Summary
As stated on the cover, the work is a survey of "Man's use of power, from the water wheel to the atomic pile." The topic is covered in short segments, titled "The Age of Engines," "Putting Energy to Work," "The First Engines," "Water and Wind Engines," "Early Steam Engines," "How a Steam Engine Works", "Steam Turbines," "Internal-combustion engines," "Otto Cycle Engines," "Two-stroke Cycle Engines," "Diesel Engines," "Gas Turbines," "Rockets," "Electric Motors," "How an Electric Motor Works," "Electric Generators and Power Systems," "Atomic Engines," and "How a Reactor Works." There is a brief one-page topical index.

An engine or motor is a machine designed to convert one or more forms of energy into mechanical energy.

A locomotive or engine is a rail transport vehicle that provides the motive power for a train. If a locomotive is capable of carrying a payload, it is usually rather referred to as a multiple unit, motor coach, railcar or power car; the use of these self-propelled vehicles is increasingly common for passenger trains, but rare for freight.

A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be transformed, by a connecting rod and crank, into rotational force for work. The term "steam engine" is generally applied only to reciprocating engines as just described, not to the steam turbine. Steam engines are external combustion engines, where the working fluid is separated from the combustion products. The ideal thermodynamic cycle used to analyze this process is called the Rankine cycle. In general usage, the term steam engine can refer to either complete steam plants, such as railway steam locomotives and portable engines, or may refer to the piston or turbine machinery alone, as in the beam engine and stationary steam engine.

In an internal combustion engine, a turbocharger is a forced induction device that is powered by the flow of exhaust gases. It uses this energy to compress the intake gas, forcing more air into the engine in order to produce more power for a given displacement.

A vehicle is a machine that transports people or cargo. Vehicles include wagons, bicycles, motor vehicles, railed vehicles, watercraft, amphibious vehicles, aircraft and spacecraft.

A machine is a physical system using power to apply forces and control movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to natural biological macromolecules, such as molecular machines. Machines can be driven by animals and people, by natural forces such as wind and water, and by chemical, thermal, or electrical power, and include a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement. They can also include computers and sensors that monitor performance and plan movement, often called mechanical systems.

A gas turbine, also called a combustion turbine, is a type of continuous flow internal combustion engine. The main parts common to all gas turbine engines form the power-producing part and are, in the direction of flow:
Mechanization is the process of changing from working largely or exclusively by hand or with animals to doing that work with machinery. In an early engineering text a machine is defined as follows:
Every machine is constructed for the purpose of performing certain mechanical operations, each of which supposes the existence of two other things besides the machine in question, namely, a moving power, and an object subject to the operation, which may be termed the work to be done. Machines, in fact, are interposed between the power and the work, for the purpose of adapting the one to the other.

A power station, also referred to as a power plant and sometimes generating station or generating plant, is an industrial facility for the generation of electric power. Power stations are generally connected to an electrical grid.

A hot air engine is any heat engine that uses the expansion and contraction of air under the influence of a temperature change to convert thermal energy into mechanical work. These engines may be based on a number of thermodynamic cycles encompassing both open cycle devices such as those of Sir George Cayley and John Ericsson and the closed cycle engine of Robert Stirling. Hot air engines are distinct from the better known internal combustion based engine and steam engine.

Turbomachinery, in mechanical engineering, describes machines that transfer energy between a rotor and a fluid, including both turbines and compressors. While a turbine transfers energy from a fluid to a rotor, a compressor transfers energy from a rotor to a fluid.

The steam-electric power station is a power station in which the electric generator is steam driven. Water is heated, turns into steam and spins a steam turbine which drives an electrical generator. After it passes through the turbine, the steam is condensed in a condenser. The greatest variation in the design of steam-electric power plants is due to the different fuel sources.

This Timeline of heat engine technology describes how heat engines have been known since antiquity but have been made into increasingly useful devices since the 17th century as a better understanding of the processes involved was gained. A heat engine is any system that converts heat to mechanical energy, which can then be used to do mechanical work.They continue to be developed today.

Man and Power: the Story of Power from the Pyramids to the Atomic Age is a science book for children by L. Sprague de Camp, illustrated with documents, photographs by Russ Kinne, Roman Vishniac, and others, and paintings by Alton S. Tobey, first published in hardcover by Golden Press in 1961.
An engine is a device that converts one form of energy into mechanical energy.

Marine propulsion is the mechanism or system used to generate thrust to move a ship or boat across water. While paddles and sails are still used on some smaller boats, most modern ships are propelled by mechanical systems consisting of an electric motor or engine turning a propeller, or less frequently, in pump-jets, an impeller. Marine engineering is the discipline concerned with the engineering design process of marine propulsion systems.

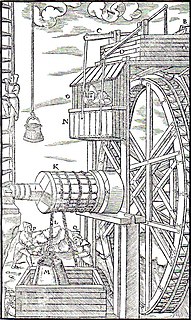
The first recorded rudimentary steam engine was the aeolipile mentioned by Vitruvius between 30 and 15 BC and, described by Heron of Alexandria in 1st-century Roman Egypt. Several steam-powered devices were later experimented with or proposed, such as Taqi al-Din's steam jack, a steam turbine in 16th-century Ottoman Egypt, and Thomas Savery's steam pump in 17th-century England. In 1712, Thomas Newcomen's atmospheric engine became the first commercially successful engine using the principle of the piston and cylinder, which was the fundamental type of steam engine used until the early 20th century. The steam engine was used to pump water out of coal mines.

Various scientists and engineers contributed to the development of internal combustion engines. In 1791, the English inventor John Barber patented a gas turbine. In 1794 Thomas Mead patented a gas engine. Also in 1794 Robert Street patented an internal-combustion engine, which was also the first to use liquid fuel (petroleum) and built an engine around that time. In 1798, John Stevens designed the first American internal combustion engine. In 1807, French engineers Nicéphore and Claude Niépce ran a prototype internal combustion engine, using controlled dust explosions, the Pyréolophore. This engine powered a boat on the Saône river, France. The same year, the Swiss engineer François Isaac de Rivaz built and patented a hydrogen and oxygen powered internal-combustion engine. The fuel was stored in a balloon and the spark was electrically ignited by a hand-operated trigger. Fitted to a crude four-wheeled wagon, François Isaac de Rivaz first drove it 100 meters in 1813, thus making history as the first car-like vehicle known to have been powered by an internal-combustion engine. In 1823, Samuel Brown patented the first internal combustion engine to be applied industrially in the U.S.; one of his engines pumped water on the Croydon Canal from 1830 to 1836. He also demonstrated a boat using his engine on the Thames in 1827, and an engine-driven carriage in 1828. Father Eugenio Barsanti, an Italian engineer, together with Felice Matteucci of Florence invented the first real internal combustion engine in 1853. Their patent request was granted in London on June 12, 1854, and published in London's Morning Journal under the title "Specification of Eugene Barsanti and Felix Matteucci, Obtaining Motive Power by the Explosion of Gasses". In 1860, Belgian Jean Joseph Etienne Lenoir produced a gas-fired internal combustion engine. In 1864, Nicolaus Otto patented the first atmospheric gas engine. In 1872, American George Brayton invented the first commercial liquid-fueled internal combustion engine. In 1876, Nicolaus Otto, working with Gottlieb Daimler and Wilhelm Maybach, patented the compressed charge, four-stroke cycle engine. In 1879, Karl Benz patented a reliable two-stroke gas engine. In 1892, Rudolf Diesel developed the first compressed charge, compression ignition engine. In 1926, Robert Goddard launched the first liquid-fueled rocket. In 1939, the Heinkel He 178 became the world's first jet aircraft. In 1954 German engineer Felix Wankel patented a "pistonless" engine using an eccentric rotary design.

An internal combustion engine is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons, turbine blades, a rotor, or a nozzle. This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important.
Wallace L. Minto had a passion for science at a very young age. For instance, at age 13, he and his father, Wallace Milton Minto, stock piled more than 50 tons of uranium rich ore in Sparta, New Jersey. He was also the first to split the uranium atom while still a teenager. This nearly created an atomic explosion in his family home. At age 16, Wallace synthesized radium and invented what is now known as "Scotchlite". He had a copyright on his own periodic chart which renamed all the elements.


















