Related Research Articles
Alexander Morrison National Park is a national park in Western Australia, located 207 kilometres (129 mi) north of Perth in the Shire of Coorow along the Green Head-Coorow Road. It was named for Alexander Morrison, the first Government Botanist of Western Australia.

The Darling Scarp, also referred to as the Darling Range or Darling Ranges, is a low escarpment running north–south to the east of the Swan Coastal Plain and Perth, Western Australia. The escarpment extends generally north of Bindoon, to the south of Pemberton. The adjacent Darling Plateau goes easterly to include Mount Bakewell near York and Mount Saddleback near Boddington. It was named after the Governor of New South Wales, Lieutenant-General Ralph Darling.

Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.

Eneabba is a town on the Brand Highway 278 kilometres (173 mi) north of Perth, Western Australia.

The Swan Coastal Plain in Western Australia is the geographic feature which contains the Swan River as it travels west to the Indian Ocean. The coastal plain continues well beyond the boundaries of the Swan River and its tributaries, as a geological and biological zone, one of Western Australia's Interim Biogeographic Regionalisation for Australia (IBRA) regions. It is also one of the distinct physiographic provinces of the larger West Australian Shield division.
The Perth Basin is a thick, elongated sedimentary basin in Western Australia. It lies beneath the Swan Coastal Plain west of the Darling Scarp, representing the western limit of the much older Yilgarn Craton, and extends further west offshore. Cities and towns including Perth, Busselton, Bunbury, Mandurah and Geraldton are built over the Perth Basin.
Banksia glaucifolia is a species of shrub that is endemic to Western Australia. It has deeply serrated, wedge-shaped leaves with sharply pointed lobes, pale yellow flowers and follicles with hairy edges.
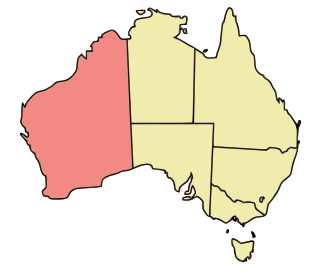
Western Australia occupies nearly one third of the Australian continent. Due to the size and the isolation of the state, considerable emphasis has been made of these features; it is the second largest administrative territory in the world, after Yakutia in Russia, despite the fact that Australia is only the sixth largest country in the world by area, and no other regional administrative jurisdiction in the world occupies such a high percentage of a continental land mass. It is also the only first level administrative subdivision to occupy the entire continental coastline in one cardinal direction.

Macrozamia dyeri, known as djeeri, is a species of plant in the family Zamiaceae. It is endemic to Western Australia, occurring near Esperance. The seeds are consumable when prepared correctly and were an important resource to people of the region, but the plant is otherwise toxic to many species.

Conospermum incurvum, commonly known as plume smokebush, is a shrub endemic to Western Australia.

Ladislav Mucina is a vegetation scientist and Professor and Iluka Chair of Vegetation Science and Biogeography at the School of Biological Science of The University of Western Australia in Perth. He was born on 28 May 1956 in Piešťany, Slovakia.

Kwongan is plant community found in south-western Western Australia. The name is a Bibbelmun (Noongar) Aboriginal term of wide geographical use defined by Beard (1976) as
...a type of country ...[that is] sandy and is open without timber-sized trees but with a scrubby vegetation. It consists of plains in an Australian sense of open country rather than in a strict sense of flat country. ... there are two principal plant formations in the kwongan, scrub heath and broombush thicket ... both ... are sclerophyll shrublands and possess a certain unity when contrasted with woodland and forest or steppe and succulent steppe communities.
Main Roads Western Australia controls the major roads in the state's Mid West region. There are four main highways through the Mid West: The north-south coastal route of Brand Highway and North West Coastal Highway, the inland alternative Great Northern Highway, and the northern section of Goldfields Highway, which links Meekatharra with Kalgoorlie. A network of main roads connects towns within the Mid West to each other, the highways, and neighbouring regions, with local roads providing additional links and access to smaller townsites. Roads are often named after the towns they connect.
Calectasia browneana, commonly known as blue tinsel lily, is a plant in the family Dasypogonaceae growing as a spreading, perennial, tufted herb. It is an uncommon species, endemic and restricted to a few areas in the south-west of Western Australia. It is similar to the other species of Calectasia and has only been recognised as a separate species since a review of the genus in 2001. It is distinguished from the others mainly by the hairiness of its leaves and lack of a rhizome.

Johnsonia pubescens, commonly called the pipe lily, is a grass-like plant in the family Asphodelaceae, subfamily Hemerocallidoideae, endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. As with others in the genus, it is distinguished by its minute flowers which are on the end of a spike and hidden by large, overlapping, papery bracts.
Calothamnus blepharospermus is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the west coast of Western Australia. It is an upright, spreading, bushy shrub with red flowers in summer. It grows in sandy soil in scrubby country called kwongan.
Eremaea × phoenicea is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is thought to be a stabilised hybrid between two subspecies of Eremaea. It is an erect to spreading shrub with pointed, elliptic leaves and small groups of flowers, a shade of pink to red, on the ends of the branches.

Beaufortia aestiva, commonly known as Kalbarri beaufortia, or summer flame, is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a dense, usually rounded shrub with small leaves and which bears yellow or red flowers in bottlebrush-like spikes near the ends of the branches in summer. It is similar to Beaufortia squarrosa but that is a smaller shrub which always has red flowers.

Beaufortia elegans, commonly known as elegant beaufortia is a plant in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, diffuse shrub with crowded, curved leaves and heads of flowers that are usually reddish purple, although other colours also occur.
Gingin scarp is a scarp that lies to the west of the Darling Scarp in Western Australia, with the Dandaragan plateau formed between the two scarps. At the southern end of the scarp it lies to the east of the Swan Coastal Plain, to the further north the adjacent sandplain is Eneabba sandplain
References
- ↑ Herath, D; Lamont, B; Enright, N; Miller, B (2009), Fire impacts on restored shrublands following mining for heavy metals near Eneabba southwestern Australia , retrieved 23 October 2016
- ↑ Strategen (Firm); Iluka Resources Limited (2009), Eneabba Mineral Sands future mining proposal : environmental scoping document, Strategen, retrieved 23 October 2016
- ↑ Tsakalos, J.L; Drskova, M.; Hruban, J.; Mucina, L.; Dobrowolski, M. (2014), Floristic patterns and drivers of kwongan vegetation patterns in Eneabba region of the Northern Sandplains, Western Australia, Kwongan Foundation, Perth, retrieved 23 October 2016
- ↑ Macintyre, Paul; Mucina, Laco; Dobrowolski, Mark; Van Niekerk, A; Stephenson, G; Pauw, T (2014), Fine-scale predictive mapping of the kwongan vegetation of the Eneabba sandplains, Western Australia, Kwongan Foundation, Perth, retrieved 23 October 2016
- ↑ Bellairs, Sean Mark; University of Western Australia. Department of Botany (1991), Seed biology, establishment ecology and vegetation development of Northern Sandplain Kwongan vegetation after mineral sand mining near Eneabba, Western Australia , retrieved 23 October 2016
Coordinates: 29°53′40″S115°16′19″E / 29.894345°S 115.271851°E