Dell-Wyse, Amulet Hotkey, Samsung, Amazon Web Services, Fujitsu, and VMware.

Turbonomic is a resource-simulation software company headquartered in Boston, MA and owned by IBM. The company was originally named VMTurbo.
Data center management is the collection of tasks performed by those responsible for managing ongoing operation of a data center. This includes Business service management and planning for the future.
References
- ↑ "10 Start-ups to watch". Network World. April 29, 2002. Archived from the original on 2008-09-27. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- ↑ Brodkin, Jon (2008-11-10). "Egenera lays off 87 workers, refocuses on software". Network World. Retrieved 2022-12-21.
- ↑ "Q&A: Vern Brownell, founder and CTO of Egenera". SearchDataCenter.com. April 28, 2005. Archived from the original on 2008-09-27. Retrieved 2008-09-16.
- ↑ "EGENERA COMPANY HISTORY TIMELINE". 27 August 2020.
- ↑ "Egenera to Carve Out Space in Software Market". ServerWatch. November 1, 2007. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- ↑ "Egenera Acquires Fort Technology". zdnet. December 5, 2012. Archived from the original on January 4, 2013.
- ↑ "Dell and Egenera Partnering to Simplify Data Center Management". Dell. March 25, 2008. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
- ↑ "Egenera bags new OEM agreement with Fujitsu". The Register. March 28, 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-07.
- ↑ "Egenera and HP Collaborate on PAN Manager Software for HP". HP. April 7, 2011. Retrieved 2011-04-07.
- ↑ "Egenera Management Software Certified for IBM BladeCenter". Talkin Cloud. May 11, 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-06.
- ↑ "NEC, Egenera tag team on cloudy infrastructure freakage". The Register. September 6, 2012. Retrieved 2013-05-06.[ permanent dead link ]