Related Research Articles

Vilhjalmur Stefansson was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada.

Rudolph Martin Anderson was an American born Canadian zoologist and explorer.
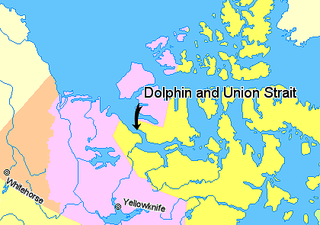
Dolphin and Union Strait lies in both the Northwest Territories and Nunavut, Canada, between the mainland and Victoria Island. It is part of the Northwest Passage. It links Amundsen Gulf, lying to the northwest, with Coronation Gulf, lying to the southeast. The southeastern end of the strait is marked by Austin Bay. It gets its name from the two boats used by the Scottish naval surgeon and explorer John Richardson, who was the first known European to explore it in 1826.
Blonde Eskimos or Blond Eskimos is a term first applied in accounts of sightings of, and encounters with, light-haired Inuit peoples of Northern Canada from the early 20th century, particularly around the Coronation Gulf between mainland Canada and Victoria Island. Sightings of light-haired natives of the Arctic have been mentioned in written accounts as far back as the 17th century.

Copper Inuit, also known as Kitlinermiut and Inuinnait, are a Canadian Inuit group who live north of the tree line, in what is now the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut and in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories. Most of them historically lived in the area around Coronation Gulf, on Victoria Island, and southern Banks Island.
Ogden Bay is an Arctic waterway in the Kitikmeot Region, Nunavut, Canada. It is located in the southern Queen Maud Gulf off Nunavut's mainland. Chester Bay is situated 32 km (20 mi) to the west, Armark is to the east, and the Keith Islands are to the north.
The Rae River (Pallirk) is a waterway that flows from Akuliakattak Lake into Richardson Bay, Coronation Gulf. Its mouth is situated northwest of Kugluktuk, Nunavut. Its shores were the ancestral home of Copper Inuit subgroups: the Kanianermiut and the Pallirmiut.
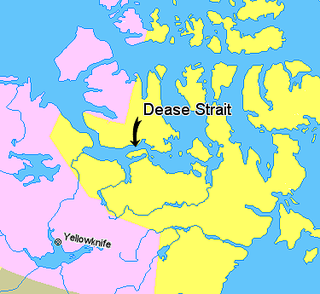
Kiillinnguyaq, is a large Arctic peninsula, almost totally surrounded by water, in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut. Were it not for a 8.0 km (5 mi) isthmus at the southeast corner it would be a long island parallel to the coast. From the isthmus it extends 169 km (105 mi) westward into the Coronation Gulf. To the south, Melville Sound separates it from the mainland. To the north is Dease Strait and then Victoria Island. To the west is Coronation Gulf and to the east, Queen Maud Gulf. Cape Flinders marks the western tip of the peninsula, Cape Franklin is at the northwestern point, and Hiiqtinniq, formerly Cape Alexander marks the northeastern point.
Albert Edward Bay is a bay on the southeast side of Victoria Island in the Arctic Archipelago. It faces Victoria Strait to the east. There are several islands in the bay, the largest of which is Admiralty Island at its mouth. Its north side is the Collinson Peninsula.
Ahiagmiut were a geographically defined Copper Inuit subgroup in the northern Canadian territory of Nunavut. They were located near Ogden Bay, on the Queen Maud Gulf, and inland towards Back River, then on towards the Akilinik River.
Akuliakattagmiut were a geographically defined Copper Inuit subgroup in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. They were located near Cape Bexley on the south shore, mainland side of Dolphin and Union Strait, and in the vicinity of the Melville Hills' Akuliakattak Lake, the source of the Rae River.
Haneragmiut were a geographically defined Copper Inuit subgroup in the Canadian territory of Nunavut. They were the most westerly band of those that hunted in southern Victoria Island. They were generally located on the north shore of Dolphin and Union Strait, north of Cape Bexley, and south of Prince Albert Sound, on Victoria Island. Though they migrated seasonally both north and south for hunting, fishing, and trade, they were unaware that Victoria Island was an island.
Sutton Island is located in northern Canada's territory of Nunavut. It is situated in the Dolphin and Union Strait immediately next to Liston Island. Rymer Point and Simpson Bay, on Victoria Island's Wollaston Peninsula are to the northeast. Bernard Harbour, on the mainland, is to the southwest, as is Chantrey Island.
Cape Bexley is a headland in the northern Canadian territory of Nunavut. It is located on the mainland, on the south shore of Dolphin and Union Strait, and bounded on the south by Souths Bay. It was named after Nicholas Vansittart, 1st Baron Bexley.

The Kangiryuarmiut are an Inuvialuit group, culturally and historically related to the Copper Inuit. They were historically located on Victoria Island in the areas of Prince Albert Sound, Cape Baring, and central Victoria island. They often travelled seasonally around their traditional territory including to Banks Island, both south to Nelson Head and as far north as Mercy Bay to collect raw materials from the wreck of the HMS Investigator. Archaeologists have also found many sites left by Kangiryuarmiut and their ancestors in what is now Aulavik National Park. Today, many Kangiryurmiut still live on Victoria Island, in the hamlet of Uluhaktok, now within the Inuvialuit Settlement Region.

The Umingmuktogmiut are a geographically defined Copper Inuit band in the northern Canadian territory of Nunavut, Kitikmeot Region. They were located on the western coast of Kiillinnguyaq, and also further south in eastern Bathurst Inlet around Everitt Point by the Barry Islands. Umingmuktogmiut were notable amongst other Copper Inuit as they had a permanent community, Umingmuktog. They could hunt and fish for Arctic char, Arctic fox, barren-ground caribou, fur seals, and muskox prevalent in the area.
The Ugyuligmiut were a geographically defined Copper Inuit band in the Canadian Arctic's Northwest Territories. They were located on Victoria Island north of Minto Inlet, and on Banks Island in the Aulavik National Park region.
The Kugaryuagmiut are a geographically defined Copper Inuit band in the northern Canadian territory of Nunavut, on the mainland, in Kitikmeot Region. According to Arctic explorer Vilhjalmur Stefansson's 1908-1912 ethnographic journals, they numbered about 25 at the time. In the summer, they hunted in the region of the Kugaryuak River, which flows into the Coronation Gulf, where they subsisted during the winter, the same as other Copper Inuit of that region.
The Roscoe River is a waterway located above the Arctic Circle on the mainland of Northern Canada.

Franklin Bay is a large inlet in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is a southern arm of the Amundsen Gulf, southeastern Beaufort Sea. The bay measures 48 kilometres (30 mi) long, and 40 kilometres (25 mi) wide at its mouth. The Parry Peninsula is to the east, and its southern area is called Langton Bay.
References
- ↑ Iqaluktuurmiutat: Life at Iqaluktuuq Archived 2011-09-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Kitikmeot Regional Groups". Archived from the original on 2011-08-27. Retrieved 2010-07-04.
- ↑ Stefansson, Vilhjalmur (1914). The Stefánsson-Anderson Arctic Expedition of the American Museum: Preliminary Ethnological Report. New York: The Trustees of the American Museum. p. 31. OCLC 13626409.
- ↑ MacDonald, Robert (1978). The uncharted nations: a reference history of the Canadian tribes (Digitized Sep 15, 2008 ed.). Calgary: Ballantrae Foundation. ISBN 9780919606029.
- ↑ Stefansson, V.; Anderson, R.M. (1913). My life with the Eskimo. Macmillan. p. 281. ISBN 9781548458317. OCLC 487176.