Alcoholic liver disease (ALD), also called alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD), is a term that encompasses the liver manifestations of alcohol overconsumption, including fatty liver, alcoholic hepatitis, and chronic hepatitis with liver fibrosis or cirrhosis.

A hepatocyte is a cell of the main parenchymal tissue of the liver. Hepatocytes make up 80% of the liver's mass. These cells are involved in:

Alcoholic hepatitis is hepatitis due to excessive intake of alcohol. Patients typically have a history of at least 10 years of heavy alcohol intake, typically 8–10 drinks per day. It is usually found in association with fatty liver, an early stage of alcoholic liver disease, and may contribute to the progression of fibrosis, leading to cirrhosis. Symptoms may present acutely after a large amount of alcoholic intake in a short time period, or after years of excess alcohol intake. Signs and symptoms of alcoholic hepatitis include jaundice, ascites, fatigue and hepatic encephalopathy. Mild cases are self-limiting, but severe cases have a high risk of death. Severity in alcoholic hepatitis is determined several clinical prediction models such as the Maddrey's Discriminant Function and the MELD score.

Autoimmune hepatitis, formerly known as lupoid hepatitis, plasma cell hepatitis, or autoimmune chronic active hepatitis, is a chronic, autoimmune disease of the liver that occurs when the body's immune system attacks liver cells, causing the liver to be inflamed. Common initial symptoms may include fatigue, nausea, muscle aches, or weight loss or signs of acute liver inflammation including fever, jaundice, and right upper quadrant abdominal pain. Individuals with autoimmune hepatitis often have no initial symptoms and the disease may be detected by abnormal liver function tests and increased protein levels during routine bloodwork or the observation of an abnormal-looking liver during abdominal surgery.

Portal hypertension is defined as increased portal venous pressure, with a hepatic venous pressure gradient greater than 5 mmHg. Normal portal pressure is 1–4 mmHg; clinically insignificant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures 5–9 mmHg; clinically significant portal hypertension is present at portal pressures greater than 10 mmHg. The portal vein and its branches supply most of the blood and nutrients from the intestine to the liver.

Fatty liver disease (FLD), also known as hepatic steatosis and steatotic liver disease (SLD), is a condition where excess fat builds up in the liver. Often there are no or few symptoms. Occasionally there may be tiredness or pain in the upper right side of the abdomen. Complications may include cirrhosis, liver cancer, and esophageal varices.

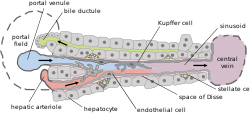
Kupffer cells, also known as stellate macrophages and Kupffer–Browicz cells, are specialized cells localized in the liver within the lumen of the liver sinusoids and are adhesive to their endothelial cells which make up the blood vessel walls. Kupffer cells comprise the largest population of tissue-resident macrophages in the body. Gut bacteria, bacterial endotoxins, and microbial debris transported to the liver from the gastrointestinal tract via the portal vein will first come in contact with Kupffer cells, the first immune cells in the liver. It is because of this that any change to Kupffer cell functions can be connected to various liver diseases such as alcoholic liver disease, viral hepatitis, intrahepatic cholestasis, steatohepatitis, activation or rejection of the liver during liver transplantation and liver fibrosis. They form part of the mononuclear phagocyte system.

Cholestasis is a condition where the flow of bile from the liver to the duodenum is impaired. The two basic distinctions are:

Congestive hepatopathy, is liver dysfunction due to venous congestion, usually due to congestive heart failure. The gross pathological appearance of a liver affected by chronic passive congestion is "speckled" like a grated nutmeg kernel; the dark spots represent the dilated and congested hepatic venules and small hepatic veins. The paler areas are unaffected surrounding liver tissue. When severe and longstanding, hepatic congestion can lead to fibrosis; if congestion is due to right heart failure, it is called cardiac cirrhosis.

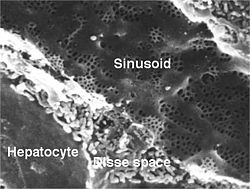
A liver sinusoid is a type of capillary known as a sinusoidal capillary, discontinuous capillary or sinusoid, that is similar to a fenestrated capillary, having discontinuous endothelium that serves as a location for mixing of the oxygen-rich blood from the hepatic artery and the nutrient-rich blood from the portal vein.

In histology, the lobules of liver, or hepatic lobules, are small divisions of the liver defined at the microscopic scale. The hepatic lobule is a building block of the liver tissue, consisting of a portal triad, hepatocytes arranged in linear cords between a capillary network, and a central vein.

Hepatic stellate cells (HSC), also known as perisinusoidal cells or Ito cells, are pericytes found in the perisinusoidal space of the liver, also known as the space of Disse. The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis, which is the formation of scar tissue in response to liver damage, in addition these cells store and concentrate vitamin A.
Hepatic veno-occlusive disease (VOD) or veno-occlusive disease with immunodeficiency is a potentially life-threatening condition in which some of the small veins in the liver are obstructed. It is a complication of high-dose chemotherapy given before a bone marrow transplant and/or excessive exposure to hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids. It is classically marked by weight gain due to fluid retention, increased liver size, and raised levels of bilirubin in the blood. The name sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (SOS) is preferred if hepatic veno-occlusive disease happens as a result of chemotherapy or bone marrow transplantation.

The liver is a major metabolic organ exclusively found in vertebrate animals, which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the synthesis of proteins and various other biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells.

Cirrhosis, also known as liver cirrhosis or hepatic cirrhosis, and end-stage liver disease, is a condition of the liver in which the normal functioning tissue, or parenchyma, is replaced with scar tissue (fibrosis) and regenerative nodules as a result of chronic liver disease. Damage to the liver leads to repair of liver tissue and subsequent formation of scar tissue. Over time, scar tissue and nodules of regenerating hepatocytes can replace the parenchyma, causing increased resistance to blood flow in the liver's capillaries—the hepatic sinusoids—and consequently portal hypertension, as well as impairment in other aspects of liver function. The disease typically develops slowly over months or years.
Pancreatic stellate cells (PaSCs) are classified as myofibroblast-like cells that are located in exocrine regions of the pancreas. PaSCs are mediated by paracrine and autocrine stimuli and share similarities with the hepatic stellate cell. Pancreatic stellate cell activation and expression of matrix molecules constitute the complex process that induces pancreatic fibrosis. Synthesis, deposition, maturation and remodelling of the fibrous connective tissue can be protective, however when persistent it impedes regular pancreatic function.

Scott L. Friedman is an American scientist, professor and physician who works in the field of hepatology. Friedman has conducted pioneering research into the underlying causes of scarring, or fibrosis, associated with chronic liver disease, by characterizing the key fibrogenic cell type, the hepatic stellate cell His laboratory has also discovered a novel tumor suppressor gene, KLF6 that is inactivated in a number of human cancers including primary liver cancer. Friedman is the Fishberg Professor of Medicine, and Chief of the Division of Liver Diseases, Mount Sinai School of Medicine in New York. Friedman has two children, a son, Leor Friedman, and a daughter, Yael Friedman.
Liver cytology is the branch of cytology that studies the liver cells and its functions. The liver is a vital organ, in charge of almost all the body’s metabolism. Main liver cells are hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, and hepatic stellate cells; each one with a specific function.

Bilirubin glucuronide is a water-soluble reaction intermediate over the process of conjugation of indirect bilirubin. Bilirubin glucuronide itself belongs to the category of conjugated bilirubin along with bilirubin di-glucuronide. However, only the latter one is primarily excreted into the bile in the normal setting.
Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) form the lining of the smallest blood vessels in the liver, also called the hepatic sinusoids. LSECs are highly specialized endothelial cells with characteristic morphology and function. They constitute an important part of the reticuloendothelial system (RES).