
Rio de Janeiro, or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of Rio de Janeiro. It is the second-most-populous city in Brazil and the sixth-most-populous city in the Americas.

Rio de Janeiro is one of the 27 federative units of Brazil. It has the second largest economy of Brazil, with the largest being that of the state of São Paulo. The state, which has 8.2% of the Brazilian population, is responsible for 9.2% of the Brazilian GDP.

Niterói is a municipality in the state of Rio de Janeiro, in the southeast region of Brazil. It lies across Guanabara Bay, facing the city of Rio de Janeiro and forming part of the Rio de Janeiro Metropolitan Area. It was the capital of Rio de Janeiro, as marked by its golden mural crown, from 1834 to 1894 and again from 1903 to 1975. It has an estimated population of 515,317 inhabitants (2020) and an area of 129.375 km2 (49.952 sq mi), making it the fifth most populous city in the state. It has the highest Human Development Index in the state and the seventh highest among Brazil's municipalities in 2010. Individually, it is the second municipality with the highest average monthly household income per capita in Brazil and appears in 13th place among the municipalities of the country according to social indicators related to education. The city has the nicknames of Cidade Sorriso.

Favela is an umbrella name for several types of working-class neighborhoods in Brazil. The term, which means slum or ghetto, was first used in the Slum of Providência in the center of Rio de Janeiro in the late 19th century, which was built by soldiers who had lived under the favela trees in Bahia and had nowhere to live following the Canudos War. Some of the last settlements were called bairros africanos. Over the years, many former enslaved Africans moved in. Even before the first favela came into being, poor citizens were pushed away from the city and forced to live in the far suburbs.
The Brazilian Navy is the naval service branch of the Brazilian Armed Forces, responsible for conducting naval operations.

Duque de Caxias is a city on Guanabara Bay and part of Rio de Janeiro metropolitan area, southeastern Brazil.

Guanabara Bay is an oceanic bay located in Southeast Brazil in the state of Rio de Janeiro. On its western shore lie the cities of Rio de Janeiro and Duque de Caxias, and on its eastern shore the cities of Niterói and São Gonçalo. Four other municipalities surround the bay's shores. Guanabara Bay is the second largest bay in area in Brazil, at 412 square kilometres (159 sq mi), with a perimeter of 143 kilometres (89 mi).

The Campeonato Carioca, officially known as Campeonato Estadual do Rio de Janeiro, also commonly known as the Cariocão, is the state football league of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It is under the authority of the FERJ or FFERJ. It is an annual tournament, started in 1906.

Nova Iguaçu is a municipality in Rio de Janeiro state in Brazil.

Barra da Tijuca is an upper-class neighborhood or bairro in the West Zone of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, located in the western portion of the city on the Atlantic Ocean. Barra is well known for its beaches, its many lakes and rivers, and its lifestyle. This neighbourhood represents 4.7% of the city population and 13% of the total area of Rio de Janeiro.

The Brazilian Naval Revolts, or the Revoltas da Armada, were armed mutinies promoted mainly by admirals Custódio José de Melo and Saldanha da Gama and their fleet of rebel Brazilian navy ships against the claimed unconstitutional staying in power of president Floriano Peixoto.

São Gonçalo is a municipality in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, in the Southest region. It is located in the Metropolitan Region of Rio de Janeiro, having land limits with the municipalities of Niterói, Maricá and Itaboraí, and a maritime limit, by Guanabara Bay, with the capital, Rio de Janeiro. According to the 2022 census, it has a population of 896,744 inhabitants, making it the second most populous municipality in the state and the 18th most populous in the country.
The current capital of Brazil, since its construction in 1960, is Brasília. Rio de Janeiro was the country's capital between 1763 and 1960. The city of Salvador served as the seat for the Portuguese colonial administration in Brazil for its first two centuries and is usually called the "first capital of Brazil."

Santa Cruz is an extensive and populous neighborhood of the high class, lower middle and low in the West Zone of the municipality of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, the farthest from the center of Rio de Janeiro. Cut by the Santa Cruz extension of the urban passenger rail network of the metropolitan region of Rio de Janeiro, it has a very diverse landscape, with commercial areas, residential and industrial.
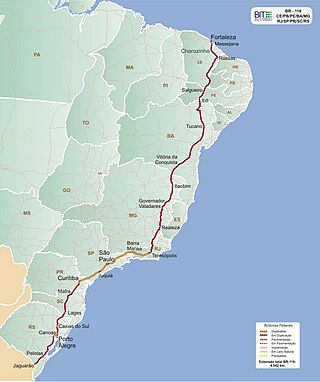
BR-116 is a federal route of highways of Brazil and the longest highway in the country, with 4,542 km (2,822 mi) of extension. The road connect Fortaleza, Ceará, one of the largest Northeast Brazil metropolises, to the southern city of Jaguarão, Rio Grande do Sul, in the border with Uruguay. It is also the longest highway in the country to be completely paved. It is considered one of the most important highways in the country, along with BR-101.

The Port of Rio de Janeiro is a seaport in the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil located in a cove on the west shore of Guanabara Bay. It is the third-busiest port in Brazil, and it is managed by Companhia Docas do Rio de Janeiro.

Morro da Providência is a favela located between the two Rio de Janeiro districts of Santo Cristo and Gamboa. It has an altitude of 115 metres and is located in the port area of the city. It is widely considered to be the first favela community in Brazil.
"The granite hump of Providencia gazes down like a stern guardian on the old port of Rio de Janeiro. It offers probably the finest viewpoint over any city I know."

The Valongo Wharf (Portuguese: Cais do Valongo) is an old dock located in the port area of Rio de Janeiro, between the current Coelho e Castro and Sacadura Cabral streets. Built in 1811, it was the site of landing and trading of enslaved Africans until 1831, with the blockade of Africa banning the Atlantic slave trade to Brazil.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Rio de Janeiro:
Samba de breque is a subgenre of samba that emerged in Rio de Janeiro between the late 1930s and early 1940s.
















