Related Research Articles
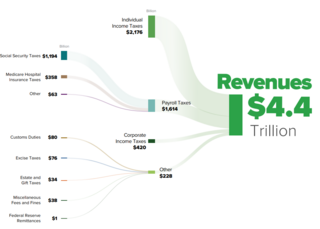
The United States has separate federal, state, and local governments with taxes imposed at each of these levels. Taxes are levied on income, payroll, property, sales, capital gains, dividends, imports, estates and gifts, as well as various fees. In 2020, taxes collected by federal, state, and local governments amounted to 25.5% of GDP, below the OECD average of 33.5% of GDP.

The abbreviation S.A. or SA, for the French Société Anonyme designates a type of limited company in certain countries, most of which have a Romance language as their official language and operates a derivative of the 1804, Napoleonic, civil law. Originally, shareholders could be literally anonymous and collect dividends by surrendering coupons attached to their share certificates. Dividends were paid to whomever held the certificate. Since share certificates could be transferred privately, corporate management would not necessarily know who owned its shares – nor did anyone but the holders.

A limited liability company (LLC) is the United States-specific form of a private limited company. It is a business structure that can combine the pass-through taxation of a partnership or sole proprietorship with the limited liability of a corporation. An LLC is not a corporation under the laws of every state; it is a legal form of a company that provides limited liability to its owners in many jurisdictions. LLCs are well known for the flexibility that they provide to business owners; depending on the situation, an LLC may elect to use corporate tax rules instead of being treated as a partnership, and, under certain circumstances, LLCs may be organized as not-for-profit. In certain U.S. states, businesses that provide professional services requiring a state professional license, such as legal or medical services, may not be allowed to form an LLC but may be required to form a similar entity called a professional limited liability company (PLLC).

Incorporation is the formation of a new corporation. The corporation may be a business, a nonprofit organization, sports club, or a local government of a new city or town.
Controlled foreign corporation (CFC) rules are features of an income tax system designed to limit artificial deferral of tax by using offshore low taxed entities. The rules are needed only with respect to income of an entity that is not currently taxed to the owners of the entity. Generally, certain classes of taxpayers must include in their income currently certain amounts earned by foreign entities they or related persons control.

A private limited company is any type of business entity in "private" ownership used in many jurisdictions, in contrast to a publicly listed company, with some differences from country to country. Examples include the LLC in the United States, private company limited by shares in the United Kingdom, GmbH in Germany and Austria, Besloten vennootschap in The Netherlands, société à responsabilité limitée in France, and sociedad de responsabilidad limitada in the Spanish-speaking world. The benefit of having a private limited company is that there is limited liability.
A corporate tax, also called corporation tax or company tax, is a type of direct tax levied on the income or capital of corporations and other similar legal entities. The tax is usually imposed at the national level, but it may also be imposed at state or local levels in some countries. Corporate taxes may be referred to as income tax or capital tax, depending on the nature of the tax.
The Employer Identification Number (EIN), also known as the Federal Employer Identification Number (FEIN) or the Federal Tax Identification Number (FTIN), is a unique nine-digit number assigned by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) to business entities operating in the United States for the purposes of identification. When the number is used for identification rather than employment tax reporting, it is usually referred to as a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN). When used for the purposes of reporting employment taxes, it is usually referred to as an EIN. These numbers are used for tax administration and must not be used for any other purpose. For example, an EIN should not be used in tax lien auction or sales, lotteries, or for any other purposes not related to tax administration.
An unlimited liability corporation (ULC) within Canadian corporate law is a Canadian corporation designation, wherein shareholders are liable up to unlimited amounts for any liability, act or default of the corporation. By comparison, in most corporations, shareholders are not usually liable due to a limited liability model. ULCs can be used by American corporations for tax planning, as ULCs are treated as corporations for Canadian tax purposes but as flow-through entities for American tax purposes.

An S corporation, for United States federal income tax, is a closely held corporation that makes a valid election to be taxed under Subchapter S of Chapter 1 of the Internal Revenue Code. In general, S corporations do not pay any income taxes. Instead, the corporation's income and losses are divided among and passed through to its shareholders. The shareholders must then report the income or loss on their own individual income tax returns.
A flow-through entity (FTE) is a legal entity where income "flows through" to investors or owners; that is, the income of the entity is treated as the income of the investors or owners. Flow-through entities are also known as pass-through entities or fiscally-transparent entities.

A C corporation, under United States federal income tax law, is any corporation that is taxed separately from its owners. A C corporation is distinguished from an S corporation, which generally is not taxed separately. Many companies, including most major corporations, are treated as C corporations for U.S. federal income tax purposes. C corporations and S corporations both enjoy limited liability, but only C corporations are subject to corporate income taxation.

The United States federal government and most state governments impose an income tax. They are determined by applying a tax rate, which may increase as income increases, to taxable income, which is the total income less allowable deductions. Income is broadly defined. Individuals and corporations are directly taxable, and estates and trusts may be taxable on undistributed income. Partnerships are not taxed, but their partners are taxed on their shares of partnership income. Residents and citizens are taxed on worldwide income, while nonresidents are taxed only on income within the jurisdiction. Several types of credits reduce tax, and some types of credits may exceed tax before credits. Most business expenses are deductible. Individuals may deduct certain personal expenses, including home mortgage interest, state taxes, contributions to charity, and some other items. Some deductions are subject to limits, and an Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) applies at the federal and some state levels.
A gōdō gaisha (合同会社), or gōdō kaisha, abbreviated GK, is a type of business organization in the Companies Act of Japan modeled after the American limited liability company (LLC), hence its nickname as the "Japanese LLC". It is a type of mochibun kaisha distinguished by offering limited liability for all investors.
A blocker corporation is a type of C Corporation in the United States that has been used by tax exempt individuals to protect their investments from taxation when they participate in private equity or with hedge funds. In addition to tax exempt individuals, foreign investors have also used blocker corporations.
For purposes of income tax in the United States, U.S. persons owning shares of a passive foreign investment company (PFIC) may choose between (i) current taxation on the income of the PFIC or (ii) deferral of such income subject to a deemed tax and interest regime. The provision was enacted as part of the Tax Reform Act of 1986 as a way of placing owners of offshore investment funds on a similar footing to owners of U.S. investment funds. The original provisions applied for all foreign corporations meeting either an income or an asset test. However, 1997 amendments limited the application in the case of U.S. Shareholders of controlled foreign corporations.
Foreign corporation is a term used in the United States to describe an existing corporation that conducts business in a state or jurisdiction other than where it was originally incorporated. The term applies both to domestic corporations that are incorporated in another state and to corporations that are incorporated in a nation other than the United States. All states require that foreign corporations register with the state before conducting business in the state.

Corporate tax is imposed in the United States at the federal, most state, and some local levels on the income of entities treated for tax purposes as corporations. Since January 1, 2018, the nominal federal corporate tax rate in the United States of America is a flat 21% following the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017. State and local taxes and rules vary by jurisdiction, though many are based on federal concepts and definitions. Taxable income may differ from book income both as to timing of income and tax deductions and as to what is taxable. The corporate Alternative Minimum Tax was also eliminated by the 2017 reform, but some states have alternative taxes. Like individuals, corporations must file tax returns every year. They must make quarterly estimated tax payments. Groups of corporations controlled by the same owners may file a consolidated return.

A Delaware statutory trust (DST) is a legally recognized trust that is set up for the purpose of business, but not necessarily in the U.S. state of Delaware. It may also be referred to as an Unincorporated Business Trust or UBO.
References
- ↑ 26 CFR 301.7701-2 Archived 2011-06-12 at the Wayback Machine and 301.7701-3 Archived 2011-06-12 at the Wayback Machine , Boris Bittker & James Eustice, Federal Income Taxation of Corporations and Shareholders, abridged paperback ISBN 978-0-7913-4101-8, chapter 2.
- ↑ 26 CFR 301.7701-2(b)(8)(i)
- 1 2 3 4 IRS Form 8832: Entity Classification Election
- ↑ Treasury regulations §301.7701-2(b)(8); latest amendment T.D. 9462, 74 FR 46904, Sept. 14, 2009
- ↑ Notice 2013-44
- ↑ Treasury regulations §301.7701-3(b)(3) and (h)(2).
- ↑ Clarifying Entity Classification Conversions, Steven M. Friedman & Samuel H. Hoppe, Commercial Investment Real Estate Magazine, July/August 1999.
- 1 2 3 4 Analyzing Subpart F in light of Check-the-Box, Cynthia Ram Sweitzer, Akron Tax Journal 20, March 2005. See pp. 9-11, 23
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 One Nation Among Many: Policy Implications of Cross-Border Tax Arbitrage, Diane M. Ring, Boston College Law Review 44(1), December 1, 2002. See pp. 96-98.
- 1 2 'Unchecking the Box' Could Lead to Fierce Debate, CFO Magazine, May 11, 2009
- 1 2 "Check-the-Box: Not Always the Right Answer for Certain Foreign Corporations". Robert Patelski, The Tax Adviser 37(4), April 2006.
- ↑ Internal revenue regulations §1.902
- 1 2 Internal Revenue Manual, Part 4. Examining Process, Chapter 61. LMSB International Program Audit Guidelines, Section 5. Entity Classification, Internal Revenue Service, May 1, 2006
- 1 2 Internal Revenue Service Adopts "Check-the-Box" Classification Regulations, Partnership Tax Bulletin, Pillsbury Winthrop Shaw Pittman, December 1996
- 1 2 Comments on changes in entity classification: special rule for certain foreign eligible entities. Tax Executive, April 4, 2000
- ↑ Entity classification simplification not that simple, Shawn Carson & John Santa Maria, The Tax Adviser, May 1, 2000
- ↑ General Explanations of the Administration's Fiscal Year 2010 Revenue Proposals Archived 2010-11-11 at the Wayback Machine , Department of the Treasury, May 2009. See p. 28.
- ↑ Obama’s 2011 Budget: Check-the-Box off the Table; Subpart F Expanded Archived 2011-07-14 at the Wayback Machine Morgan Lewis Tax Flash, February 2, 2010