Software architecture is the set of structures needed to reason about a software system and the discipline of creating such structures and systems. Each structure comprises software elements, relations among them, and properties of both elements and relations.
In software engineering, a Design Pattern describes a relatively small, well-defined aspect of a computer program in terms of how to write the code.
Software configuration management (SCM), a.k.a. software change and configuration management (SCCM), is the software engineering practice of tracking and controlling changes to a software system; part of the larger cross-disciplinary field of configuration management (CM). SCM includes version control and the establishment of baselines.

A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e., unstructured and semi-structured decision problems. Decision support systems can be either fully computerized or human-powered, or a combination of both.
Information technology (IT)governance is a subset discipline of corporate governance, focused on information technology (IT) and its performance and risk management. The interest in IT governance is due to the ongoing need within organizations to focus value creation efforts on an organization's strategic objectives and to better manage the performance of those responsible for creating this value in the best interest of all stakeholders. It has evolved from The Principles of Scientific Management, Total Quality Management and ISO 9001 Quality Management System.
Information technology service management (ITSM) are the activities performed by an organization to design, build, deliver, operate and control IT services offered to customers.
In the context of software engineering, software quality refers to two related but distinct notions:
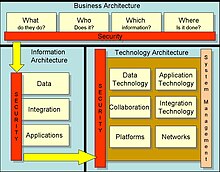
Enterprise architecture (EA) is a business function concerned with the structures and behaviours of a business, especially business roles and processes that create and use business data. The international definition according to the Federation of Enterprise Architecture Professional Organizations is "a well-defined practice for conducting enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation, using a comprehensive approach at all times, for the successful development and execution of strategy. Enterprise architecture applies architecture principles and practices to guide organizations through the business, information, process, and technology changes necessary to execute their strategies. These practices utilize the various aspects of an enterprise to identify, motivate, and achieve these changes."

The Open Group Architecture Framework (TOGAF) is the most used framework for enterprise architecture as of 2020 that provides an approach for designing, planning, implementing, and governing an enterprise information technology architecture. TOGAF is a high-level approach to design. It is typically modeled at four levels: Business, Application, Data, and Technology. It relies heavily on modularization, standardization, and already existing, proven technologies and products.
Data architecture consist of models, policies, rules, and standards that govern which data is collected and how it is stored, arranged, integrated, and put to use in data systems and in organizations. Data is usually one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture or solution architecture.

An enterprise architecture framework defines how to create and use an enterprise architecture. An architecture framework provides principles and practices for creating and using the architecture description of a system. It structures architects' thinking by dividing the architecture description into domains, layers, or views, and offers models – typically matrices and diagrams – for documenting each view. This allows for making systemic design decisions on all the components of the system and making long-term decisions around new design requirements, sustainability, and support.
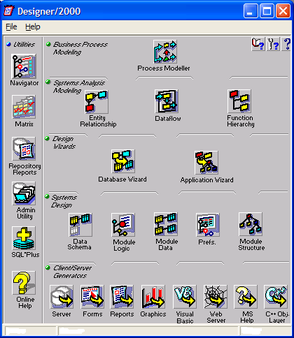
Oracle Designer was Oracle's CASE tool for designing an information system and generating it. After generating the information system one is able to edit the generated code with Oracle Developer Suite.

Enterprise modelling is the abstract representation, description and definition of the structure, processes, information and resources of an identifiable business, government body, or other large organization.

In the business sector, business architecture is a discipline that "represents holistic, multidimensional business views of: capabilities, end-to-end value delivery, information, and organizational structure; and the relationships among these business views and strategies, products, policies, initiatives, and stakeholders."
SABSA is a model and methodology for developing a risk-driven enterprise information security architecture and service management, to support critical business processes. It was developed independently from the Zachman Framework, but has a similar structure. The primary characteristic of the SABSA model is that everything must be derived from an analysis of the business requirements for security, especially those in which security has an enabling function through which new business opportunities can be developed and exploited.
In information systems, applications architecture or application architecture is one of several architecture domains that form the pillars of an enterprise architecture (EA).

Business reference model (BRM) is a reference model, concentrating on the functional and organizational aspects of the core business of an enterprise, service organization or government agency.

FDIC Enterprise Architecture Framework was the enterprise architecture framework of the United States Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (FDIC). A lot of the current article is about the enterprise architecture framework developed around 2005, and currently anno 2011 out-of-date.

Technical Architecture Framework for Information Management (TAFIM) was a 1990s reference model for enterprise architecture by and for the United States Department of Defense (DoD).
The history of business architecture has its origins in the 1980s. In the next decades business architecture has developed into a discipline of "cross-organizational design of the business as a whole" closely related to enterprise architecture. The concept of business architecture has been proposed as a blueprint of the enterprise, as a business strategy, and also as the representation of a business design.