
In fluid dynamics, a stall is a reduction in the lift coefficient generated by a foil as angle of attack increases. This occurs when the critical angle of attack of the foil is exceeded. The critical angle of attack is typically about 15°, but it may vary significantly depending on the fluid, foil, and Reynolds number.

An airfield traffic pattern is a standard path followed by aircraft when taking off or landing while maintaining visual contact with the airfield.

In flight dynamics a spin is a special category of stall resulting in autorotation about the aircraft's longitudinal axis and a shallow, rotating, downward path approximately centred on a vertical axis. Spins can be entered intentionally or unintentionally, from any flight attitude if the aircraft has sufficient yaw while at the stall point. In a normal spin, the wing on the inside of the turn stalls while the outside wing remains flying. It is possible for both wings to stall, but the angle of attack of each wing, and consequently its lift and drag, are different.
A ground proximity warning system (GPWS) is a system designed to alert pilots if their aircraft is in immediate danger of flying into the ground or an obstacle. The United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) defines GPWS as a type of terrain awareness warning system (TAWS). More advanced systems, introduced in 1996, are known as enhanced ground proximity warning systems (EGPWS), a modern type of TAWS.
In aeronautics, a descent is any time period during air travel where an aircraft decreases altitude, and is the opposite of an ascent or climb.

A radio-controlled aircraft is a small flying machine that is controlled remotely by an operator on the ground using a hand-held radio transmitter. The transmitter continuously communicates with a receiver within the craft that sends signals to servomechanisms (servos) which move the control surfaces based on the position of joysticks on the transmitter. The control surfaces, in turn, directly affect the orientation of the plane.

Pilot certification in the United States is typically required for an individual to act as a pilot-in-command of an aircraft. It is regulated by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), a branch of the U.S. Department of Transportation (USDOT). A pilot may be certified under 14 Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) Part 61 or 14 CFR Part 141. Pilots may also be certified under 14 CFR Part 107 for commercial drone operations.

In aviation, an instrument approach or instrument approach procedure (IAP) is a series of predetermined maneuvers for the orderly transfer of an aircraft operating under instrument flight rules from the beginning of the initial approach to a landing, or to a point from which a landing may be made visually. These approaches are approved in the European Union by EASA and the respective country authorities and in the United States by the FAA or the United States Department of Defense for the military. The ICAO defines an instrument approach as, "a series of predetermined maneuvers by reference to flight instruments with specific protection from obstacles from the initial approach fix, or where applicable, from the beginning of a defined arrival route to a point from which a landing can be completed and thereafter, if landing is not completed, to a position at which holding or enroute obstacle clearance criteria apply."
Competition aerobatics is an air sport in which ground-based judges rate the skill of pilots performing aerobatic flying. It is practised in both piston-powered single-engine airplanes and also gliders.

A barrel roll is an aerial maneuver in which an airplane makes a complete rotation on both its longitudinal and lateral axes, causing it to follow a helical path, approximately maintaining its original direction. It is sometimes described as a "combination of a loop and a roll". The g-force is kept positive on the object throughout the maneuver, commonly between 2 and 3g, and no less than 0.5g. The barrel roll is commonly confused with an aileron roll.
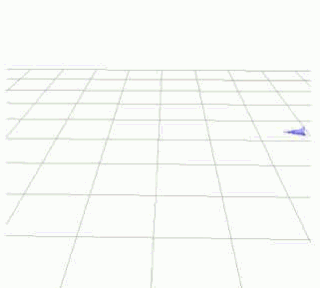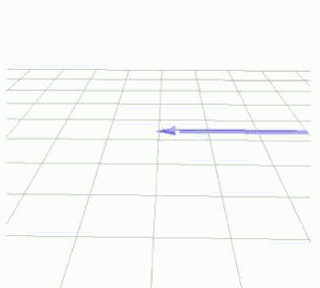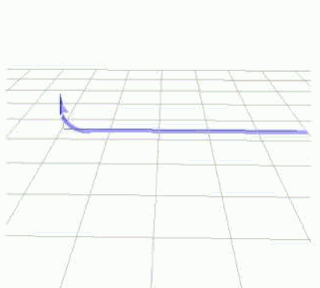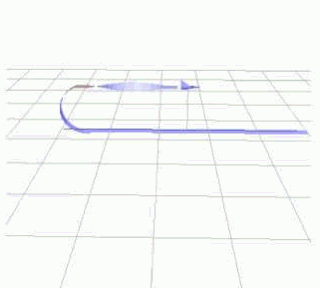
The term Immelmann turn, named after German World War I Eindecker fighter ace Lieutnant Max Immelmann, refers to two different aircraft maneuvers. In World War I aerial combat, an Immelmann turn was a maneuver used after an attack on another aircraft to reposition the attacking aircraft for another attack. In modern aerobatics, an Immelmann turn is an aerobatic maneuver that results in level flight in the opposite direction at a higher altitude.

On October 11, 2006, a Cirrus SR20 aircraft crashed into the Belaire Apartments in the Upper East Side of Manhattan, New York City, at about 2:42 p.m. EDT. The aircraft struck the north side of the building, causing a fire in several apartments, that was extinguished within two hours.

A pylon turn is a flight maneuver in which an aircraft banks into a circular turn, in such a way that an imaginary line projecting straight out the side of the aircraft points to a fixed point on the ground. The maneuver originated early in the 20th century in air racing.
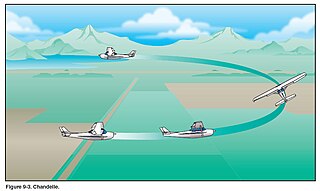
The chandelle is an aircraft control maneuver where the pilot combines a 180° turn with a climb.

Alliance Air Flight 7412 was a scheduled Indian domestic passenger flight from Calcutta to Delhi, operated by Indian regional airliner Alliance Air. On 17 July 2000, while on approach to its first stopover in Patna, the Boeing 737-2A8 operating the route nose-dived and crashed into a residential area in Patna, killing 60 people including 5 on the ground.

First-person view (FPV), also known as remote-person view (RPV), or simply video piloting, is a method used to control a radio-controlled vehicle from the driver or pilot's view point. Most commonly it is used to pilot a radio-controlled aircraft or other type of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV). The vehicle is either driven or piloted remotely from a first-person perspective via an onboard camera, fed wirelessly to video FPV goggles or a video monitor. More sophisticated setups include a pan-and-tilt gimbaled camera controlled by a gyroscope sensor in the pilot's goggles and with dual onboard cameras, enabling a true stereoscopic view.
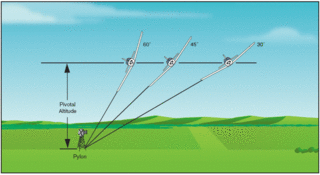
Pivotal altitude is the height for a given ground speed at which the line of sight from the cockpit directly parallel to the lateral axis of the aircraft will remain stationary on an object on the ground. A good rule of thumb for estimating the pivotal altitude is to square the groundspeed, then divide by 15 or divide by 11.3, and then add the mean sea level (MSL) altitude of the ground reference. The pivotal altitude is the altitude at which, for a given groundspeed, the projection of the visual reference line to the pylon appears to pivot. The pivotal altitude does not vary with the angle of bank unless the bank is steep enough to affect the groundspeed.

TAME Flight 120 was a Boeing 727-134 airliner, registration HC-BLF, named El Oro, operating as a scheduled international passenger flight between Quito, Ecuador and Cali, Colombia, with a scheduled stopover at the Ecuadorian border town of Tulcán. The aircraft crashed while on approach to Tulcán's Teniente Coronel Luis A. Mantilla International Airport on January 28, 2002. The pilot flew the approach incorrectly in reportedly foggy conditions, and the aircraft crashed into the side of the Cumbal Volcano, located near Ipiales, Colombia, at 10:23 in the morning. All passengers and crew were killed in the crash.

A slow roll is a roll made by an airplane, in which the plane makes a complete rotation around its roll axis while keeping the aircraft flying a straight and level flightpath. A slow roll is performed more slowly than an aileron roll; although it is not necessarily performed very slowly, it is performed slowly enough to allow the pilot to maintain balance, keeping a steady flightpath, pitch angle, and height (altitude) throughout the maneuver. The maneuver is performed by rolling the airplane at a controlled rate with the ailerons, and moving the elevators and rudder in opposition, or "cross-controlling," to keep the plane on a steady, level flightpath.
A power-off accuracy approach, also known as a glide approach, is an aviation exercise used to simulate a landing with an engine failure. The purpose of this training technique is to better develop one's ability to estimate distance and glide ratios. The variation in each angle refers to the degrees an aircraft must turn to be aligned with the runway. Consideration of the wind and use of flaps are important factors in executing power-off accuracy approaches.

















