The Kingdom of Butua or Butwa was a pre-colonial African state located in what is now southwestern Zimbabwe. Butua was renowned as the source of gold for Arab and Portuguese traders. The region was first mentioned in Portuguese records in 1512.

The Sara people are Nilotes originating from the Upper Nile. They predominantly reside in southern Chad, the northwestern areas of the Central African Republic, and the southern border of North Sudan. They speak the Sara languages, a dialect or sub-group of the Nilo-Saharan family. They are also the largest ethnic group in Chad.

The Banda people are an ethnic group of the Central African Republic. They are also found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Cameroon, and South Sudan. They were severely affected by slave raids of the 19th century and slave trading out of Africa. Under French colonial rule, most converted to Christianity but retained elements of their traditional religious systems and values.

Maba people are a minority ethnic group found primarily in the mountainous Ouaddaï region of eastern Chad, with some across its border with Sudan and Central African Republic. Their population is estimated to be about 300,000 in Chad. Other estimates place the total number of Maba people in north-Central Africa to be about 700,000.

The Susu people, also called Soso or Soussou, are a West African ethnic group, one of the Mandé peoples living primarily in Guinea and Northwestern Sierra Leone, particularly in Kambia District. Influential in Guinea, smaller communities of Susu people are also found in the neighboring Guinea-Bissau, Senegal and Mali.

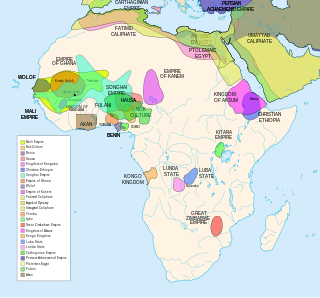
The history of external colonisation of Africa can be divided into two stages: Classical antiquity and European colonialism. In popular parlance, discussions of colonialism in Africa usually focus on the European conquests that resulted in the Scramble for Africa after the Berlin Conference in the 19th century. Settlements established by Europeans while incorporated abjection of natives, also brought with it governing and academic institutions as well as agricultural and technological innovations that offset the extractive institutions commonly attributed to colonialism by Western powers.

Botswana is a Christian majority nation, and allows freedom of religious practice. A country of an estimated 2.26 million people in 2015, Christianity arrived in Botswana in mid 1870s, with the arrival of Christian missionaries. The conversion process was relatively quick than neighboring southern African countries, because regional hereditary tribal chiefs locally called Dikgosi converted to Christianity, which triggered the entire group they led to convert as well.
Lawrence Chola Katilungu was a Northern Rhodesian trade union leader. Katilungu was the first President of the African Mineworkers' Union.
The Daily Times is a daily newspaper published in Blantyre, Malawi. It is the oldest newspaper in the country, founded as the monthly Central African Planter in 1895. Around 1900 the title Central African Times was adopted, and weekly publication. Later the title was changed again, to Nyasaland Times. With Malawian independence in 1964 it became simply The Times, and finally the Daily Times in 1972.

An independence referendum was held in the French Territory of the Afars and the Issas on 8 May 1977 alongside an election for a Constituent Assembly. Previous referendums were held in 1958 and 1967, which rejected independence. This referendum backed independence from France. The territory became independent as Djibouti on 27 June 1977.

Presidential elections were held for the first time in Mauritania in August 1961 to elect the President for the next five years. Moktar Ould Daddah, who had been acting head of state since independence from France in 1960 was the only candidate, and was elected unopposed. Although he was a member of the ruling Mauritanian Regroupment Party, his candidacy was also supported by the Mauritanian National Union. Voter turnout was 93.6%.

Presidential elections were held in Mauritania on 7 August 1966. Following the merger of all the country's political parties into the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM), the country had become a one-party state in December 1961. Its leader, incumbent President Moktar Ould Daddah, was the only candidate, and was re-elected unopposed. Voter turnout was 96.2%.

General elections were held in Mauritania on 8 August 1971 to elect a President and National Assembly, the first time the two elections had been held together. At the time, the country was a one-party state with the Mauritanian People's Party (PPM) as the sole legal party. Its leader, incumbent President Moktar Ould Daddah, was the only candidate in the presidential election, and was re-elected unopposed to a third term in office, whilst the PPM won all 50 seats in the National Assembly election. Voter turnout for the parliamentary election was reported to be 95.6%.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Lusaka, Zambia.
The following is a timeline of the history of the city of Kano, Nigeria.
The Liberal Constitutional Party was an Egyptian political party founded in 1922 by a group of politicians that left the Wafd Party.
Theodore Dakpogan is a Beninois Vodou artist. His work is influenced by 19th century Fon sculpture. He is noted for his scrap metal sculptures.

General elections were held in Northern Rhodesia in 1938. An additional unofficial member was appointed to the Legislative Council to represent African interests.