Webster County is a county located in center of the U.S. state of Mississippi, bordered on the south by the Big Black River. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,926.

Pontotoc County is a county located in the U.S. state of Mississippi. As of the 2020 census, the population was 31,184. Its county seat is Pontotoc. It was created on February 9, 1836, from lands ceded to the United States under the Chickasaw Cession. Pontotoc is a Chickasaw word meaning "land of hanging grapes". The original Natchez Trace and the current-day Natchez Trace Parkway both pass through the southeast corner of Pontotoc County.

Natchez is the only city in and the county seat of Adams County, Mississippi, United States. The population was 14,520 at the 2020 census. Located on the Mississippi River across from Vidalia, Louisiana, Natchez was a prominent city in the antebellum years, a center of cotton planters and Mississippi River trade.

Vicksburg is a historic city in Warren County, Mississippi, United States. It is the county seat. The population was 21,573 at the 2020 census. Located on a high bluff on the east bank of the Mississippi River across from Louisiana, Vicksburg was built by French colonists in 1719. The outpost withstood an attack from the native Natchez people. It was incorporated as Vicksburg in 1825 after Methodist missionary Newitt Vick. The area that is now Vicksburg was long occupied by the Natchez Native Americans as part of their historical territory along the Mississippi. The first Europeans who settled the area were French colonists who built Fort Saint Pierre in 1719 on the high bluffs overlooking the Yazoo River at present-day Redwood. They conducted fur trading with the Natchez and others, and started plantations. During the American Civil War, it was a key Confederate river-port, and its July 1863 surrender to Ulysses S. Grant, along with the concurrent Battle of Gettysburg, marked the turning-point of the war.

The Natchez Trace, also known as the Old Natchez Trace, is a historic forest trail within the United States which extends roughly 440 miles (710 km) from Nashville, Tennessee, to Natchez, Mississippi, linking the Cumberland, Tennessee, and Mississippi rivers.

The Natchez Trace Parkway is a limited-access national parkway in the Southeastern United States that commemorates the historic Natchez Trace and preserves sections of that original trail. Its central feature is a two-lane road that extends 444 miles (715 km) from Natchez, Mississippi, to Nashville, Tennessee. Access to the parkway is limited, with more than 50 access points in Mississippi, Alabama, and Tennessee. The southern end of the route is in Natchez at its intersection with Liberty Road, and the northern end is northeast of Fairview, Tennessee, in the suburban community of Pasquo, at an intersection with Tennessee State Route 100. In addition to Natchez and Nashville, larger cities along the route include Jackson and Tupelo, Mississippi, and Florence, Alabama.

Washington is an unincorporated community in Adams County, Mississippi, United States. Located along the lower Mississippi, 6 miles (9.7 km) east of Natchez, it was the second and longest-serving capital of the Mississippi Territory.

Jefferson College is a former school in Washington, Mississippi. Named in honor of Thomas Jefferson, the college was chartered in 1802, but did not begin operation until 1811. Jefferson College was founded as an all-male college, but operated primarily as a college-preparatory school, and later became a military boarding school, which it remained for most of its history.

McRaven was built c. 1797 by Andrew Glass in a town called Walnut Hills, which is now Vicksburg, Mississippi. In the Civil War era, it was known as the Bobb House, and it is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as such. McRaven got its current name from the street it is located on, which was formerly called McRaven Street, but is now Harrison Street. McRaven has been on the Mississippi Department of Archives and History's Historic Preservation list since January 8, 1978. It is also believed by many to be haunted and has been called "the most haunted house in Mississippi."

The Emerald Mound site, also known as the Selsertown site, is a Plaquemine culture Mississippian period archaeological site located on the Natchez Trace Parkway near Stanton, Mississippi, United States. The site dates from the period between 1200 and 1730 CE. It is the type site for the Emerald Phase of the Natchez Bluffs Plaquemine culture chronology and was still in use by the later historic Natchez people for their main ceremonial center. The platform mound is the second-largest Mississippian period earthwork in the country, after Monk's Mound at Cahokia, Illinois.
A Mississippi Landmark is a building officially nominated by the Mississippi Department of Archives and History and approved by each county's chancery clerk. The Mississippi Landmark designation is the highest form of recognition bestowed on properties by the state of Mississippi, and designated properties are protected from changes that may alter the property's historic character. Currently there are 890 designated landmarks in the state. Mississippi Landmarks are spread out between eighty-one of Mississippi's eighty-two counties; only Issaquena County has no such landmarks.

Seven segments of the historic Natchez Trace are listed on the National Register of Historic Places (NRHP). Also there are additional NRHP-listed structures and other sites along the Natchez Trace, which served the travelers of the trace and survive from the era of its active use.

The Boyd Mounds Site (22MD512) is an archaeological site from the Late Woodland and Early Mississippian period located in Madison County, Mississippi near Ridgeland. Many of the mounds were excavated by The National Park Service in 1964. It is located at mile 106.9 on the old Natchez Trace, now the Natchez Trace Parkway. It was added to the NRHP on July 14, 1989 as NRIS number 89000784.

The John Gordon House is a historic brick home located along the Old Natchez Trace near Williamsport, Tennessee, within the boundaries of the Natchez Trace Parkway, a National Park Service unit.

Rocky Springs is a ghost town and historic site located in Claiborne County, Mississippi, United States, between Old Port Gibson Road and the Natchez Trace Parkway. The old town site can be viewed by the public during daylight hours. Rocky Springs and the surrounding area is maintained by the National Park Service.
Chappell Hill Female College was a private college in Chappell Hill, a rural community in Washington County, Texas, United States. It was founded in 1850 as part of the coeducational school Chappell Hill Male and Female Institute. First chartered by the Texas Legislature in 1852 as a non-denominational preparatory school, the charter was amended to affiliate the school with the Methodist Church in 1854, and was rechartered as a women's college after the male department was spun off as Soule University in 1856. It was closed in 1912 and the building became a public school until a replacement was built in 1927 that preserves the college's bell. The site was added to the National Register of Historic Places in 1985.
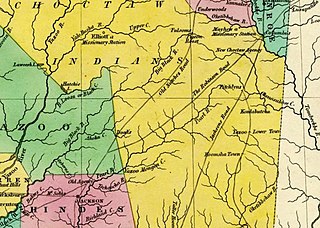
The Robinson Road is a historical road in the US state of Mississippi. It ran from Columbus to the Natchez Trace via Agency, Louisville, and Carthage. From the Natchez Trace intersection, the road continued to Canton; and the road's southwestern terminus was near Ridgeland, ten miles north of Jackson.
The Union School in Natchez was the first public, co-educational school by the city for African American students formed in 1871 and closed c. 1925, and was located at the southeast corner of North Union and Monroe Streets in Natchez, Mississippi.

Brumfield High School, formerly G. W.Brumfield School, was a segregated public high school for African American students built in 1925 and closed in 1990; located in Natchez, Mississippi.