
The zebrafish is a freshwater fish belonging to the minnow family (Cyprinidae) of the order Cypriniformes. Native to India and South Asia, it is a popular aquarium fish, frequently sold under the trade name zebra danio.

Reelin, encoded by the RELN gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates synaptic plasticity by enhancing the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. It also stimulates dendrite and dendritic spine development and regulates the continuing migration of neuroblasts generated in adult neurogenesis sites like the subventricular and subgranular zones. It is found not only in the brain but also in the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, fallopian tube, breast and in comparatively lower levels across a range of anatomical regions.

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM), also called intercellular matrix (ICM), is a network consisting of extracellular macromolecules and minerals, such as collagen, enzymes, glycoproteins and hydroxyapatite that provide structural and biochemical support to surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.
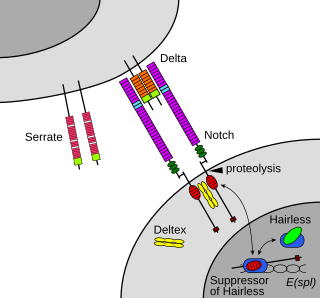
The Notch signaling pathway is a highly conserved cell signaling system present in most animals. Mammals possess four different notch receptors, referred to as NOTCH1, NOTCH2, NOTCH3, and NOTCH4. The notch receptor is a single-pass transmembrane receptor protein. It is a hetero-oligomer composed of a large extracellular portion, which associates in a calcium-dependent, non-covalent interaction with a smaller piece of the notch protein composed of a short extracellular region, a single transmembrane-pass, and a small intracellular region.

EGR-1 also known as ZNF268 or NGFI-A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EGR1 gene.

L1, also known as L1CAM, is a transmembrane protein member of the L1 protein family, encoded by the L1CAM gene. This protein, of 200 to 220 kDa, is a neuronal cell adhesion molecule with a strong implication in cell migration, adhesion, neurite outgrowth, myelination and neuronal differentiation. It also plays a key role in treatment-resistant cancers due to its function. It was first identified in 1984 by M. Schachner who found the protein in post-mitotic mice neurons.

The Disabled-1 (Dab1) gene encodes a key regulator of Reelin signaling. Reelin is a large glycoprotein secreted by neurons of the developing brain, particularly Cajal-Retzius cells. DAB1 functions downstream of Reln in a signaling pathway that controls cell positioning in the developing brain and during adult neurogenesis. It docks to the intracellular part of the Reelin very low density lipoprotein receptor (VLDLR) and apoE receptor type 2 (ApoER2) and becomes tyrosine-phosphorylated following binding of Reelin to cortical neurons. In mice, mutations of Dab1 and Reelin generate identical phenotypes. In humans, Reelin mutations are associated with brain malformations and mental retardation. In mice, Dab1 mutation results in the scrambler mouse phenotype.
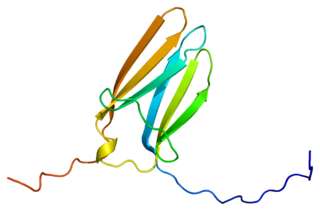
Tropomyosin receptor kinase C (TrkC), also known as NT-3 growth factor receptor, neurotrophic tyrosine kinase receptor type 3, or TrkC tyrosine kinase is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NTRK3 gene.

CD133 antigen, also known as prominin-1, is a glycoprotein that in humans is encoded by the PROM1 gene. It is a member of pentaspan transmembrane glycoproteins, which specifically localize to cellular protrusions. When embedded in the cell membrane, the membrane topology of prominin-1 is such that the N-terminus extends into the extracellular space and the C-terminus resides in the intracellular compartment. The protein consists of five transmembrane segments, with the first and second segments and the third and fourth segments connected by intracellular loops while the second and third as well as fourth and fifth transmembrane segments are connected by extracellular loops. While the precise function of CD133 remains unknown, it has been proposed that it acts as an organizer of cell membrane topology.
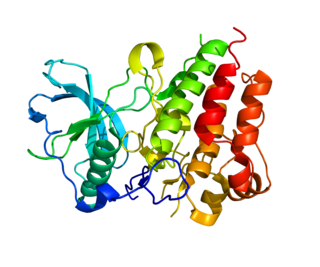
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), and CD115, is a cell-surface protein encoded by the human CSF1R gene. CSF1R is a receptor that can be activated by two ligands: colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF-1) and interleukin-34 (IL-34). CSF1R is highly expressed in myeloid cells, and CSF1R signaling is necessary for the survival, proliferation, and differentiation of many myeloid cell types in vivo and in vitro. CSF1R signaling is involved in many diseases and is targeted in therapies for cancer, neurodegeneration, and inflammatory bone diseases.

Reticulon 4 receptor (RTN4R) also known as Nogo-66 Receptor (NgR) or Nogo receptor 1 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the RTN4R gene. This gene encodes the receptor for reticulon 4, oligodendrocytemyelin glycoprotein and myelin-associated glycoprotein. This receptor mediates axonal growth inhibition and may play a role in regulating axonal regeneration and plasticity in the adult central nervous system.

CUB domain-containing protein 1 (CDCP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDCP1 gene. CDCP1 has also been designated as CD318 and Trask. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.

Ectoderm-neural cortex protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ENC1 gene.

Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase T is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PTPRT gene.

Cadherin-1 or Epithelial cadherin(E-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDH1 gene. Mutations are correlated with gastric, breast, colorectal, thyroid, and ovarian cancers. CDH1 has also been designated as CD324. It is a tumor suppressor gene.

T-box, brain, 1 is a transcription factor protein important in vertebrate embryo development. It is encoded by the TBR1 gene. This gene is also known by several other names: T-Brain 1, TBR-1, TES-56, and MGC141978. TBR1 is a member of the TBR1 subfamily of T-box family transcription factors, which share a common DNA-binding domain. Other members of the TBR1 subfamily include EOMES and TBX21. TBR1 is involved in the differentiation and migration of neurons and is required for normal brain development. TBR1 interacts with various genes and proteins in order to regulate cortical development, specifically within layer VI of the developing six-layered human cortex. Studies show that TBR1 may play a role in major neurological diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD).

Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein is a plasticity protein that in humans is encoded by the ARC gene. The gene is believed to derive from a retrotransposon. The protein is found in the neurons of tetrapods and other animals where it can form virus-like capsids that transport RNA between neurons.

In molecular biology, miR-137 is a short non-coding RNA molecule that functions to regulate the expression levels of other genes by various mechanisms. miR-137 is located on human chromosome 1p22 and has been implicated to act as a tumor suppressor in several cancer types including colorectal cancer, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma via cell cycle control.

Günther K.H. Zupanc is a German-American neurobiologist, researcher, university teacher, book author, journal editor, and educational reformer. He is a Professor in the Department of Biology at Northeastern University in Boston, Massachusetts.
Dedifferentiation is a transient process by which cells become less specialized and return to an earlier cell state within the same lineage. This suggests an increase in cell potency, meaning that, following dedifferentiation, a cell may possess the ability to re-differentiate into more cell types than it did before dedifferentiation. This is in contrast to differentiation, where differences in gene expression, morphology, or physiology arise in a cell, making its function increasingly specialized.



















