Related Research Articles

Waverly is the largest village in Tioga County, New York, United States. According to the 2010 U.S. Census, Waverly had a population of 4,177. It is located southeast of Elmira in the Southern Tier region. This village was incorporated as the southwest part of the town of Barton in 1854. The village name is attributed to Joseph "Uncle Joe" Hallett, founder of its first Fire Department and pillar of the community, who conceived the name by dropping the second "e" from the name of his favorite author's novel, Waverley by Sir Walter Scott. The former village hall is listed on the National Historic Places list.

New York State Route 17 (NY 17) is a major state highway that extends for 397 miles (638.91 km) through the Southern Tier and Downstate regions of New York in the United States. It begins at the Pennsylvania state line in Mina and follows the Southern Tier Expressway east through Corning to Binghamton and the Quickway from Binghamton east to Woodbury, where it turns south to follow the Orange Turnpike to the New Jersey state line near Suffern, where it connects to New Jersey Route 17. From the Pennsylvania border to the village of Waverly and from Binghamton to Windsor, NY 17 is concurrent with Interstate 86 (I-86). Eventually, the entire east–west portion of NY 17 from the Pennsylvania border to Woodbury will become I-86 as projects to upgrade the route to Interstate Highway standards are completed.

The Interurban is a type of electric railway, with streetcar-like electric self-propelled rail cars which run within and between cities or towns. They were very prevalent in North America between 1900 and 1925 and were used primarily for passenger travel between cities and their surrounding suburban and rural communities. The concept spread to countries such as Japan, the Netherlands, Switzerland, Belgium, Italy and Poland. Interurban as a term encompassed the companies, their infrastructure, their cars that ran on the rails, and their service. In the United States, the early 1900s interurban was a valuable economic institution. Most roads between towns and many town streets were unpaved. Transportation and haulage was by horse-drawn carriages and carts. The interurban provided reliable transportation, particularly in winter weather, between the town and countryside. In 1915, 15,500 miles (24,900 km) of interurban railways were operating in the United States and, for a few years, interurban railways, including the numerous manufacturers of cars and equipment, were the fifth-largest industry in the country. By 1930, most interurbans in North America were gone with a few surviving into the 1950s.

The Southern Tier is a geographic subregion of the broader Upstate New York region of New York State, consisting of counties west of the Catskill Mountains in Delaware County and geographically situated along or very near the northern border of Pennsylvania. Definitions of the region vary widely, but generally encompass localities in counties surrounding the Binghamton and Elmira-Corning metropolitan areas. This region is bordered to the south by the Northern Tier of Pennsylvania and both these regions together are known as the Twin Tiers.

The Chemung River is a tributary of the Susquehanna River, approximately 46.4 miles (74.7 km) long, in south central New York and northern Pennsylvania in the United States. It drains a mountainous region of the northern Allegheny Plateau in the Southern Tier of New York. The valley of the river has long been an important manufacturing center in the region but has suffered a decline in the late 20th century.

Tower City Center is a large mixed-use facility in Downtown Cleveland, Ohio, on its Public Square. The facility is composed of a number of interconnected office buildings, including Terminal Tower, the Avenue shopping mall, Jack Cleveland Casino, Renaissance Cleveland Hotel, Chase Financial Plaza, and Tower City station, the main hub of Cleveland's four RTA Rapid Transit lines.
The Lehigh Valley Railroad was a railroad built in the Northeastern United States to haul anthracite coal from the Coal Region in Pennsylvania. The railroad was authorized on April 21, 1846, for freight and transportation of passengers, goods, wares, merchandise and minerals in Pennsylvania and the railroad was incorporated and established on September 20, 1847, as the Delaware, Lehigh, Schuylkill and Susquehanna Railroad Company. On January 7, 1853, the railroad's name was changed to Lehigh Valley Railroad. It was sometimes known as the Route of the Black Diamond, named after the anthracite it transported. At the time, anthracite was transported by boat down the Lehigh River. The railroad ended operations in 1976 and merged into Conrail along with several northeastern railroads that same year.

Interstate 86 (I-86) is an Interstate Highway that extends for 223.39 miles (359.51 km) through northwestern Pennsylvania and the Southern Tier region of New York, in the United States. The highway has two segments: the longer of the two begins at an interchange with I-90 east of Erie, Pennsylvania, and ends just beyond the Chemung-Tioga county line at the Pennsylvania border, while the second extends from I-81 east of Binghamton to New York State Route 79 (NY 79) in Windsor. When projects to upgrade the existing NY 17 to Interstate Highway standards are completed, I-86 will extend from I-90 near Erie to the New York State Thruway (I-87) in Woodbury. The portion in Erie County, Pennsylvania, is known as the Hopkins-Bowser Highway and is signed as such at each end. In New York, the current and future alignment of I-86 is known as the Southern Tier Expressway west of I-81 in Binghamton and the Quickway east of I-81.

New York State Railways was a subsidiary of the New York Central Railroad that controlled several large city streetcar and electric interurban systems in upstate New York. It included the city transit lines in Rochester, Syracuse, Utica, Oneida and Rome, plus various interurban lines connecting those cities. New York State Railways also held a 50% interest in the Schenectady Railway Company, but it remained a separate independent operation. The New York Central took control of the Rochester Railway Company, the Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway and the Rochester and Sodus Bay Railway in 1905, and the Mohawk Valley Company was formed by the railroad to manage these new acquisitions. New York State Railways was formed in 1909 when the properties controlled by the Mohawk Valley Company were merged. In 1912 it added the Rochester and Suburban Railway, the Syracuse Rapid Transit Railway, the Oneida Railway, and the Utica and Mohawk Valley Railway. The New York Central Railroad was interested in acquiring these lines in an effort to control the competition and to gain control of the lucrative electric utility companies that were behind many of these streetcar and interurban railways. Ridership across the system dropped through the 1920s as operating costs continued to rise, coupled with competition from better highways and private automobile use. New York Central sold New York State Railways in 1928 to a consortium led by investor E. L. Phillips, who was looking to gain control of the upstate utilities. Phillips sold his stake to Associated Gas & Electric in 1929, and the new owners allowed the railway bonds to default. New York State Railways entered receivership on December 30, 1929. The company emerged from receivership in 1934, and local operations were sold off to new private operators between 1938 and 1948.

New York State Route 352 (NY 352) is a state highway in the Southern Tier of New York in the United States. It generally parallels the Southern Tier Expressway from the village of Riverside (exit 45) east through the city of Corning to the city of Elmira (exit 56). The portion of NY 352 west of the hamlet of Big Flats was once part of NY 17; the rest was originally New York State Route 17E. Construction of and improvements to the Southern Tier Expressway have resulted in extensions of NY 352, primarily along the former NY 17 right-of-way.
The Elmira and Lake Ontario Railroad was a subsidiary of the Northern Central Railway and later the Pennsylvania Railroad, formed to give the Northern Central an outlet for coal traffic on Lake Ontario.
The Vaca Valley and Clear Lake Railroad was a standard gauge railroad that operated at Vacaville, California in the late 19th century. The Vaca Valley Railroad was incorporated on April 12, 1869 to run a branch from the mainline of the California Pacific Railroad at Elmira to Rumsey.

The New York Museum of Transportation (NYMT), founded in 1975, is a non-profit organization located at 6393 East River Road, in the Rochester suburb of Rush. A private rail line built by volunteers connects NYMT with the Rochester & Genesee Valley Railroad Museum, over a distance of two miles. This demonstration railway allows both museums to offer train rides with their collections of vintage railroad equipment. NYMT operates the only electric trolley ride in New York State, not to be confused with the similarly named Trolley Museum of New York located in Kingston, New York.

The Corning train wreck was a railway accident that occurred at 5.21 a.m. on July 4, 1912, on the Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad at East Corning freight station in Gibson three miles east of Corning in New York State, leaving 39 dead and 88 injured.
Chartered in 1886, the Canandaigua Street Railroad was a local streetcar line serving the lakeside city of Canandaigua, New York beginning in 1887. The railroad was sold to the Canandaigua Electric Light and Railroad which rebuilt and electrified the line in 1892. The Ontario Light and Traction Company purchased it in 1900, and leased the line to the Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway in 1903. In 1905, the line came under the control of the Mohawk Valley Company, and in turn, New York State Railways in 1909. Operation was converted to bus operation some time in the 1920s, but this service ended when the Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway shut down on July 31, 1930. The lease of the former Canandaiua lines was allowed to lapse.
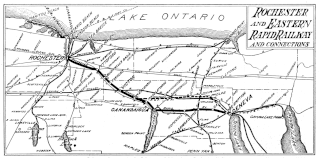
The Rochester and Eastern Rapid Railway (R&ER) was an electric interurban railway in New York State, USA, connecting Rochester, Canandaigua, and Geneva.
The Utica and Mohawk Valley Railway was the result of the unification of all city and suburban streetcar lines serving Utica, New York, on November 27, 1901. The railway operated city streetcar service as well as a double-track interurban railway between Rome and Little Falls via Utica. The Utica and Mohawk Valley Railway was merged into New York State Railways in 1912. At its peak, the Utica Lines consisted of 17 transit routes operated with more than 100 cars. The line ceased operation in 1933, except for the section between Utica and Whitesboro that survived until 1938. The last city streetcars operated on May 31, 1941. The remaining transit routes were operated with buses and the franchise would be reorganized as the Utica Transit Corporation in 1948.
The Newark and Marion Railway operated between Newark, New York, and Marion, New York. Chartered in 1900, it opened for business in 1906. The railroad was constructed by the Beebe Syndicate, a conglomeration of streetcar and interurban lines across New York State, though the Newark and Marion was never electrified. The company entered receivership in 1915, and control by the Beebe Syndicate ended. The railroad was reorganized as the Marion Railway Corporation in 1917. The Pennsylvania Railroad acquired the line in 1930. It continued to operate as a spur of the Elmira Branch through the Penn Central and Conrail eras. Operation passed to short line Ontario Midland Railroad in 1979. Dwindling freight traffic and deteriorating track conditions led to the line's closure in July 1984.

The Waterloo, Cedar Falls and Northern Railway (WCF&N) was an electric interurban railway that operated in the US state of Iowa.
References
- ↑ Reifschneider, Felix E. (1947). Toonervilles of the Empire State. Orlando, Florida. p. 14.
- ↑ "Interurban Railways in New York and New Jersey". ChicagoRailFan.
The last surviving car from this line, complete with its trucks, motors and control equipment is in the permanent collection of the New York Museum of Transportation, Rush, New York.