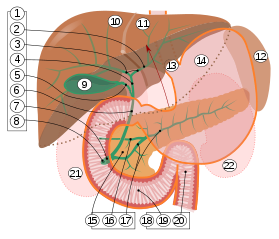
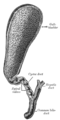
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and stores it. The bile is then released via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats.

A bile duct is any of a number of long tube-like structures that carry bile, and is present in most vertebrates. The bile duct is separated into three main parts: the fundus (superior), the body (middle), and the neck (inferior).

Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique.
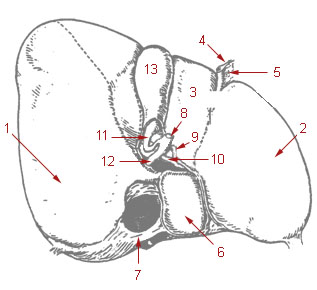
The cystic duct is the duct that (typically) joins the gallbladder and the common hepatic duct; the union of the cystic duct and common hepatic duct forms the bile duct. Its length varies.
Courvoisier's principle states that a painless palpably enlarged gallbladder accompanied with mild jaundice is unlikely to be caused by gallstones. Usually, the term is used to describe the physical examination finding of the right-upper quadrant of the abdomen. This sign implicates possible malignancy of the gallbladder or pancreas and the swelling is unlikely due to gallstones.

Common bile duct stone, also known as choledocholithiasis, is the presence of gallstones in the common bile duct (CBD). This condition can cause jaundice and liver cell damage. Treatments include choledocholithotomy and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP).

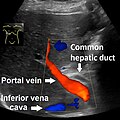
The common hepatic duct is the first part of the biliary tract. It joins the cystic duct coming from the gallbladder to form the common bile duct.
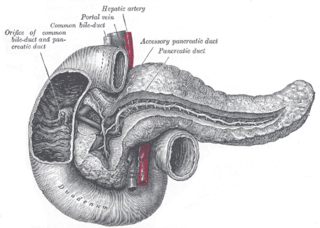
The pancreatic duct or duct of Wirsung is a duct joining the pancreas to the common bile duct. This supplies it with pancreatic juice from the exocrine pancreas, which aids in digestion.

In anatomy, the gastroduodenal artery is a small blood vessel in the abdomen. It supplies blood directly to the pylorus and proximal part of the duodenum. It also indirectly supplies the pancreatic head.

Ascending cholangitis, also known as acute cholangitis or simply cholangitis, is inflammation of the bile duct, usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum. It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.

The major duodenal papilla is a rounded projection in the duodenum into which the common bile duct and pancreatic duct drain. The major duodenal papilla is, in most people, the primary mechanism for the secretion of bile and other enzymes that facilitate digestion.

The biliary tract refers to the liver, gallbladder and bile ducts, and how they work together to make, store and secrete bile. Bile consists of water, electrolytes, bile acids, cholesterol, phospholipids and conjugated bilirubin. Some components are synthesized by hepatocytes ; the rest are extracted from the blood by the liver.

Percutaneous transhepatic cholangiography, percutaneous hepatic cholangiogram (PTHC) is a radiological technique used to visualize the anatomy of the biliary tract. A contrast medium is injected into a bile duct in the liver, after which X-rays are taken. It allows access to the biliary tree in cases where endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography has been unsuccessful. Initially reported in 1937, the procedure became popular in 1952.
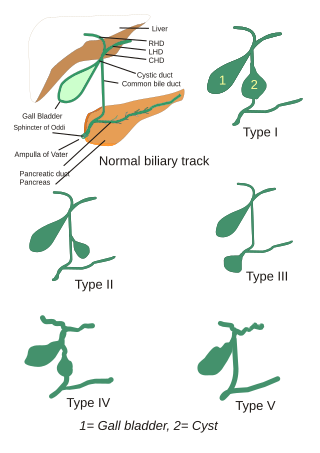
Choledochal cysts are congenital conditions involving cystic dilatation of bile ducts. They are uncommon in western countries but not as rare in East Asian nations like Japan and China.
Biliary dyskinesia is a disorder of some component of biliary part of the digestive system in which bile cannot physically move in the proper direction through the tubular biliary tract. It most commonly involves abnormal biliary tract peristalsis muscular coordination within the gallbladder in response to dietary stimulation of that organ to squirt the liquid bile through the common bile duct into the duodenum. Ineffective peristaltic contraction of that structure produces postprandial right upper abdominal pain (cholecystodynia) and almost no other problem. When the dyskinesia is localized at the biliary outlet into the duodenum just as increased tonus of that outlet sphincter of Oddi, the backed-up bile can cause pancreatic injury with abdominal pain more toward the upper left side. In general, biliary dyskinesia is the disturbance in the coordination of peristaltic contraction of the biliary ducts, and/or reduction in the speed of emptying of the biliary tree into the duodenum.

Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction refers to a group of functional disorders leading to abdominal pain due to dysfunction of the Sphincter of Oddi: functional biliary sphincter of Oddi and functional pancreatic sphincter of Oddi disorder. The sphincter of Oddi is a sphincter muscle, a circular band of muscle at the bottom of the biliary tree which controls the flow of pancreatic juices and bile into the second part of the duodenum. The pathogenesis of this condition is recognized to encompass stenosis or dyskinesia of the sphincter of Oddi ; consequently the terms biliary dyskinesia, papillary stenosis, and postcholecystectomy syndrome have all been used to describe this condition. Both stenosis and dyskinesia can obstruct flow through the sphincter of Oddi and can therefore cause retention of bile in the biliary tree and pancreatic juice in the pancreatic duct.
Pancreaticobiliary maljunction(PBM) is a congenital malformation where the pancreatic and bile ducts meet outside of the duodenum. There are two varieties of PBM: one with biliary dilatation and the other without. When an abnormally long common channel is visible on direct cholangiography, such as endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, PBM is diagnosed.

The sphincter of Oddi, abbreviated as SO, is a muscular valve that in some animals, including humans, controls the flow of bile and pancreatic juice out of the gallbladder and pancreas respectively through the ampulla of Vater into the second part of the duodenum. It is named after Ruggero Oddi.

Choledochoduodenostomy (CDD) is a surgical procedure to create an anastomosis, a surgical connection, between the common bile duct (CBD) and an alternative portion of the duodenum. In healthy individuals, the CBD meets the pancreatic duct at the ampulla of Vater, which drains via the major duodenal papilla to the second part of duodenum. In cases of benign conditions such as narrowing of the distal CBD or recurrent CBD stones, performing a CDD provides the diseased patient with CBD drainage and decompression. A side-to-side anastomosis is usually performed.

Biliary endoscopic sphincterotomy is a procedure where the sphincter of Oddi and the segment of the common bile duct where it enters the duodenum are cannulated and then cut with a sphincterotome, a device that includes a wire which cuts with an electric current (electrocautery).