Related Research Articles

The vagus nerve, also known as the tenth cranial nerve, cranial nerve X, or simply CN X, is a cranial nerve that carries sensory fibers that create a pathway that interfaces with the parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and digestive tract.

Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) is a noninvasive form of brain stimulation in which a changing magnetic field is used to induce an electric current at a specific area of the brain through electromagnetic induction. An electric pulse generator, or stimulator, is connected to a magnetic coil connected to the scalp. The stimulator generates a changing electric current within the coil which creates a varying magnetic field, inducing a current within a region in the brain itself.

The hypoglossal nerve, also known as the twelfth cranial nerve, cranial nerve XII, or simply CN XII, is a cranial nerve that innervates all the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles of the tongue except for the palatoglossus, which is innervated by the vagus nerve.

Palpitations are perceived abnormalities of the heartbeat characterized by awareness of cardiac muscle contractions in the chest, which is further characterized by the hard, fast and/or irregular beatings of the heart.
Daclizumab is a therapeutic humanized monoclonal antibody which was used for the treatment of adults with relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis (MS). Daclizumab works by binding to CD25, the alpha subunit of the IL-2 receptor of T-cells.

A transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation is a device that produces mild electric current to stimulate the nerves for therapeutic purposes. TENS, by definition, covers the complete range of transcutaneously applied currents used for nerve excitation, but the term is often used with a more restrictive intent, namely, to describe the kind of pulses produced by portable stimulators used to reduce pain. The unit is usually connected to the skin using two or more electrodes which are typically conductive gel pads. A typical battery-operated TENS unit is able to modulate pulse width, frequency, and intensity. Generally, TENS is applied at high frequency (>50 Hz) with an intensity below motor contraction or low frequency (<10 Hz) with an intensity that produces motor contraction. More recently, many TENS units use a mixed frequency mode which alleviates tolerance to repeated use. Intensity of stimulation should be strong but comfortable with greater intensities, regardless of frequency, producing the greatest analgesia. While the use of TENS has proved effective in clinical studies, there is controversy over which conditions the device should be used to treat.

Amgen Inc. is an American multinational biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Thousand Oaks, California. One of the world's largest independent biotechnology companies, As of 2022, Amgen has approximately 24,000 staff in total.

A mind machine uses pulsing rhythmic sound, flashing light, or a combination of these. Mind machines can induce deep states of relaxation or concentration.
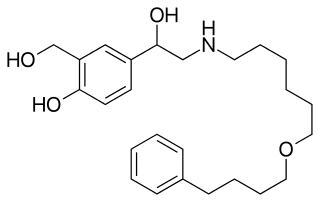
Salmeterol is a long-acting β2 adrenergic receptor agonist (LABA) used in the maintenance and prevention of asthma symptoms and maintenance of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) symptoms. Symptoms of bronchospasm include shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing and chest tightness. It is also used to prevent breathing difficulties during exercise.

Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) is a medical treatment that involves delivering electrical impulses to the vagus nerve. It is used as an add-on treatment for certain types of intractable epilepsy, cluster headaches, treatment-resistant depression and stroke rehabilitation.

Radionics—also called electromagnetic therapy (EMT) and the Abrams method—is a form of alternative medicine that claims that disease can be diagnosed and treated by applying electromagnetic radiation (EMR), such as radio waves, to the body from an electrically powered device. It is similar to magnet therapy, which also applies EMR to the body but uses a magnet that generates a static electromagnetic field.

Stephen Michael Hahn is an American physician who served as the commissioner of food and drugs from 2019 to 2021. Before becoming commissioner, he was an oncologist serving as chief medical executive of the MD Anderson Cancer Center. In 2021, he became chief medical officer at Flagship Pioneering, the venture capital firm that launched Moderna.

Kevin J. Tracey, a neurosurgeon and inventor, is the president and CEO of the Feinstein Institute for Medical Research, professor of neurosurgery and molecular medicine at the Zucker School of Medicine, and president of the Elmezzi Graduate School of Molecular Medicine in Manhasset, New York. The Public Library of Science Magazine, PLOS Biology, recognized Tracey in 2019 as one of the most cited researchers in the world.

Diaphragm pacing is the rhythmic application of electrical impulses to the diaphragm to provide artificial ventilatory support for respiratory failure or sleep apnea. Historically, this has been accomplished through the electrical stimulation of a phrenic nerve by an implanted receiver/electrode, though today an alternative option of attaching percutaneous wires to the diaphragm exists.
Neurostimulation is the purposeful modulation of the nervous system's activity using invasive or non-invasive means. Neurostimulation usually refers to the electromagnetic approaches to neuromodulation.
Acadia Pharmaceuticals Inc. is a biopharmaceutical company headquartered in Sorrento Valley, San Diego, California.
Neuromodulation is "the alteration of nerve activity through targeted delivery of a stimulus, such as electrical stimulation or chemical agents, to specific neurological sites in the body". It is carried out to normalize – or modulate – nervous tissue function. Neuromodulation is an evolving therapy that can involve a range of electromagnetic stimuli such as a magnetic field (rTMS), an electric current, or a drug instilled directly in the subdural space. Emerging applications involve targeted introduction of genes or gene regulators and light (optogenetics), and by 2014, these had been at minimum demonstrated in mammalian models, or first-in-human data had been acquired. The most clinical experience has been with electrical stimulation.

Oliceridine, sold under the brand name Olinvyk, is an opioid medication that is used for the treatment of moderate to severe acute pain in adults. It is given by intravenous (IV) injection.
Peter Sean Staats is an American physician, specializing in interventional pain medicine. He is the founder of the Division of Pain Medicine at the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, and was the Division's chief for nearly a decade. He is a past president of the North American Neuromodulation Society, the New Jersey Society of Interventional Pain Medicine,the American Society of Interventional Pain Physicians ( ASIPP) the World Institute of Pain ( WIP), The Southern Pain Society.
Drug-resistant epilepsy (DRE), also known as refractory epilepsy, intractable epilepsy, or pharmacoresistant epilepsy refers to a state in which an individual with a diagnosis of epilepsy is unresponsive to multiple first line therapies. Based on the 2010 guidelines from the International League against Epilepsy (ILAE), DRE is officially diagnosed following a lack of therapeutic relief in the form of continued seizure burden after trialing at least two antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) at the appropriate dosage and duration. The probability that the next medication will achieve seizure freedom drops with every failed AED. For example, after two failed AEDs, the probability that the third will achieve seizure freedom is around 4%. Drug-resistant epilepsy is commonly diagnosed after several years of uncontrolled seizures, however, in most cases, it is evident much earlier. Approximately 30% of people with epilepsy have a drug-resistant form. Achieving seizure control in DRE patients is critical as uncontrolled seizures can lead to irreversible damage to the brain, cognitive impairment, and increased risk for sudden unexpected death in epilepsy called SUDEP. Indirect consequences of DRE include seizure related injuries and/or accidents, impairment in daily life, adverse medication effects, increased co-morbidities especially psychological, and increased economic burden, etc.
References
- 1 2 "electroCore Inc. Company & People | ECOR". Barron's. Retrieved 2024-12-12.
- ↑ "Nerve stimulation device maker electroCore goes public with $78M IPO | FierceBiotech". www.fiercebiotech.com. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
- ↑ "This hand-held device is approved to treat cluster headaches". NBC News. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
- ↑ "ElectroCore wins cluster headache FDA 510(k) indication for GammaCore". MassDevice. 2018-11-28. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
- ↑ "Nerve Stimulator Approved for Cluster Headache". Pain News Network. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
- ↑ "Term Sheet -- Friday, June 22". Fortune. Retrieved 2019-03-06.
- ↑ Hale, Conor (2018-06-22). "Nerve stimulation device maker electroCore goes public with $78M IPO | Fierce Biotech". www.fiercebiotech.com. Retrieved 2024-12-16.
- ↑ "BRIEF-electroCore Announces Common Stock Purchase Agreement For Up To $25 Mln With Lincoln Park Capital". Reuters. 2020-03-27. Retrieved 2020-03-31.
- ↑ electroCore (2020-07-13). "electroCore Announces FDA Emergency Use Authorization for use of gammaCore Sapphire™ CV for the Acute Treatment of Asthma Exacerbations in Known or Suspected COVID-19 Patients". GlobeNewswire News Room. Retrieved 2020-07-15.
- ↑ https://www.truvaga.com/vagus-nerve-science/