
PJSC Gazprom is a Russian majority state-owned multinational energy corporation headquartered in the Lakhta Center in Saint Petersburg. As of 2019, with sales over $120 billion, it was, until 2023, ranked as the largest publicly listed natural gas company in the world and the largest company in Russia by revenue. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Gazprom was ranked as the 32nd largest public company in the world. The Gazprom name is a contraction of the Russian words gazovaya promyshlennost. In January 2022, Gazprom displaced Sberbank from the first place in the list of the largest companies in Russia by market capitalization. In 2022, the company's revenue amounted to 8 trillion rubles. In 2023, the company is delisted from international markets, and continues substantial constriction in its operational results.
OMV Petrom S.A. is a Romanian integrated oil company, controlled by Austria's OMV. It is one of the largest corporations in Romania and the largest oil and gas producer in Southeast Europe. Since 2004 it is a subsidiary of OMV. With 2022 profits of EUR 12.5 billion, as of 2023, OMV Petrom is the largest company in Romania.
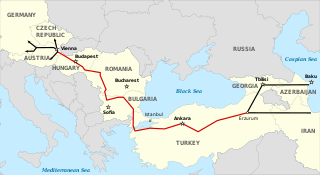
The Nabucco pipeline was a failed natural gas pipeline project from Erzurum, Turkey to Baumgarten an der March, Austria to diversify natural gas suppliers and delivery routes for Europe. The pipeline was to lessen European dependence on Russian energy. The project was backed by several European Union states and the United States and was seen as rival to the Gazprom-Eni South Stream pipeline project. The main supplier was to be Iraq with potential supplies from Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan, and Egypt.
Petrol Ofisi A.Ş. is a fuel products distribution and lubricants company in Turkey. It is owned by Dutch Vitol Group. Vitol completed its acquisition of Petrol Ofisi from OMV AG in June 2017.

The Trans Austria Gas (TAG) pipeline is a natural gas pipeline that leads from the Slovak-Austrian border at Baumgarten an der March to Arnoldstein in the south, near the border with Italy. Natural gas originating from Russia is transported to and used in Italy and Austria. In addition, it supplies Slovenia through the SOL Pipeline System, which branch-off at Weitendorf.

The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline is a proposed subsea pipeline between Türkmenbaşy in Turkmenistan, and Baku in Azerbaijan. According to some proposals it would also include a connection between the Tengiz Field in Kazakhstan, the Sangachal Terminal in Baku, and Türkmenbaşy. The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline project would transport natural gas from Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan to European Union member countries, circumventing both Russia and Iran. It would do this by feeding the Southern Gas Corridor. This project attracts significant interest since it would connect vast Turkmen gas resources to major consumers Turkey and Europe.

The National Iranian Gas Company (NIGC) was established in 1965 as one of the four principal companies affiliated to the Ministry of Petroleum of the Islamic Republic of Iran with 25,000 million Rials initial capital.
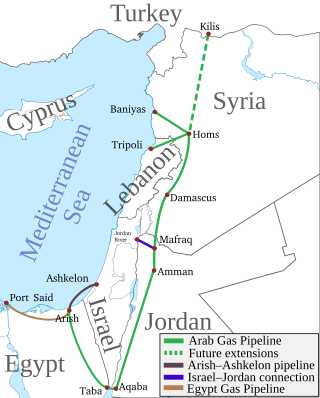
The Arab Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in the Middle East. It originates near Arish in the Sinai Peninsula and was built to export Egyptian natural gas to Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, with branch underwater and overland pipelines to and from Israel. It has a total length of 1,200 kilometres (750 mi), constructed at a cost of US$1.2 billion.

Energy in Bulgaria is among the most important sectors of the national economy and encompasses energy and electricity production, consumption and transportation in Bulgaria. The national energy policy is implemented by the National Assembly and the Government of Bulgaria, conducted by the Ministry of Energy and regulated by the Energy and Water Regulatory Commission. The completely state-owned company Bulgarian Energy Holding owns subsidiaries operating in different energy sectors, including electricity: Kozloduy Nuclear Power Plant, Maritsa Iztok 2 Thermal Power Plant, NEK EAD and Elektroenergien sistemen operator (ESO); natural gas: Bulgargaz and Bulgartransgaz; coal mining: Maritsa Iztok Mines. In Bulgaria, energy prices for households are state-controlled, while commercial electricity prices are determined by the market.

South Stream is a canceled pipeline project to transport natural gas of the Russian Federation through the Black Sea to Bulgaria and through Serbia, Hungary and Slovenia further to Austria. It was never finished.

Wind power generates about 10% of Turkey's electricity, mainly in the west in the Aegean and Marmara regions, and is gradually becoming a larger share of renewable energy in the country. As of 2024, Turkey has 12 gigawatts (GW) of wind turbines. The Energy Ministry plans to have almost 30 GW by 2035, including 5 GW offshore.

According to the Iran Petroleum Ministry, the proved natural gas reserves of Iran are about 1,201 trillion cubic feet (34.0 trillion cubic metres) or about 17.8% of world's total reserves, of which 33% are as associated gas and 67% is in non associated gas fields. It has the world's second largest reserves after Russia. As it takes approximately 5,850 cubic feet (166 m3) of gas to equal the energy content of 1-barrel (0.16 m3) of oil, Iran's gas reserves represent the equivalent of about 205 billion barrels (3.26×1010 m3) of oil.
Bosphorus Gaz Corporation is a gas importer and distributor in Turkey. It controls about 25% of Turkey's private natural gas market.
The Egyptian Natural Gas Holding Company (EGAS) is an Egyptian state-owned holding company, which owns and manages state stakes in different gas project. The company was established in August 2001. EGAS is also responsible for issuing of natural gas exploration licenses in Egypt.

Iran is an energy superpower and the petroleum industry in Iran plays an important part in it. In 2004, Iran produced 5.1 percent of the world's total crude oil, which generated revenues of US$25 billion to US$30 billion and was the country's primary source of foreign currency. At 2006 levels of production, oil proceeds represented about 18.7% of gross domestic product (GDP). However, the importance of the hydrocarbon sector to Iran's economy has been far greater. The oil and gas industry has been the engine of economic growth, directly affecting public development projects, the government's annual budget, and most foreign exchange sources.

Romania has proven natural gas reserves of 726 billion cubic meters and is ranked 30th among countries with proved reserves of natural gas. About 75% of Romania's natural gas resources are located in Transylvania, especially in Mureș and Sibiu counties. The largest natural gas field in Romania is the Deleni gas field discovered in 1912 and located in Băgaciu commune, Mureș County, with proven reserves of 85 billion cubic meters or 3 trillion cubic feet. Other important gas fields include the Filitelnic gas field, the Roman-Secuieni gas field, the Voitinel gas field, the Ghercești gas field and the Sărmașel gas field all with reserves larger than 10 billion cubic meters or 350 billion cubic feet. Currently Romania has the second largest natural gas reserves in the European Union just after the Netherlands.

Energy consumption per person in Turkey is similar to the world average, and over 85 per cent is from fossil fuels. From 1990 to 2017 annual primary energy supply tripled, but then remained constant to 2019. In 2019, Turkey's primary energy supply included around 30 per cent oil, 30 per cent coal, and 25 per cent gas. These fossil fuels contribute to Turkey's air pollution and its above average greenhouse gas emissions. Turkey mines its own lignite but imports three-quarters of its energy, including half the coal and almost all the oil and gas it requires, and its energy policy prioritises reducing imports.

The Trans-Anatolian Natural Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in Turkey. It is the central part of the Southern Gas Corridor, which connects the giant Shah Deniz gas field in Azerbaijan to Europe through the South Caucasus Pipeline and the Trans Adriatic Pipeline. The pipeline has a strategic importance for both Azerbaijan and Turkey. It allows the first Azerbaijani gas exports to Europe, beyond Turkey. It also strengthens the role of Turkey as a regional energy hub.

Fossil gas supplies over a quarter of Turkey's energy. The country consumes 50 to 60 billion cubic metres of this natural gas each year, nearly all of which is imported. A large gas field in the Black Sea however started production in 2023.

The Russia–EU gas dispute flared up in March 2022 following the invasion of Ukraine on 24 February 2022. Russia and the major EU countries clashed over the issue of payment for natural gas pipelined to Europe by Russia's Gazprom, amidst sanctions on Russia that were expanded in response to Russia's 2022 invasion of Ukraine. In June, Gazprom claimed it was obliged to cut the flow of gas to Germany by more than half, as a result of such sanctions that prevented the Russian company from receiving its turbine component from Canada. On 26 September 2022, three of the four pipes of the Nord Stream 1 and 2 gas pipelines were sabotaged. This resulted in a record release of 115,000 tonnes of methane (CH4) – an equivalent of 15 million tonnes of carbon dioxide (CO2) – and is believed to have made a contribution to global warming.















