Related Research Articles

Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges,vacuum gauges or compound gauges. The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge.
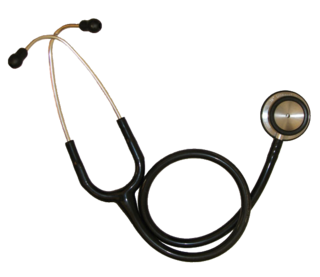
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, with either one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. A stethoscope can be used to listen to the sounds made by the heart, lungs or intestines, as well as blood flow in arteries and veins. In combination with a manual sphygmomanometer, it is commonly used when measuring blood pressure.
A communications system or communication system is a collection of individual telecommunications networks, transmission systems, relay stations, tributary stations, and terminal equipment usually capable of interconnection and interoperation to form an integrated whole. The components of a communications system serve a common purpose, are technically compatible, use common procedures, respond to controls, and operate in union.

A microphone, colloquially called a mic or mike, is a transducer that converts sound into an electrical signal. Microphones are used in many applications such as telephones, hearing aids, public address systems for concert halls and public events, motion picture production, live and recorded audio engineering, sound recording, two-way radios, megaphones, and radio and television broadcasting. They are also used in computers for recording voice, speech recognition, VoIP, and for other purposes such as ultrasonic sensors or knock sensors.

Capacitance is the capability of a material object or device to store electric charge. It is measured by the change in charge in response to a difference in electric potential, expressed as the ratio of those quantities. Commonly recognized are two closely related notions of capacitance: self capacitance and mutual capacitance. An object that can be electrically charged exhibits self capacitance, for which the electric potential is measured between the object and ground. Mutual capacitance is measured between two components, and is particularly important in the operation of the capacitor, an elementary linear electronic component designed to add capacitance to an electric circuit.
A transducer is a device that converts energy from one form to another. Usually a transducer converts a signal in one form of energy to a signal in another. Transducers are often employed at the boundaries of automation, measurement, and control systems, where electrical signals are converted to and from other physical quantities. The process of converting one form of energy to another is known as transduction.

A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an electronic device.

A pickup is a transducer that captures or senses mechanical vibrations produced by musical instruments, particularly stringed instruments such as the electric guitar, and converts these to an electrical signal that is amplified using an instrument amplifier to produce musical sounds through a loudspeaker in a speaker enclosure. The signal from a pickup can also be recorded directly.

A pressure sensor is a device for pressure measurement of gases or liquids. Pressure is an expression of the force required to stop a fluid from expanding, and is usually stated in terms of force per unit area. A pressure sensor usually acts as a transducer; it generates a signal as a function of the pressure imposed. For the purposes of this article, such a signal is electrical.

A ribbon microphone, also known as a ribbon velocity microphone, is a type of microphone that uses a thin aluminum, duraluminum or nanofilm of electrically conductive ribbon placed between the poles of a magnet to produce a voltage by electromagnetic induction. Ribbon microphones are typically bidirectional, meaning that they pick up sounds equally well from either side of the microphone.

A variable capacitor is a capacitor whose capacitance may be intentionally and repeatedly changed mechanically or electronically. Variable capacitors are often used in L/C circuits to set the resonance frequency, e.g. to tune a radio, or as a variable reactance, e.g. for impedance matching in antenna tuners.
Level sensors detect the level of liquids and other fluids and fluidized solids, including slurries, granular materials, and powders that exhibit an upper free surface. Substances that flow become essentially horizontal in their containers because of gravity whereas most bulk solids pile at an angle of repose to a peak. The substance to be measured can be inside a container or can be in its natural form. The level measurement can be either continuous or point values. Continuous level sensors measure level within a specified range and determine the exact amount of substance in a certain place, while point-level sensors only indicate whether the substance is above or below the sensing point. Generally the latter detect levels that are excessively high or low.

A capacitor is a device that stores electrical energy in an electric field by virtue of accumulating electric charges on two close surfaces insulated from each other. It is a passive electronic component with two terminals.
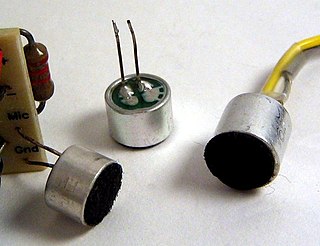
An electret microphone is a type of electrostatic capacitor-based microphone, which eliminates the need for a polarizing power supply by using a permanently charged material.
A touch switch is a type of switch that only has to be touched by an object to operate. It is used in many lamps and wall switches that have a metal exterior as well as on public computer terminals. A touchscreen includes an array of touch switches on a display. A touch switch is the simplest kind of tactile sensor.
Liquid capacitive inclinometers are inclinometers whose sensing elements are made with a liquid-filled differential capacitor; they sense the local direction of acceleration due to gravity. A capacitive inclinometer has a disc-like cavity that is partly filled with a dielectric liquid. One of the sides of the cavity has an etched conductor plate that is used to form one of the conductors of a variable parallel plate capacitor. The liquid along with the other side of the cavity forms the other plate of the capacitor. In operation, the sensor is mounted so that the disc is in a vertical plane with its axis horizontal. Gravity then acts on the liquid pulling it down in the cavity forming a semicircle. As the sensor is rotated the liquid remains in this semicircular pattern covering a different area of the etched plate. This change in area results in a change in the capacitance. The change in capacitance is then electronically converted into an output signal that is linear with respect to the input angle.

Ultrasonic transducers and ultrasonic sensors are devices that generate or sense ultrasound energy. They can be divided into three broad categories: transmitters, receivers and transceivers. Transmitters convert electrical signals into ultrasound, receivers convert ultrasound into electrical signals, and transceivers can both transmit and receive ultrasound.
In electrical engineering, capacitive sensing is a technology, based on capacitive coupling, that can detect and measure anything that is conductive or has a dielectric constant different from air. Many types of sensors use capacitive sensing, including sensors to detect and measure proximity, pressure, position and displacement, force, humidity, fluid level, and acceleration. Human interface devices based on capacitive sensing, such as touchpads, can replace the computer mouse. Digital audio players, mobile phones, and tablet computers will sometimes use capacitive sensing touchscreens as input devices. Capacitive sensors can also replace mechanical buttons.

Capacitors have many uses in electronic and electrical systems. They are so ubiquitous that it is rare that an electrical product does not include at least one for some purpose. Capacitors allow only AC signals to pass when they are charged blocking DC signals. The main components of filters are capacitors. Capacitors have the ability to connect one circuit segment to another. Capacitors are used by Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) devices to represent binary information as bits.

Capacitive displacement sensors "are non-contact devices capable of high-resolution measurement of the position and/or change of position of any conductive target". They are also able to measure the thickness or density of non-conductive materials. Capacitive displacement sensors are used in a wide variety of applications including semiconductor processing, assembly of precision equipment such as disk drives, precision thickness measurements, machine tool metrology and assembly line testing. These types of sensors can be found in machining and manufacturing facilities around the world.
References
- 1 2 "Electromagnetic Diaphragm (EmD)". Thinklabs. thinklabsmedical.com. Archived from the original on 17 July 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2011.
- ↑ "Transducer for sensing body sounds". patft.uspto.gov. 9 December 2003. Retrieved 4 June 2011.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ "Transducer for sensing body sounds". United States Patent and Trademark Office . patft.uspto.gov. 10 May 2011. Retrieved 4 June 2011.[ permanent dead link ]
- ↑ Busch, David (2020). David Busch's Nikon Z50 Guide to Digital Photography. Rocky Nook. ISBN 978-1681986289 . Retrieved 14 September 2021.