Related Research Articles

Clinical chemistry is a division in medical laboratory sciences focusing on qualitative tests of important compounds, referred to as analytes or markers, in bodily fluids and tissues using analytical techniques and specialized instruments. This interdisciplinary field includes knowledge from medicine, biology, chemistry, biomedical engineering, informatics, and an applied form of biochemistry.

Creatinine is a breakdown product of creatine phosphate from muscle and protein metabolism. It is released at a constant rate by the body.

In physiology, dehydration is a lack of total body water that disrupts metabolic processes. It occurs when free water loss exceeds intake, often resulting from excessive sweating, health conditions, or inadequate consumption of water. Mild dehydration can also be caused by immersion diuresis, which may increase risk of decompression sickness in divers.
Hyponatremia or hyponatraemia is a low concentration of sodium in the blood. It is generally defined as a sodium concentration of less than 135 mmol/L (135 mEq/L), with severe hyponatremia being below 120 mEq/L. Symptoms can be absent, mild or severe. Mild symptoms include a decreased ability to think, headaches, nausea, and poor balance. Severe symptoms include confusion, seizures, and coma; death can ensue.

Blood plasma is a light amber-colored liquid component of blood in which blood cells are absent, but which contains proteins and other constituents of whole blood in suspension. It makes up about 55% of the body's total blood volume. It is the intravascular part of extracellular fluid. It is mostly water, and contains important dissolved proteins, glucose, clotting factors, electrolytes, hormones, carbon dioxide, and oxygen. It plays a vital role in an intravascular osmotic effect that keeps electrolyte concentration balanced and protects the body from infection and other blood-related disorders.
Reference ranges for blood tests are sets of values used by a health professional to interpret a set of medical test results from blood samples. Reference ranges for blood tests are studied within the field of clinical chemistry, the area of pathology that is generally concerned with analysis of bodily fluids.
In physiology, body water is the water content of an animal body that is contained in the tissues, the blood, the bones and elsewhere. The percentages of body water contained in various fluid compartments add up to total body water (TBW). This water makes up a significant fraction of the human body, both by weight and by volume. Ensuring the right amount of body water is part of fluid balance, an aspect of homeostasis.
Thyroid-stimulating hormone (also known as thyrotropin, thyrotropic hormone, or abbreviated TSH) is a pituitary hormone that stimulates the thyroid gland to produce thyroxine (T4), and then triiodothyronine (T3) which stimulates the metabolism of almost every tissue in the body. It is a glycoprotein hormone produced by thyrotrope cells in the anterior pituitary gland, which regulates the endocrine function of the thyroid.

Serum is the fluid and solvent component of blood which does not play a role in clotting. It may be defined as blood plasma without the clotting factors, or as blood with all cells and clotting factors removed. Serum contains all proteins except clotting factors, including all electrolytes, antibodies, antigens, hormones; and any exogenous substances. Serum also does not contain all the formed elements of blood, which include blood cells, white blood cells, red blood cells (erythrocytes), and platelets.
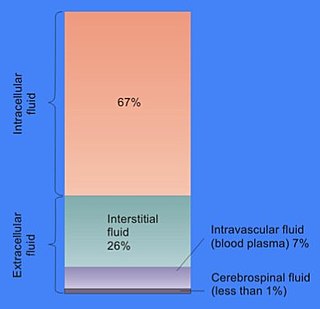
In cell biology, extracellular fluid (ECF) denotes all body fluid outside the cells of any multicellular organism. Total body water in healthy adults is about 50–60% of total body weight; women and the obese typically have a lower percentage than lean men. Extracellular fluid makes up about one-third of body fluid, the remaining two-thirds is intracellular fluid within cells. The main component of the extracellular fluid is the interstitial fluid that surrounds cells.

Hereditary spherocytosis (HS) is a congenital hemolytic disorder wherein a genetic mutation coding for a structural membrane protein phenotype causes the red blood cells to be sphere-shaped (spherocytosis), rather than the normal biconcave disk shape. This abnormal shape interferes with the cells' ability to flex during blood circulation, and also makes them more prone to rupture under osmotic stress, mechanical stress, or both. Cells with the dysfunctional proteins are degraded in the spleen, which leads to a shortage of erythrocytes and results in hemolytic anemia.

Electrolyte imbalance, or water-electrolyte imbalance, is an abnormality in the concentration of electrolytes in the body. Electrolytes play a vital role in maintaining homeostasis in the body. They help to regulate heart and neurological function, fluid balance, oxygen delivery, acid–base balance and much more. Electrolyte imbalances can develop by consuming too little or too much electrolyte as well as excreting too little or too much electrolyte. Examples of electrolytes include calcium, chloride, magnesium, phosphate, potassium, and sodium.
D-dimer is a dimer that is a fibrin degradation product (FDP), a small protein fragment present in the blood after a blood clot is degraded by fibrinolysis. It is so named because it contains two D fragments of the fibrin protein joined by a cross-link, hence forming a protein dimer.
Hypernatremia, also spelled hypernatraemia, is a high concentration of sodium in the blood. Early symptoms may include a strong feeling of thirst, weakness, nausea, and loss of appetite. Severe symptoms include confusion, muscle twitching, and bleeding in or around the brain. Normal serum sodium levels are 135–145 mmol/L. Hypernatremia is generally defined as a serum sodium level of more than 145 mmol/L. Severe symptoms typically only occur when levels are above 160 mmol/L.
In pharmacology, the volume of distribution is the theoretical volume that would be necessary to contain the total amount of an administered drug at the same concentration that it is observed in the blood plasma. In other words, it is the ratio of amount of drug in a body (dose) to concentration of the drug that is measured in blood, plasma, and un-bound in interstitial fluid.
The anion gap is a value calculated from the results of multiple individual medical lab tests. It may be reported with the results of an electrolyte panel, which is often performed as part of a comprehensive metabolic panel.

Fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is a blood product made from the liquid portion of whole blood. It is used to treat conditions in which there are low blood clotting factors or low levels of other blood proteins. It may also be used as the replacement fluid in plasma exchange. Using ABO compatible plasma, while not required, may be recommended. Use as a volume expander is not recommended. It is administered by slow injection into a vein.
The fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) is the percentage of the sodium filtered by the kidney which is excreted in the urine. It is measured in terms of plasma and urine sodium, rather than by the interpretation of urinary sodium concentration alone, as urinary sodium concentrations can vary with water reabsorption. Therefore, the urinary and plasma concentrations of sodium must be compared to get an accurate picture of kidney clearance. In clinical use, the fractional excretion of sodium can be calculated as part of the evaluation of acute kidney failure in order to determine if hypovolemia or decreased effective circulating plasma volume is a contributor to the kidney failure.
Blood plasma fractionation are the general processes separating the various components of blood plasma, which in turn is a component of blood obtained through blood fractionation. Plasma-derived immunoglobulins are giving a new narrative to healthcare across a wide range of autoimmune inflammatory diseases.
Isotonic hyponatremia is a form of hyponatremia with mOsm measured between 280 and 295. It can be associated with pseudohyponatremia, or with isotonic infusion of glucose or mannitol.
References
- 1 2 Burtis CA, Ashwood ER, Bruns DE (2012). Tietz Textbook of Clinical Chemistry and Molecular Diagnostics. Elsevier Health Sciences. ISBN 978-1-4160-6164-9.
- ↑ Aziz, Fahad; Sam, Ramin; Lew, Susie Q.; Massie, Larry; Misra, Madhukar; Roumelioti, Maria-Eleni; Argyropoulos, Christos P.; Ing, Todd S.; Tzamaloukas, Antonios H. (2023-06-15). "Pseudohyponatremia: Mechanism, Diagnosis, Clinical Associations and Management". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 12 (12). MDPI AG: 4076. doi: 10.3390/jcm12124076 . ISSN 2077-0383.
- ↑ Dhatt, Gurjit; Talor, Zvi; Kazory, Amir (2012). "Direct Ion-selective Electrode Method is Useful in Diagnosis of Pseudohyponatremia". The Journal of Emergency Medicine. 43 (2). Elsevier BV: 348–349. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2011.07.021. ISSN 0736-4679.
- ↑ Bangert SK, Marshall WJ (2008). Clinical Biochemistry: Metabolic and Clinical Aspects (2nd ed.). Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone/Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-443-10186-1.
- ↑ Goldwasser, P.; Ayoub, I.; Barth, R. (2015). Pseudohypernatremia and Pseudohyponatremia: A linear correction. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 30:252-257.