Related Research Articles

Health care, or healthcare, is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. The term includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health.

Health informatics is the study and implementation of computer structures and algorithms to improve communication, understanding, and management of medical information. It can be viewed as branch of engineering and applied science.
Stryker Corporation is an American multinational medical technologies corporation based in Kalamazoo, Michigan. Stryker's products include implants used in joint replacement and trauma surgeries; surgical equipment and surgical navigation systems; endoscopic and communications systems; patient handling and emergency medical equipment; neurosurgical, neurovascular and spinal devices; as well as other medical device products used in a variety of medical specialties.
An orphan drug is a pharmaceutical agent that is developed to treat certain rare medical conditions. An orphan drug would not be profitable to produce without government assistance, due to the small population of patients affected by the conditions. The conditions that orphan drugs are used to treat are referred to as orphan diseases. The assignment of orphan status to a disease and to drugs developed to treat it is a matter of public policy that depends on the legislation of the country.

GE HealthCare Technologies, Inc., doing business as GE HealthCare, is an American multinational medical technology company headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. It was spun-off from General Electric on January 4, 2023, with GE retaining 10.24%. As of 2017, it is a manufacturer and distributor of diagnostic imaging agents and radiopharmaceuticals for imaging modalities used in medical imaging procedures. It offers dyes used in magnetic-resonance-imaging procedures; manufactures medical diagnostic equipment, including CT image machines; MRI, XRAY; Ultrasound; Cath Labs; Mammogram; Nuclear Medicine Cameras; and develops Health technology for medical imaging and information technologies, medical diagnostics, patient monitoring systems, disease research, drug discovery, and biopharmaceutical manufacturing. It was incorporated in 1994 and operates in more than 100 countries.

Medtronic plc is an American medical device company. The company's operational and executive headquarters are in Minneapolis, Minnesota, and its legal headquarters are in Ireland due to its acquisition of Irish-based Covidien in 2015. While it primarily operates in the United States, it operates in more than 150 countries and employs over 90,000 people. It develops and manufactures healthcare technologies and therapies.
Pharmacovigilance, also known as drug safety, is the pharmaceutical science relating to the "collection, detection, assessment, monitoring, and prevention" of adverse effects with pharmaceutical products. The etymological roots for the word "pharmacovigilance" are: pharmakon and vigilare. As such, pharmacovigilance heavily focuses on adverse drug reactions (ADR), which are defined as any response to a drug which is noxious and unintended, including lack of efficacy. Medication errors such as overdose, and misuse and abuse of a drug as well as drug exposure during pregnancy and breastfeeding, are also of interest, even without an adverse event, because they may result in an adverse drug reaction.

A medical device is any device intended to be used for medical purposes. Significant potential for hazards are inherent when using a device for medical purposes and thus medical devices must be proved safe and effective with reasonable assurance before regulating governments allow marketing of the device in their country. As a general rule, as the associated risk of the device increases the amount of testing required to establish safety and efficacy also increases. Further, as associated risk increases the potential benefit to the patient must also increase.

A health or medical library is designed to assist physicians, health professionals, students, patients, consumers, medical researchers, and information specialists in finding health and scientific information to improve, update, assess, or evaluate health care. Medical libraries are typically found in hospitals, medical schools, private industry, and in medical or health associations. A typical health or medical library has access to MEDLINE, a range of electronic resources, print and digital journal collections, and print reference books. The influence of open access (OA) and free searching via Google and PubMed has a major impact on the way medical libraries operate.

ResMed Inc. is a San Diego, California-based medical equipment company. It primarily provides cloud-connectable medical devices for the treatment of sleep apnea, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and other respiratory conditions. ResMed produced hundreds of thousands of ventilators and bilevel devices to help treat the respiratory symptoms of patients with COVID-19. ResMed also provides software to out-of-hospital care agencies to streamline transitions of care into and between these care settings for seniors and their care providers.
St. Jude Medical, Inc. was an American global medical device company headquartered in Little Canada, Minnesota, U.S., a suburb of Saint Paul. The company had more than 20 principal operations and manufacturing facilities worldwide with products sold in more than 100 countries. Its major markets include the United States, Europe, Latin America and Asia-Pacific. The company was named after Jude the Apostle, the patron saint of lost causes.
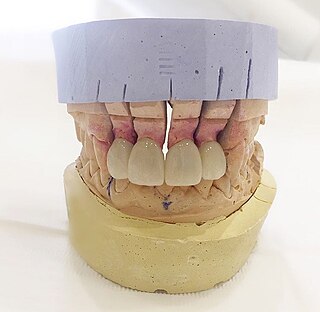
Dental laboratories manufacture or customize a variety of products to assist in the provision of oral health care by a licensed dentist. These products include crowns, bridges, dentures and other dental products. Dental lab technicians follow a prescription from a licensed dentist when manufacturing these items, which include prosthetic devices and therapeutic devices. The FDA regulates these products as medical devices and they are therefore subject to FDA's good manufacturing practice ("GMP") and quality system ("QS") requirements. In most cases, however, they are exempt from manufacturer registration requirements. Some of the most common restorations manufactured include crowns, bridges, dentures, and dental implants. Dental implants is one of the most advanced dental technologies in the field of dentistry.
The Institute of Biomedical Science (IBMS) is the professional body for biomedical scientists in the United Kingdom. The IBMS was founded in 1912 and represents approximately 20,000 members employed mainly in the National Health Service and UK Health Security Agency and private healthcare laboratories. Other members also work in veterinary laboratories, the National Blood Authority, Health Protection Agency, Medical Research Council and Department for Environment, Food and Rural Affairs, as well as related commercial fields and in teaching. Most members, around 96%, live and work in the United Kingdom and Ireland and some are employed overseas. It aims to promote and develop biomedical science and its practitioners.
AdvaMed, or the Advanced Medical Technology Association, is an American medical device trade association, based in Washington, D.C. It is the largest medical device association in the world with U.S. and international members who are medical technology companies that collectively represents 80% of U.S. medical technology firms in the United States, that produce close to 90% of annual health care technology purchases in the United States and more than 40% globally.

MAKO Surgical Corp. was a publicly traded medical device company based in Florida. On September 25, 2013, the Board of Directors of Mako Surgical accepted a deal to be acquired by Stryker for $1.65B. The deal closed in December 2013.
MedTech Europe is the European trade association representing the medical technology industries, from diagnosis to cure. It represents Diagnostics and Medical Devices manufacturers operating in Europe. It is born as an alliance of two European medical technology associations, EDMA and Eucomed, representing the European IVD and medical device industries, respectively. It was established with the aim to represent the common policy goals of both organisations more effectively, promoting the interests of its members and of the medical technology industry in general. There are more than 33,000 medical technology companies in Europe. The highest number of them are based in Germany, followed by Italy, the UK, France and Switzerland.

Jeroen Tas is a Dutch entrepreneur and senior executive in the healthcare, information technology and financial services industries. In February 2017, he assumed the role as Chief Innovation & Strategy Officer at Philips Healthcare, a position he held until July 2021. He currently works on Strategic Business Development and is also a member of the executive committee at Royal Philips.
The Medical Device Radiocommunications Service (MedRadio) is a specification and communication spectrum created for and set aside by the U.S. Federal Communications Commission (FCC) for the communication needs of diagnostic and therapeutic medical implants and body-worn medical devices. Devices operating on MedRadio include cardiac pacemakers, defibrillators, neuromuscular stimulators, and drug delivery systems. As of February 2016, communications spectrum for these and other similar devices is set aside at various points in the 400 MHz frequency band, as well as the 2360-2400 MHz band, though specifically for medical body area network (MBAN) devices. The specification supersedes and incorporates a previous specification called the Medical Implant Communication Service (MICS).
The Association of British HealthTech Industries, formerly the Association of British Healthcare Industries is a trade association for the medical technology sector in the UK. It has about 250 member companies which together provide 80% of the medical technology used in the NHS. It has offices in London. Members include the UK operations of multinational companies.

Andhra Pradesh MedTech Zone(AMTZ) is the medical technology park with Common Manufacturing Facilities & Common Scientific Facilities located in Nadupuru village area of Visakhapatnam, adjacent to the Visakhapatnam Steel Plant. The AMTZ is spread over an area of 270 acres and it has over 10 manufacturing units.
References
- ↑ "Medical Devices Today: Eucomed: Finding Its Seat at the Table: An Interview with Guy Lebeau". Archived from the original on 2 December 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- 1 2 "Current Eucomed members". Archived from the original on 21 August 2008. Retrieved 22 February 2008.
- ↑ Edma Eucomed join together to establish industry federation Archived 2013-12-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ↑ "Eucomed organigramme". Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2013.
- ↑ "Home". Citeline. Archived from the original on 4 March 2016.
- ↑ "EHTI official website". Archived from the original on 21 October 2016. Retrieved 8 July 2022.
- ↑ "- Swedish Medtech". Archived from the original on 3 December 2013. Retrieved 25 November 2013.