Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For electric utilities in the electric power industry, it is the first stage in the delivery of electricity to end users, the other stages being transmission, distribution, energy storage and recovery, using the pumped-storage method.

Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources, which are naturally replenished on a human timescale, such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves, and geothermal heat. Renewable energy often provides energy in four important areas: electricity generation, air and water heating/cooling, transportation, and rural (off-grid) energy services.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant or powerhouse and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Most power stations contain one or more generators, a rotating machine that converts mechanical power into electrical power. The relative motion between a magnetic field and a conductor creates an electrical current. The energy source harnessed to turn the generator varies widely. Most power stations in the world burn fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas to generate electricity. Others use nuclear power, but there is an increasing use of cleaner renewable sources such as solar, wind, wave and hydroelectric.

Sustainable energy is a principle in which human use of energy "meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Another definition of sustainable energy is that it is consumed at insignificant rates compared to its supply and with manageable collateral effects, especially environmental effects. Sustainable energy strategies generally have two pillars: cleaner methods of producing energy and energy conservation.
Electrical energy is energy derived from electric potential energy or kinetic energy. When used loosely, "electrical energy" refers to energy that has been converted from electric potential energy. This energy is supplied by the combination of electric current and electric potential that is delivered by an electrical circuit. At the point that this electric potential energy has been converted to another type of energy, it ceases to be electric potential energy.
Thus, all electrical energy is potential energy before it is delivered to the end-use. Once converted from potential energy, electrical energy can always be called another type of energy.

Grid energy storage is a collection of methods used to store electrical energy on a large scale within an electrical power grid. Electrical energy is stored during times when production exceeds consumption, and returned to the grid when production falls below consumption.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to energy:
Walkaway is a small town in the City of Greater Geraldton local government area of Western Australia. At the 2016 census, Walkaway had a population of 270.

Microgeneration is the small-scale generation of heat and electric power by individuals, small businesses and communities to meet their own needs, as alternatives or supplements to traditional centralized grid-connected power. Although this may be motivated by practical considerations, such as unreliable grid power or long distance from the electrical grid, the term is mainly used currently for environmentally conscious approaches that aspire to zero or low-carbon footprints or cost reduction. It differs from micropower in that it is principally concerned with fixed power plants rather than for use with mobile devices.

Renewable energy in Australia deals with efforts that have been and continue to be made in Australia to quantify and expand the use of renewable energy in the generation of electricity, as fuel in transport and in thermal energy. Renewable energy is created through electricity generation using renewable sources, such as wind, hydro, landfill gas, geothermal, solar PV and solar thermal.

Renewable energy commercialization involves the deployment of three generations of renewable energy technologies dating back more than 100 years. First-generation technologies, which are already mature and economically competitive, include biomass, hydroelectricity, geothermal power and heat. Second-generation technologies are market-ready and are being deployed at the present time; they include solar heating, photovoltaics, wind power, solar thermal power stations, and modern forms of bioenergy. Third-generation technologies require continued R&D efforts in order to make large contributions on a global scale and include advanced biomass gasification, hot-dry-rock geothermal power, and ocean energy. As of 2012, renewable energy accounts for about half of new nameplate electrical capacity installed and costs are continuing to fall.

Renewable energy accounted for 12.2 % of total primary energy consumption and 14.94 % of the domestically produced electricity in the United States in 2016.
Hydroelectric power is currently the largest producer of renewable electricity in the country, generating around 6.5% of the nation's total electricity in 2016 as well as 45.71% of the total renewable electricity generation.
The United States is the fourth largest producer of hydroelectricity in the world after China, Canada and Brazil.
In Honduras, there is an important potential of untapped indigenous renewable energy resources. Due to the variability of high oil prices and declining renewable infrastructure costs, such resources could be developed at competitive prices.

El Paso Electric is Texas based public utility company, engaging in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity in west Texas and southern New Mexico. Its energy sources consist of nuclear fuel, natural gas, purchased power, solar and wind turbines. The company owns 6 electrical generating facilities with a net dependable generating capability of approximately 2,010 megawatts. It serves approximately 400,000 residential, commercial, industrial, public authority, and wholesale customers.
The distinct ways of electricity generation can incur significantly different costs. Calculations of these costs can be made at the point of connection to a load or to the electricity grid. The cost is typically given per kilowatt-hour or megawatt-hour. It includes the initial capital, discount rate, as well as the costs of continuous operation, fuel, and maintenance. This type of calculation assists policymakers, researchers and others to guide discussions and decision making.

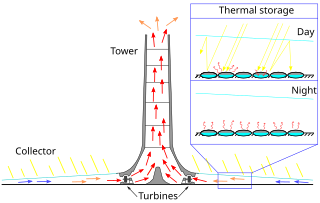
Sierra SunTower was a 5 MW commercial concentrating solar power (CSP) plant built and operated by eSolar. The plant is located in Lancaster, California. As of mid-August, 2018, the two towers that were the center of the facility are no longer standing. The plant, however, is still present.
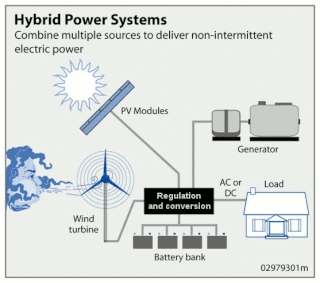
Solar hybrid power systems are hybrid power systems that combine solar power from a photovoltaic system with another power generating energy source. A common type is a photovoltaic diesel hybrid system, combining photovoltaics (PV) and diesel generators, or diesel gensets, as PV has hardly any marginal cost and is treated with priority on the grid. The diesel gensets are used to constantly fill in the gap between the present load and the actual generated power by the PV system.