Related Research Articles

Armenians are an ethnic group and nation native to the Armenian highlands of West Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and constituted the main population of the breakaway Republic of Artsakh until the 2023 Azerbaijani offensive in Nagorno-Karabakh and the subsequent flight of Nagorno-Karabakh Armenians. There is a wide-ranging diaspora of around five million people of full or partial Armenian ancestry living outside modern Armenia. The largest Armenian populations today exist in Russia, the United States, France, Georgia, Iran, Germany, Ukraine, Lebanon, Brazil, Argentina, Syria, and Turkey. The present-day Armenian diaspora was formed mainly as a result of the Armenian genocide with the exceptions of Iran, former Soviet states, and parts of the Levant.

Rize Province is a province of northeast Turkey, on the eastern Black Sea coast between Trabzon and Artvin. The province of Erzurum is to the south. Its area is 3,835 km2, and its population is 344,016 (2022). The capital is the city of Rize. It was formerly known as Lazistan, however the designation of the term of Lazistan was officially banned in 1926.

The Hemshin people, also known as Hemshinli or Hamshenis or Homshetsi, are a bilingual small group of Armenians who practice Sunni Islam after they had been converted from Christianity in the beginning of the 18th century and are affiliated with the Hemşin and Çamlıhemşin districts in the province of Rize, Turkey. They are Armenian in origin, and were originally Christian members of the Armenian Apostolic Church, but over the centuries evolved into a distinct community and converted to Sunni Islam after the conquest of the region by the Ottomans during the second half of the 15th century. In Turkey, apart from those living in provinces of Artvin and Sakarya, Hemshin people do not speak the Homshetsi dialect and their mother tongue is Turkish.
Homshetsi is an archaic Armenian dialect spoken by the eastern and northern group of Hemshin peoples (Hemşinli), a people living in northeastern Turkey, Abkhazia, Russia, and Central Asia.

Grigor Narekatsi was an Armenian mystical and lyrical poet, monk, and theologian. He is venerated as a saint in the Armenian Apostolic and Catholic Churches and was declared a Doctor of the Church by Pope Francis in 2015.

Agathangelos is the pseudonym of the author of a life of the first apostle of Armenia, Gregory the Illuminator, who died about 332. The history attributed to Agathangelos is the main source for the Christianization of Armenia in the early 4th century.

Klarjeti was a province of ancient and medieval Georgia, which is now part of Turkey's Artvin Province. Klarjeti, the neighboring province of Tao and several other smaller districts, constituted a larger region with shared history and culture conventionally known as Tao-Klarjeti.
Paulicianism was a heretical medieval Christian sect which originated in Armenia in the 7th century. Followers of the sect were called Paulicians and referred to themselves as Good Christians. Little is known about the Paulician faith and various influences have been suggested, including Gnosticism, Marcionism, Manichaeism and Adoptionism, with other scholars arguing that doctrinally the Paulicians were a largely conventional Christian reform movement unrelated to any of these currents.
Vaspurakan was the eighth province of the ancient kingdom of Armenia, which later became an independent kingdom during the Middle Ages, centered on Lake Van. Located in what is now southeastern Turkey and northwestern Iran, the region is considered to be the cradle of Armenian civilization.

Hemşin, is a town in Rize Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey, 57 km from the city of Rize. It is the seat of Hemşin District. Its population is 1,472 (2021).
The Treaty of Zuhab, also called Treaty of Qasr-e Shirin, was an accord signed between the Safavid Empire and the Ottoman Empire on May 17, 1639. The accord ended the Ottoman-Safavid War of 1623–1639 and was the last conflict in almost 150 years of intermittent wars between the two states over territorial disputes. It can roughly be seen as a confirmation of the previous Peace of Amasya from 1555.

Tovma Artsruni was a ninth- to tenth-century Armenian historian who authored the History of the House of Artsrunik. Despite its title, the four-volume work not only relates the history of the Artsruni royal family, of which Tovma was a member, but also comprehensively covers the history of Armenia.

Ashkharhatsuyts, often translated as Geography in English sources, is an early medieval Armenian geography attributed to Anania Shirakatsi.

Narekavank was a tenth-century Armenian monastery in the historic province of Vaspurakan, near the southern shores of Lake Van, in present-day Gevaş district in the Van Province in eastern Turkey. The monastery was one of the most prominent in medieval Armenia and had a major school. The poet Gregory of Narek notably flourished at the monastery. It was abandoned in 1915 during the Armenian genocide, and reportedly demolished around 1951. A mosque now stands on its location.
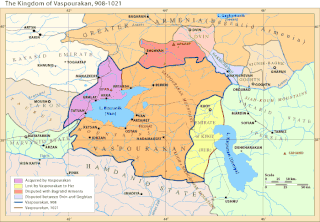
The Kingdom of Vaspurakan was a medieval Armenian kingdom centered on Lake Van, located in what is now eastern Turkey and northwestern Iran. It was named after Vaspurakan, a province of historic Greater Armenia. Ruled by the Artsruni dynasty, it competed and cooperated with the Bagratuni-ruled Kingdom of Armenia for a little over a century until its last king ceded the kingdom to the Byzantine Empire in 1021.
The Principality of Hamamshen was a small principality established in about 790 by Armenians who fled the Arab invasions of Armenia and the creation of the Muslim Arab-ruled state of Arminiya.

The Karin dialect is a Western Armenian dialect originally spoken in and around the city of Erzurum, now located in eastern Turkey.

Armash was a small Armenian-populated town located in the Ottoman Empire, near the Sea of Marmara. With its seminary and monastery of Charkhapan Surb Astvatsatsin, Armash served as the spiritual center of Armenians in western Asia Minor until 1915, when its inhabitants were rounded up and sent on death marches to the Syrian desert by orders of the leaders of the Committee of Union and Progress party.
Sırakonak is a neighbourhood in the municipality and district of İspir, Erzurum Province in Turkey. Its population is 251 (2022). It was formerly known as Hodiçor, Xodiçur and Xodorçur. The former names are derived from the Armenian name of the whole valley, the Khodorchur or Khotorjur. Before the Armenian genocide the settlement was the centre of a group of thirteen villages populated by Catholic Christian Armenians
Azordats-por(Ազորդաց փոր) was the southernmost canton of the province of Tayk in the kingdom of Armenia. it corresponds with the modern province of Tortum in the republic of Turkey. It was under the control of the Mamikonian noble family in the kingdom of Armenia, later passing to the rule of the Bagratuni princes of Tayk. The Bagratids line of Tayk converted to Chalcedonian Christianity and many of the Armenian villages and towns of the region became Chalcedonians. Later under Georgian rule, the Armenian Chalcedonian bishops joined the Georgian Catholicos and became part of the Georgian Orthodox Church while still retaining the use of Armenian in their liturgy while fully adopting the Byzantine rite.
References
- ↑ Simonian, Hovann H. (2001). "Review of The Armenians". Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies, University of London . 64 (1): 112–112. ISSN 0041-977X.
- ↑ Thomson, Robert W. (January 2000). "The Armenians. By A. E. Redgate. (The Peoples of Europe.) Pp. xix+331 incl. 14 plates, 3 figs and 22 maps. Oxford: Blackwell, 1998. £40. 0 631 14372 6". The Journal of Ecclesiastical History . 51 (1): 116–201. doi:10.1017/S0022046999243394. ISSN 1469-7637.
- ↑ Yannopoulos, P. (2001). "Review of The Armenians (Coll. The Peoples of Europe)". Byzantion. 71 (1): 278–280. ISSN 0378-2506.
- ↑ Pearson, Raymond (2000). "Review of The Armenians". The English Historical Review . 115 (460): 170–170. ISSN 0013-8266.
- ↑ Papazian, Dennis R. (January 1999). "The Armenians: Redgate, A. E.: Maiden: Blackwell 320 pp., Publication Date: February 1999". History: Reviews of New Books. 28 (1): 35–36. doi:10.1080/03612759.1999.10527783. ISSN 0361-2759.