Related Research Articles

A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates.

Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique.

Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of the biliary or pancreatic ductal systems. It is primarily performed by highly skilled and specialty trained gastroenterologists. Through the endoscope, the physician can see the inside of the stomach and duodenum, and inject a contrast medium into the ducts in the biliary tree and pancreas so they can be seen on radiographs.

Gallbladder cancer is a relatively uncommon cancer, with an incidence of fewer than 2 cases per 100,000 people per year in the United States. It is particularly common in central and South America, central and eastern Europe, Japan and northern India; it is also common in certain ethnic groups e.g. Native American Indians and Hispanics. If it is diagnosed early enough, it can be cured by removing the gallbladder, part of the liver and associated lymph nodes. Most often it is found after symptoms such as abdominal pain, jaundice and vomiting occur, and it has spread to other organs such as the liver.

A pancreatic pseudocyst is a circumscribed collection of fluid rich in pancreatic enzymes, blood, and non-necrotic tissue, typically located in the lesser sac of the abdomen. Pancreatic pseudocysts are usually complications of pancreatitis, although in children they frequently occur following abdominal trauma. Pancreatic pseudocysts account for approximately 75% of all pancreatic masses.

Pseudocysts are like cysts, but lack epithelial or endothelial cells. Initial management consists of general supportive care. Symptoms and complications caused by pseudocysts require surgery. Computed tomography (CT) scans are used for initial imaging of cysts, and endoscopic ultrasounds are used in differentiating between cysts and pseudocysts. Endoscopic drainage is a popular and effective method of treating pseudocysts.

Cholestasis is a condition where bile cannot flow from the liver to the duodenum. The two basic distinctions are an obstructive type of cholestasis where there is a mechanical blockage in the duct system that can occur from a gallstone or malignancy, and metabolic types of cholestasis which are disturbances in bile formation that can occur because of genetic defects or acquired as a side effect of many medications. Classification is further divided into acute or chronic and extrahepatic or intrahepatic.
Pancreatic divisum is a congenital anomaly in the anatomy of the ducts of the pancreas in which a single pancreatic duct is not formed, but rather remains as two distinct dorsal and ventral ducts. Most individuals with pancreas divisum remain without symptoms or complications. A minority of people with pancreatic divisum may develop episodes of abdominal pain, nausea or vomiting due to acute or chronic pancreatitis. The presence of pancreas divisum is usually identified with cross sectional diagnostic imaging, such as MRI or computed tomography (CT) imaging. In some cases, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is performed, revealing the diagnosis of pancreas divisum. If no symptoms or complications are present, then treatment is not necessary. However, if there is recurrent pancreatitis, then a sphincterotomy of the minor papilla may be indicated.
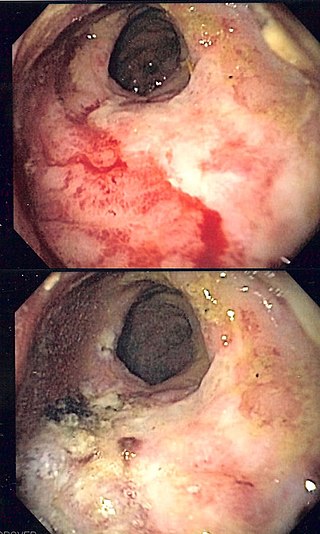
Radiation proctitis or radiation proctopathy is a condition characterized by damage to the rectum after exposure to x-rays or other ionizing radiation as a part of radiation therapy. Radiation proctopathy may occur as acute inflammation called "acute radiation proctitis" or with chronic changes characterized by radiation associated vascular ectasiae (RAVE) and chronic radiation proctopathy. Radiation proctitis most commonly occurs after pelvic radiation treatment for cancers such as cervical cancer, prostate cancer, bladder cancer, and rectal cancer. RAVE and chronic radiation proctopathy involves the lower intestine, primarily the sigmoid colon and the rectum, and was previously called chronic radiation proctitis, pelvic radiation disease and radiation enteropathy.

A biliary fistula is a type of fistula in which bile flows along an abnormal connection from the bile ducts into nearby hollow structure. Types of biliary fistula include:

Double-balloon enteroscopy, also known as push-and-pull enteroscopy, is an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel. It was developed by Hironori Yamamoto in 2001. It is novel in the field of diagnostic gastroenterology as it is the first endoscopic technique that allows for the entire gastrointestinal tract to be visualized in real time.

Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum. It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.
Postcholecystectomy syndrome (PCS) describes the presence of abdominal symptoms after a cholecystectomy.

A self-expandable metallic stent is a metallic tube, or stent that holds open a structure in the gastrointestinal tract to allow the passage of food, chyme, stool, or other secretions related to digestion. Surgeons insert SEMS by endoscopy, inserting a fibre optic camera—either through the mouth or colon—to reach an area of narrowing. As such, it is termed an endoprosthesis. SEMS can also be inserted using fluoroscopy where the surgeon uses an X-ray image to guide insertion, or as an adjunct to endoscopy.
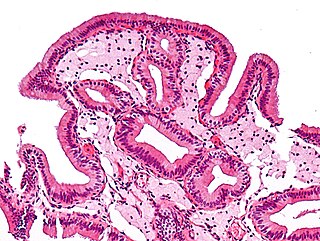
Gallbladder diseases are diseases involving the gallbladder and is closely linked to biliary disease, with the most common cause being gallstones (cholelithiasis).

Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, percutaneous hepatic cholangiogram (PTHC) is a radiological technique used to visualize the anatomy of the biliary tract. A contrast medium is injected into a bile duct in the liver, after which X-rays are taken. It allows access to the biliary tree in cases where endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography has been unsuccessful. Initially reported in 1937, the procedure became popular in 1952.

An esophageal stent is a stent (tube) placed in the esophagus to keep a blocked area open so the patient can swallow soft food and liquids. They are effective in the treatment of conditions causing intrinsic esophageal obstruction or external esophageal compression. For the palliative treatment of esophageal cancer most esophageal stents are self-expandable metallic stents. For benign esophageal disease such as refractory esophageal strictures, plastic stents are available. Common complications include chest pain, overgrowth of tissue around the stent and stent migration.
Cystogastrostomy is a surgery to create an opening between a pancreatic pseudocyst and the stomach when the cyst is in a suitable position to be drained into the stomach. This conserves pancreatic juices that would otherwise be lost. This surgery is performed by a pancreatic surgeon to avoid a life-threatening rupture of the pancreatic pseudocyst.
Buried bumper syndrome (BBS) is a condition that affects feeding tubes placed into the stomach through the abdominal wall. Gastrostomy tubes include an internal bumper, which secures the inner portion of the tube inside the stomach, and external bumper, which secures the outer portion of the tube and opposes the abdomen. Buried bumper syndrome occurs when the internal bumper of a gastrostomy tube erodes into the wall of the stomach. The internal bumper may become entirely buried within the fistulous tract. The main causative factor is excessive tightening of the external bumper, leading to increased pressure of the internal bumper on the wall of the stomach. Additional risk factors include: obesity, weight gain, malnutrition, corticosteroid therapy, and poor wound healing.

Biliary endoscopic sphincterotomy is a procedure where the sphincter of Oddi and the segment of the common bile duct where it enters the duodenum are cannulated and then cut with a sphincterotome, a device that includes a wire which cuts with an electric current (electrocautery).
References
- 1 2 Lam R, Muniraj T (October 2021). "Fully covered metal biliary stents: A review of the literature". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 27 (38): 6357–6373. doi:10.3748/wjg.v27.i38.6357. PMC 8517778 . PMID 34720527.
- ↑ McLoughlin MT, Byrne MF (June 2008). "Endoscopic stenting: where are we now and where can we go?". World Journal of Gastroenterology. 14 (24): 3798–3803. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.3798. PMC 2721435 . PMID 18609702.
- ↑ "Pancreatic, Gallbladder and Biliary Surgery". Keck Medicine. University of Southern California (USC).