
A heat exchanger is a system used to transfer heat between a source and a working fluid. Heat exchangers are used in both cooling and heating processes. The fluids may be separated by a solid wall to prevent mixing or they may be in direct contact. They are widely used in space heating, refrigeration, air conditioning, power stations, chemical plants, petrochemical plants, petroleum refineries, natural-gas processing, and sewage treatment. The classic example of a heat exchanger is found in an internal combustion engine in which a circulating fluid known as engine coolant flows through radiator coils and air flows past the coils, which cools the coolant and heats the incoming air. Another example is the heat sink, which is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, often air or a liquid coolant.

A boiler is a closed vessel in which fluid is heated. The fluid does not necessarily boil. The heated or vaporized fluid exits the boiler for use in various processes or heating applications, including water heating, central heating, boiler-based power generation, cooking, and sanitation.

A high pressure watertube boiler is a type of boiler in which water circulates in tubes heated externally by the fire. Fuel is burned inside the furnace, creating hot gas which boils water in the steam-generating tubes. In smaller boilers, additional generating tubes are separate in the furnace, while larger utility boilers rely on the water-filled tubes that make up the walls of the furnace to generate steam.

Babcock & Wilcox is an American renewable, environmental and thermal energy technologies and service provider that is active and has operations in many international markets across the globe with its headquarters in Akron, Ohio, USA. Historically, the company is best known for their steam boilers.
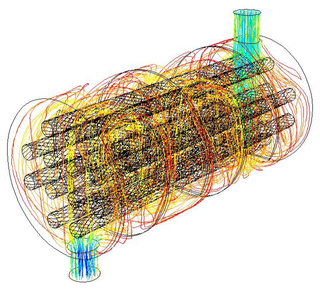
A shell and tube heat exchanger is a class of heat exchanger designs. It is the most common type of heat exchanger in oil refineries and other large chemical processes, and is suited for higher-pressure applications. As its name implies, this type of heat exchanger consists of a shell with a bundle of tubes inside it. One fluid runs through the tubes, and another fluid flows over the tubes to transfer heat between the two fluids. The set of tubes is called a tube bundle, and may be composed of several types of tubes: plain, longitudinally finned, etc.

A thermal power station is a type of power station in which heat energy is converted to electrical energy. In a steam-generating cycle heat is used to boil water in a large pressure vessel to produce high-pressure steam, which drives a steam turbine connected to an electrical generator. The low-pressure exhaust from the turbine enters a steam condenser where it is cooled to produce hot condensate which is recycled to the heating process to generate more high pressure steam. This is known as a Rankine cycle.
A deaerator is a device that removes oxygen and other dissolved gases from liquids and pumpable compounds.
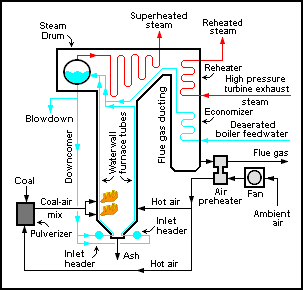
An air preheater is any device designed to heat air before another process (for example, combustion in a boiler With the primary objective of increasing the thermal efficiency of the process. They may be used alone or to replace a recuperative heat system or to replace a steam coil.
Smith Corona is an American manufacturer of thermal labels, direct thermal labels, and thermal ribbons used in warehouses for primarily barcode labels. Once a large U.S. typewriter and mechanical calculator manufacturer, it expanded aggressively during the 1960s to become a broad-based industrial conglomerate whose products extended to paints, foods, and paper. The mechanical calculator sector was wiped out in the early 1970s by the production of cheap electronic calculators, and the typewriter business collapsed in the mid-1980s due to the introduction of PC-based word processing.

A surface condenser is a water-cooled shell and tube heat exchanger installed to condense exhaust steam from a steam turbine in thermal power stations. These condensers are heat exchangers which convert steam from its gaseous to its liquid state at a pressure below atmospheric pressure. Where cooling water is in short supply, an air-cooled condenser is often used. An air-cooled condenser is however, significantly more expensive and cannot achieve as low a steam turbine exhaust pressure as a water-cooled surface condenser.

Elliott Company designs, manufactures, installs, and services turbo-machinery for prime movers and rotating machinery. Headquartered in Jeannette, Pennsylvania, Elliott Company is a wholly owned subsidiary of the Japan-based company, Ebara Corporation, and is a unit of Elliott Group, Ebara Corporation's worldwide turbomachinery business. Elliott Group employs more than 2000 employees worldwide at 32 locations, with approximately 900 in Jeannette.

MAPNA Group is a group of Iranian companies involved in development and execution of thermal and renewable power plants, oil & gas, railway transportation and other industrial projects as well as manufacturing main equipment including gas and steam turbines, electrical generator, turbine blade and vane, HRSG and conventional boilers, electric and control systems, gas compressor, locomotive and other pertinent equipment.

Advanced steam technology reflects an approach to the technical development of the steam engine intended for a wider variety of applications than has recently been the case. Particular attention has been given to endemic problems that led to the demise of steam power in small- to medium-scale commercial applications: excessive pollution, maintenance costs, labour-intensive operation, low power/weight ratio, and low overall thermal efficiency; where steam power has generally now been superseded by the internal combustion engine or by electrical power drawn from an electrical grid. The only steam installations that are in widespread use are the highly efficient thermal power plants used for generating electricity on a large scale. In contrast, the proposed steam engines may be for stationary, road, rail or marine use.
Energy recycling is the energy recovery process of utilizing energy that would normally be wasted, usually by converting it into electricity or thermal energy. Undertaken at manufacturing facilities, power plants, and large institutions such as hospitals and universities, it significantly increases efficiency, thereby reducing energy costs and greenhouse gas pollution simultaneously. The process is noted for its potential to mitigate global warming profitably. This work is usually done in the form of combined heat and power or waste heat recovery.

BGR Energy Systems Limited is a company headquartered at Chennai, operating in the utility industry, offering services ranging from product manufacturing to project execution. The Company operates in two segments: capital goods and construction and engineering procurement construction (EPC) Contracts.

A waste heat recovery unit (WHRU) is an energy recovery heat exchanger that transfers heat from process outputs at high temperature to another part of the process for some purpose, usually increased efficiency. The WHRU is a tool involved in cogeneration. Waste heat may be extracted from sources such as hot flue gases from a diesel generator, steam from cooling towers, or even waste water from cooling processes such as in steel cooling.
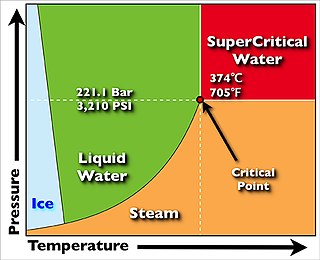
A supercritical steam generator is a type of boiler that operates at supercritical pressure and temperature, frequently used in the production of electric power.

Isgec Heavy Engineering Ltd is an Indian heavy engineering company. Established in 1933 as Saraswati Sugar Syndicate, company held a revenue of ₹5,477 crore (US$690 million) in 2021 with exports to approximate across 91 countries. It was ranked 252 in the ET 2021 listing, and 253 in the Fortune India 500 Listings.
Lagonda is a British luxury car marque now owned by Aston Martin.
Computational fluid dynamics (CFD) are used to understand complex thermal flow regimes in power plants. The thermal power plant may be divided into different subsectors and the CFD analysis applied to critical equipment/components - mainly different types of heat exchangers - which are of crucial significance for efficient and trouble free long-term operation of the plant.















