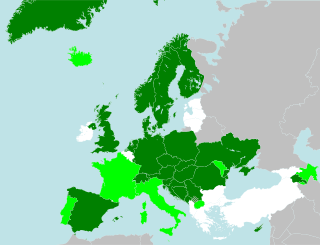
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, the charter does not provide any criterion or definition for an idiom to be a minority or a regional language, and the classification stays in the hands of the national state.

The European Convention on Human Rights is an international convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe. Drafted in 1950 by the then newly formed Council of Europe, the convention entered into force on 3 September 1953. All Council of Europe member states are party to the convention and new members are expected to ratify the convention at the earliest opportunity.
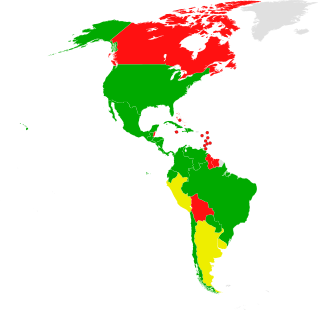
The Montevideo Convention on the Rights and Duties of States is a treaty signed at Montevideo, Uruguay, on December 26, 1933, during the Seventh International Conference of American States. The Convention codifies the declarative theory of statehood as accepted as part of customary international law. At the conference, United States President Franklin D. Roosevelt and Secretary of State Cordell Hull declared the Good Neighbor Policy, which opposed U.S. armed intervention in inter-American affairs. The convention was signed by 19 states. The acceptance of three of the signatories was subject to minor reservations. Those states were Brazil, Peru and the United States.

Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories have the power to make legislation relevant to the area, thus granting them a higher level of autonomy.

A popular initiative is a form of direct democracy by which a petition meeting certain hurdles can force a legal procedure on a proposition. The hurdles the petition has to meet vary between countries, typically signatures by a certain number of registered voters.

The Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe was an unratified international treaty intended to create a consolidated constitution for the European Union (EU). It would have replaced the existing European Union treaties with a single text, given legal force to the Charter of Fundamental Rights, and expanded qualified majority voting into policy areas which had previously been decided by unanimity among member states.

A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority, and that the recipient admits a limited status within the relationship, and it is within that sense that charters were historically granted, and it is that sense which is retained in modern usage of the term.
Subsidiarity is a principle of social organization that holds that social and political issues should be dealt with at the most immediate or local level that is consistent with their resolution. The Oxford English Dictionary defines subsidiarity as "the principle that a central authority should have a subsidiary function, performing only those tasks which cannot be performed at a more local level". The concept is applicable in the fields of government, political science, neuropsychology, cybernetics, management and in military command. The OED adds that the term "subsidiarity" in English follows the early German usage of "Subsidiarität". More distantly, it is derived from the Latin verb subsidio, and the related noun subsidium.

Election monitoring involves the observation of an election by one or more independent parties, typically from another country or from a non-governmental organization (NGO). The monitoring parties aim primarily to assess the conduct of an election process on the basis of national legislation and of international election standards. There are national and international election observers. Monitors do not directly prevent electoral fraud, but rather record and report instances of suspicious practices. Election observation increasingly looks at the entire electoral process over a long period of time, rather than at election-day proceedings only. The legitimacy of an election can be affected by the criticism of monitors, unless they are themselves seen as biased. A notable individual is often appointed honorary leader of a monitoring organization in an effort to enhance legitimacy of the monitoring process.

The Committee of Ministers of the Council of Europe or Committee of Ministers is the Council of Europe's decision-making body. It comprises the Foreign Affairs Ministers of all the member states, or their permanent diplomatic representatives in Strasbourg. It is both a governmental body, where national approaches to problems facing European society can be discussed on an equal footing, as well as a collective forum, where Europe-wide responses to such challenges are formulated. In collaboration with the Parliamentary Assembly, it is the guardian of the Council's fundamental values; it monitors member states' compliance with their undertakings. The Holy See, Japan, Mexico, and the US are observer states in the Committee of Ministers.
In many parts of the world, local elections take place to select office-holders in local government, such as mayors and councillors. Elections to positions within a city or town are often known as "municipal elections". Their form and conduct vary widely across jurisdictions.
The Valletta Treaty (formally the European Convention on the Protection of the Archaeological Heritage (Revised), also known as the Malta Convention) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe. The 1992 treaty aims to protect the European archaeological heritage "as a source of European collective memory and as an instrument for historical and scientific study". All remains and objects and any other traces of humankind from past times are considered to be elements of the archaeological heritage. The archaeological heritage shall include structures, constructions, groups of buildings, developed sites, moveable objects, monuments of other kinds as well as their context, whether situated on land or under water." (Art. 1)

The Congress of Local and Regional Authorities is the pan-European political assembly representing local and regional authorities from the forty-six member states of the Council of Europe. Its role is to promote local and regional democracy, improve local and regional governance and strengthen authorities' self-government, according to the principles laid down in the European Charter of Local Self-Government. It is made up of two chambers, the Chamber of Local Authorities and the Chamber of Regions and holds its plenary sessions twice a year at the Palace of Europe in Strasbourg, where its permanent Secretariat is located.
The Chamber of Local Authorities is one of the two Chambers of the Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of the Council of Europe. The Chamber is the voice of local authorities in the Council of Europe. It consists of 306 representatives from the Council's 46 member states, who either hold a general local authority mandate from direct elections or are politically accountable to a directly elected assembly. The Chamber provides an opportunity for local officials to discuss common concerns, share their experiences and develop relevant policies.
The Constitutional law on the Modernisation of the Institutions of the Fifth Republic was enacted into French constitutional law by the Parliament of France in July 2008, to reform state institutions.

The law of Italy is the system of law across the Italian Republic. The Italian legal system has a plurality of sources of production. These are arranged in a hierarchical scale, under which the rule of a lower source cannot conflict with the rule of an upper source.

Andreas Kiefer is an Austrian politician. Since 2010, he is Secretary General of the Congress of Local and Regional Authorities of the Council of Europe, an institution representing local and regional authorities of the 47 member states of the Council of Europe.

The Treaties of the European Union are a set of international treaties between the European Union (EU) member states which sets out the EU's constitutional basis. They establish the various EU institutions together with their remit, procedures and objectives. The EU can only act within the competences granted to it through these treaties and amendment to the treaties requires the agreement and ratification of every single signatory.

Local government in Spain refers to the government and administration of what the Constitution calls "local entities", which are primarily municipalities, but also groups of municipalities including provinces, metropolitan areas, comarcas and mancomunidades and sub-municipal groups known as Minor local entities.
The 1973 United Nations International Convention on the Suppression and Punishment of the Crime of Apartheid was the first binding international treaty which declared the crime of apartheid and racial segregation under international law. It was adopted by the General Assembly on 30 November 1973 and came into force on 18 July 1976. It passed by 91 votes in favor, four against and 26 abstentions. 110 countries are currently parties to the convention, with 26 signatories.













