Related Research Articles

The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger and improve nutrition and food security. Its Latin motto, fiat panis, translates to "let there be bread". It was founded on 16 October 1945.

The World Food Programme (WFP) is an international organization within the United Nations that provides food assistance worldwide. It is the world's largest humanitarian organization and the leading provider of school meals. Founded in 1961, WFP is headquartered in Rome and has offices in 87 countries. In 2023 it supported over 152 million people, and it is present in more than 120 countries and territories.

A farmer is a person engaged in agriculture, raising living organisms for food or raw materials. The term usually applies to people who do some combination of raising field crops, orchards, vineyards, poultry, or other livestock. A farmer might own the farmland or might work as a laborer on land owned by others. In most developed economies, a "farmer" is usually a farm owner (landowner), while employees of the farm are known as farm workers. However, in other older definitions a farmer was a person who promotes or improves the growth of plants, land, or crops or raises animals by labor and attention.

A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasants existed: non-free slaves, semi-free serfs, and free tenants. Peasants might hold title to land outright, or by any of several forms of land tenure, among them socage, quit-rent, leasehold, and copyhold.
The International Treaty on Plant Genetic Resources for Food and Agriculture is a comprehensive international agreement in harmony with the Convention on Biological Diversity, which aims at guaranteeing food security through the conservation, exchange and sustainable use of the world's plant genetic resources for food and agriculture (PGRFA), the fair and equitable benefit sharing arising from its use, as well as the recognition of farmers' rights. It was signed in 2001 in Madrid, and entered into force on 29 June 2004.

A family farm is generally understood to be a farm owned and/or operated by a family. It is sometimes considered to be an estate passed down by inheritance.

La Vía Campesina is an international farmers organization founded in 1993 in Mons, Belgium, formed by 182 organisations in 81 countries, and describing itself as "an international movement which coordinates peasant organizations of small and middle-scale producers, agricultural workers, rural women, and indigenous communities from Asia, Africa, America, and Europe".

The International Union for the Protection of New Varieties of Plants or UPOV is a treaty body with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland. Its objective is to provide an effective system for plant variety protection. It does so by defining a blueprint regulation to be implemented by its members in national law. The expression UPOV Convention also refers to one of the three instruments that relate to the union, namely the 1991 Act of the UPOV Convention, 1978 Act of the UPOV Convention and 1961 Act of the UPOV Convention with Amendments of 1972.
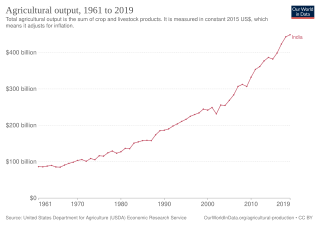
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.
Information and communication technology in agriculture, also known as e-agriculture, is a subset of agricultural technology focused on improved information and communication processes. More specifically, e-agriculture involves the conceptualization, design, development, evaluation and application of innovative ways to use information and communication technologies (ICTs) in the rural domain, with a primary focus on agriculture. ICT includes devices, networks, mobiles, services and applications; these range from innovative Internet-era technologies and sensors to other pre-existing aids such as fixed telephones, televisions, radios and satellites. Provisions of standards, norms, methodologies, and tools as well as development of individual and institutional capacities, and policy support are all key components of e-agriculture.

Agriculture in Kenya dominates Kenya's economy. 15–17 percent of Kenya's total land area has sufficient fertility and rainfall to be farmed, and 7–8 percent can be classified as first-class land. In 2006, almost 75 percent of working Kenyans made their living by farming, compared with 80 percent in 1980. About one-half of Kenya's total agricultural output is non-marketed subsistence production.
The term food system describes the interconnected systems and processes that influence nutrition, food, health, community development, and agriculture. A food system includes all processes and infrastructure involved in feeding a population: growing, harvesting, processing, packaging, transporting, marketing, consumption, distribution, and disposal of food and food-related items. It also includes the inputs needed and outputs generated at each of these steps.
Purchase for Progress (P4P) is an initiative of the United Nations World Food Programme (WFP), involving over 500 partnerships, including Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Howard G. Buffett Foundation, FAO, ACDI/VOCA, TechnoServe and others. Launched in September 2008 as a five-year pilot, P4P sought to explore programming and procurement modalities with the greatest potential to stimulate agricultural and market development in ways that maximized benefits to smallholder farmers. The program, largely developed by the eleventh Executive Director of the WFP, Josette Sheeran, arose as the WFP desired to purchase food in a way that was part of the "solution to hunger". These efforts are aligned with recommendations issued by the UN Committee on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights that call for an establishment of programs in support of socially vulnerable groups. and to the Zero Hunger Challenge launched by the UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon. Special UN Reporter 2012–2014, Olivier De Schutter, claimed that public procurement systems favour economically strong bidders, thus excluding smallholder farmers. His conclusion was that public procurement schemes supportive of smallholders could have "powerful impacts on the reduction of rural poverty." P4P is built upon this very principle as it enables low-income farmers to supply food to the WFP's operations. Eventually, the transaction can be regulated by a forward contract, with the farmer agreeing to sell in the future a certain amount of output at a fixed price. Essentially, the P4P program aims to create a wide and sophisticated market for commodities in developing countries.

The Committee on World Food Security (CFS) is an intergovernmental body within the United Nations System.

The Committee on Sustainability Assessment (COSA) is a global consortium of development institutions that work collaboratively to advance sustainability learning with systematic and science-based measurement. COSA applies a pragmatic and collective approach for using scientific methods to develop indicators, tools, and technologies to measure the distinct social, environmental, and economic impacts and are applied in performance monitoring, evaluation, return on investment (ROI) calculation, and impact assessment. COSA has a public mission to open its scientific methods and metrics up to widespread use.
Joyce Boye is a former federal food research scientist with Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada with a specialty in value-added food processing, food safety and food quality. She has expertise on plant proteins and their importance in helping to improve human health and nutrition. The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations appointed Boye to be a Special Ambassador for North America for the 2016 International Year of Pulses.
The Declaration on the Rights of Peasants is a United Nations General Assembly resolution on human rights with "universal understanding", adopted by the United Nations in 2018. The resolution was passed by a vote of 121-8, with 54 members abstaining.
Guy Kastler is a French peasant farmer, philosopher, activist for the rights of farmers and peasants, and documentary director. He is a representative of the European chapter of la Via Campesina and at French Réseau semences paysannes.
A number of movements seek to expand the practice of agroecology in West Africa. Agroecology is a scientific discipline, movement and practice that integrates ecology in agriculture with strong emphasis on diversification, food sovereignty, energy efficiency and sustainability. Agroecological practices apply the systems and knowledge that traditional farmers in the region have developed and inherited. The agroecological social movement empowers smallholder farmers that hold the knowledge of indigenous farming systems, however are recently engulfed by larger farms or are migrating to urban areas, looking for better paying jobs.

Squatting in Zimbabwe is the settlement of land or buildings without the permission of the owner. Squatting began under colonialism. After Zimbabwe was created in 1980, peasant farmers and squatters disputed the distribution of land. Informal settlements have developed on the periphery of cities such as Chitungwiza and the capital Harare. In 2005, Operation Murambatsvina evicted an estimated 700,000 people.
References
- 1 2 Davies, Sara (31 December 2016). "Elizabeth Mpofu, Africa's Pulse Ambassador". Naturally Zimbabwean. Archived from the original on 10 August 2019. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ "20 Heroines Revolutionizing Food Activism". Food Tank. 5 March 2020. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ L. Biron, Carey (18 December 2019). "Global recognition 'opens doors' for peasant groups, right to land". news.trust.org. Thomson Reuters. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ Bafana, Busani (16 October 2016). "The Beating Pulse of Food Security in Africa". www.ipsnews.net. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- 1 2 "Women are the Ones Who Take Care of Mother Earth". Radio Mundo Real. 12 July 2013. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ "Elizabeth Mpofu". EAT. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ "UN Human Rights Council passes a resolution adopting the peasant rights declaration in Geneva". www.cadtm.org. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ A. Wise, Timothy (24 January 2019). "UN Backs Seed Sovereignty in Landmark Peasants' Rights Declaration". Resilience. Archived from the original on 10 March 2020. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ Mpofu, Elizabeth (23 March 2016). "Women farm through knowledge sharing". Farming Matters. Retrieved 10 March 2020.
- ↑ Mpofu, Elizabeth; Nyoni, Ndabezinhle. "Role of pulses and smallholders in the transformation of Africa's agriculture". Nature & Faune. 31 (1). ISSN 2026-5611.