
Niagara-on-the-Lake is a town in Ontario, Canada. It is located on the Niagara Peninsula at the point where the Niagara River meets Lake Ontario, across the river from New York, United States. Niagara-on-the-Lake is in the Niagara Region of Ontario and is the only town in Canada that has a lord mayor. It has a population of 17,511 (2016).
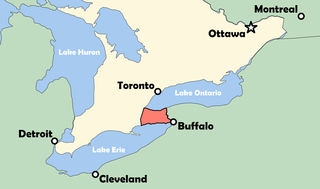
The Niagara Peninsula is an area of land lying between the southwestern shore of Lake Ontario and the northeastern shore of Lake Erie, in Ontario, Canada. Technically an isthmus rather than a peninsula, it stretches from the Niagara River in the east to Hamilton, Ontario, in the west. The peninsula is located in the Golden Horseshoe region of Southern Ontario, and has a population of roughly 1,000,000 residents. The region directly across the Niagara River and Lake Erie in New York State is known as the Niagara Frontier.

The New York Central Railroad was a railroad primarily operating in the Great Lakes and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The railroad primarily connected greater New York and Boston in the east with Chicago and St. Louis in the Midwest, along with the intermediate cities of Albany, Buffalo, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Detroit, Rochester and Syracuse. New York Central was headquartered in New York City's New York Central Building, adjacent to its largest station, Grand Central Terminal.

The Regional Municipality of Niagara, also colloquially known as the Niagara Region or Region of Niagara, is a regional municipality comprising twelve municipalities of Southern Ontario, Canada. The regional seat is in Thorold. It is the southern end of the Golden Horseshoe, the largest megalopolis in Canada.

Queenston is a compact rural community and unincorporated place 5 kilometres (3.1 mi) north of Niagara Falls in the Town of Niagara-on-the-Lake, Ontario, Canada. It is bordered by Highway 405 to the south and the Niagara River to the east; its location at the eponymous Queenston Heights on the Niagara Escarpment led to the establishment of the Queenston Quarry in the area. Across the river and the Canada–US border is the village of Lewiston, New York. The Lewiston-Queenston Bridge links the two communities. This village is at the point where the Niagara River began eroding the Niagara Escarpment. During the ensuing 12,000 years the Falls cut an 11 kilometres (6.8 mi) long gorge in the Escarpment southward to its present-day position.
Chippawa is a community located within the city of Niagara Falls, Ontario.

The Great Western Railway was a railway that operated in Canada West, today's province of Ontario, Canada. It was the first railway chartered in the province, receiving its original charter as the London and Gore Railroad on March 6, 1834, before receiving its final name when it was rechartered in 1845.
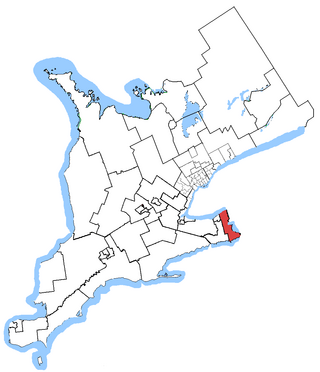
Niagara Falls is a federal electoral district in Ontario, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1953.

The Michigan Central Railroad was originally incorporated in 1846 to establish rail service between Detroit, Michigan, and St. Joseph, Michigan. The railroad later operated in the states of Michigan, Indiana, and Illinois in the United States and the province of Ontario in Canada. After about 1867 the railroad was controlled by the New York Central Railroad, which later became part of Penn Central and then Conrail. After the 1998 Conrail breakup, Norfolk Southern Railway now owns much of the former Michigan Central trackage.
The Buffalo and Niagara Falls Railroad was a part of the New York Central Railroad system, connecting Buffalo, New York to Niagara Falls. It is still used by CSX for freight and Amtrak for passenger service.

The Canada Southern Railway, also known as CSR, was a railway in southwestern Ontario, Canada, founded on February 28, 1868 as the Erie and Niagara Extension Railway. Its name was changed to Canada Southern Railway on December 24, 1869. The 1868 Act specified that it was to be constructed at a broad gauge of 5 ft 6 in, but that requirement was repealed in the 1869 Act, thus allowing construction at the standard gauge of 4 ft 8+1⁄2 in.
The Niagara Parks Commission, commonly shortened to Niagara Parks, is an agency of the Government of Ontario which maintains the Ontario shoreline of the Niagara River.

Transit Windsor provides public transportation in the city of Windsor, Ontario, Canada as well as LaSalle, Essex, Kingsville, Amherstburg and Leamington and serves more than 6 million passengers each year, covering an area of 310 km2 (120 sq mi) and a population of 218,000. They operate a cross border service between the downtown areas of Windsor and Detroit, Michigan via the Tunnel Bus, and service to events at Detroit's Comerica Park, Little Caesars Arena, TCF Center, and Ford Field. The Windsor International Transit Terminal neighbours with the Windsor International Aquatic and Training Centre.
The Niagara Parkway, formerly known as Niagara Boulevard and historically as the Niagara Road, is a scenic road in the province of Ontario that travels on the Canadian side of the Niagara River from the town of Fort Erie to Niagara-on-the-Lake. The portion north of Table Rock in the city of Niagara Falls is designated as an Ontario Scenic Highway. Niagara Boulevard originally referred only to the section from Fort Erie to Chippawa.

The Niagara Gorge Railroad was an interurban railway which ran at the bottom of the Niagara Gorge from Niagara Falls, New York to Lewiston, New York.
The Elmira and Lake Ontario Railroad was a subsidiary of the Northern Central Railway and later the Pennsylvania Railroad, formed to give the Northern Central an outlet for coal traffic on Lake Ontario.

The Montrose Swing Bridge is located on the Welland River at the junction with the Queenston Power Canal in the southeast portion of the City of Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada. It was built ca. 1910 to carry the Canada Southern Railway over the river. It is a two-track bridge, although only one track remains in use today. It crosses the river at roughly a 45-degree angle.












