Related Research Articles

Sinusitis, also known as rhinosinusitis, is inflammation of the mucous membranes that line the sinuses resulting in symptoms that may include thick nasal mucus, a plugged nose, and facial pain. Other signs and symptoms may include fever, headaches, a poor sense of smell, sore throat, and cough. It is defined as acute sinusitis if it lasts less than 4 weeks, and as chronic sinusitis if it lasts for more than 12 weeks.

A nosebleed, also known as epistaxis, is bleeding from the nose. Blood can flow down into the stomach, and cause nausea and vomiting. In more severe cases, blood may come out of both nostrils. Rarely, bleeding may be so significant that low blood pressure occurs. Blood may also come up the nasolacrimal duct and out from the eye.
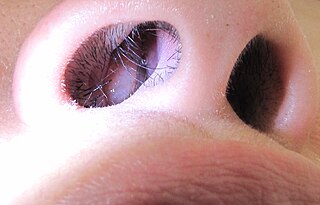
Nasal polyps (NP) are noncancerous growths within the nose or sinuses. Symptoms include trouble breathing through the nose, loss of smell, decreased taste, post nasal drip, and a runny nose. The growths are sac-like, movable, and nontender, though face pain may occasionally occur. They typically occur in both nostrils in those who are affected. Complications may include sinusitis and broadening of the nose.

Septoplasty [ˈsɛp.toˌplæ.sti] (Etymology: L, saeptum, septum; Gk, πλάσσειν plassein – to shape), or alternatively submucous septal resection and septal reconstruction, is a corrective surgical procedure done to straighten a deviated nasal septum – the nasal septum being the partition between the two nasal cavities. Ideally, the septum should run down the center of the nose. When it deviates into one of the cavities, it narrows that cavity and impedes airflow. Deviated nasal septum or “crooked” internal nose can occur at childbirth or as the result of an injury or other trauma. If the wall that functions as a separator of both sides of the nose is tilted towards one side at a degree greater than 50%, it might cause difficulty breathing. Often the inferior turbinate on the opposite side enlarges, which is termed compensatory hypertrophy. Deviations of the septum can lead to nasal obstruction. Most surgeries are completed in 60 minutes or less, while the recovery time could be up to several weeks. Put simply, septoplasty is a surgery that helps repair the passageways in the nose making it easier to breathe. This surgery is usually performed on patients with a deviated septum, recurrent rhinitis, or sinus issues.

Epidural hematoma is when bleeding occurs between the tough outer membrane covering the brain and the skull. Often there is loss of consciousness following a head injury, a brief regaining of consciousness, and then loss of consciousness again. Other symptoms may include headache, confusion, vomiting, and an inability to move parts of the body. Complications may include seizures.
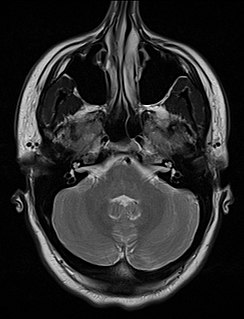
Nasal septum deviation is a physical disorder of the nose, involving a displacement of the nasal septum. Some displacement is common, affecting 80% of people, mostly without their knowledge.

Aerosinusitis, also called barosinusitis, sinus squeeze or sinus barotrauma is a painful inflammation and sometimes bleeding of the membrane of the paranasal sinus cavities, normally the frontal sinus. It is caused by a difference in air pressures inside and outside the cavities.

The pyramid-shaped maxillary sinus is the largest of the paranasal sinuses, and drains into the middle meatus of the nose through the osteomeatal complex.
Phycomycosis is an uncommon condition of the gastrointestinal tract and skin most commonly found in dogs and horses. The condition is caused by a variety of molds and fungi, and individual forms include pythiosis, zygomycosis, and lagenidiosis. Pythiosis is the most common type and is caused by Pythium, a type of water mould. Zygomycosis can also be caused by two types of zygomycetes, Entomophthorales and Mucorales. The latter type of zygomycosis is also referred to as mucormycosis. Lagenidiosis is caused by a Lagenidium species, which like Pythium is a water mould. Since both pythiosis and lagenidiosis are caused by organisms from the class Oomycetes, they are sometimes collectively referred to as oomycosis.
Equine nasal cysts are abnormal fluid filled sacs which occur inside the nasal sinuses of horses. The cysts are lined with epithelium, and usually occur in the ventral conchae or maxillary sinuses, most commonly in horses less than one year old. Surgical removal of the cyst has a good prognosis for the horse.
Chronic atrophic rhinitis, or simply atrophic rhinitis, is a chronic inflammation of the nose characterised by atrophy of nasal mucosa, including the glands, turbinate bones and the nerve elements supplying the nose. Chronic atrophic rhinitis may be primary and secondary. Special forms of chronic atrophic rhinitis are rhinitis sicca anterior and ozaena. It can also be described as the empty nose syndrome.

Functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) is a minimally invasive procedure which uses nasal endoscopes to enlarge the nasal drainage pathways of the paranasal sinuses to improve sinus ventilation and allow access of topical medications. This procedure is generally used to treat inflammatory and infectious sinus diseases, including chronic rhinosinusitis that do not respond to drugs, nasal polyps, some cancers, and decompression of eye sockets/optic nerve in Graves ophthalmopathy.

The human nose is the most protruding part of the face. It bears the nostrils and is the first organ of the respiratory system. It is also the principal organ in the olfactory system. The shape of the nose is determined by the nasal bones and the nasal cartilages, including the nasal septum which separates the nostrils and divides the nasal cavity into two. On average the nose of a male is larger than that of a female.
A sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue. In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it. Most individuals have four paired cavities located in the cranial bone or skull.

Nasal septal hematoma is a condition affecting the nasal septum. It can be associated with trauma.

Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma is an angiofibroma also known as juvenile nasal angiofibroma, fibromatous hamartoma, and angiofibromatous hamartoma of the nasal cavity. It is a histologically benign but locally aggressive vascular tumor of the nasopharynx that arises from the superior margin of the sphenopalatine foramen and grows in the back of the nasal cavity. It most commonly affects adolescent males . Though it is a benign tumor, it is locally invasive and can invade the nose, cheek, orbit, or brain. Patients with nasopharyngeal angiofibroma usually present with one-sided nasal obstruction with profuse epistaxis.

A Le Fort fracture of the skull is a classic transfacial fracture of the midface, involving the maxillary bone and surrounding structures in either a horizontal, pyramidal or transverse direction. The hallmark of Lefort fractures is traumatic pterygomaxillary separation, which signifies fractures between the pterygoid plates, horseshoe-shaped bony protuberances which extend from the inferior margin of the maxilla, and the maxillary sinuses. Continuity of this structure is a keystone for stability of the midface, involvement of which impacts surgical management of trauma victims, as it requires fixation to a horizontal bar of the frontal bone. The pterygoid plates lie posterior to the upper dental row, or alveolar ridge, when viewing the face from an anterior view. The fractures are named after French surgeon René Le Fort (1869–1951), who discovered the fracture patterns by examining crush injuries in cadavers.

The respiratory system of the horse is the biological system by which a horse circulates air for the purpose of gaseous exchange.
Endoscopic endonasal surgery is a minimally invasive technique used mainly in neurosurgery and otolaryngology. A neurosurgeon or an otolaryngologist, using an endoscope that is entered through the nose, fixes or removes brain defects or tumors in the anterior skull base. Normally an otolaryngologist performs the initial stage of surgery through the nasal cavity and sphenoid bone; a neurosurgeon performs the rest of the surgery involving drilling into any cavities containing a neural organ such as the pituitary gland. The use of endoscope was first introduced in Transsphenoidal Pituitary Surgery by R Jankowsky, J Auque, C Simon et al. in 1992 G.

Oroantral fistula (OAF) is an epithelialised oroantral communication (OAC). OAC refers to an abnormal connection between the oral cavity and antrum. The creation of an OAC is most commonly due to the extraction of a maxillary (upper) tooth closely related to the antral floor. A small OAC may heal spontaneously but a larger OAC would require surgical closure to prevent the development of persistent OAF and chronic sinusitis.
References
- ↑ "Ethmoid Hematoma". The Merck Veterinary Manual. 2014. Retrieved 2021-02-02.