
The European Free Trade Association (EFTA) is a regional trade organization and free trade area consisting of four European states: Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. The organization operates in parallel with the European Union (EU), and all four member states participate in the European Single Market and are part of the Schengen Area. They are not, however, party to the European Union Customs Union.
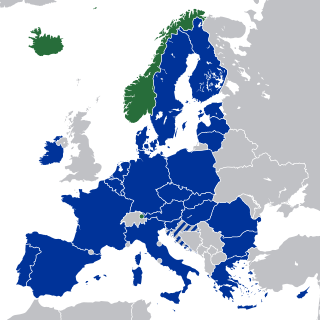
The European Economic Area (EEA) was established via the Agreement on the European Economic Area, an international agreement which enables the extension of the European Union's single market to member states of the European Free Trade Association. The EEA links the EU member states and three EFTA states into an internal market governed by the same basic rules. These rules aim to enable free movement of persons, goods, services, and capital within the European single market, including the freedom to choose residence in any country within this area. The EEA was established on 1 January 1994 upon entry into force of the EEA Agreement. The contracting parties are the EU, its member states, and Iceland, Liechtenstein, and Norway.

A European Capital of Culture is a city designated by the European Union (EU) for a period of one calendar year during which it organises a series of cultural events with a strong pan-European dimension. Being a European Capital of Culture can be an opportunity for a city to generate considerable cultural, social and economic benefits and it can help foster urban regeneration, change the city's image and raise its visibility and profile on an international scale. Multiple cities can be a European Capital of Culture simultaneously.

Eurostat is a Directorate-General of the European Commission located in the Kirchberg quarter of Luxembourg City, Luxembourg. Eurostat's main responsibilities are to provide statistical information to the institutions of the European Union (EU) and to promote the harmonisation of statistical methods across its member states and candidates for accession as well as EFTA countries. The organisations in the different countries that cooperate with Eurostat are summarised under the concept of the European Statistical System.

Multi-speed Europe or two-speed Europe is the idea that different parts of the European Union should integrate at different levels and pace depending on the political situation in each individual country. Indeed, multi-speed Europe is currently a reality, with only a subset of EU countries being members of the eurozone and of the Schengen area. Like other forms of differentiatedintegration such as à la carte and variable geometry, "multi-speed Europe" arguably aims to salvage the "widening and deepening of the European Union" in the face of political opposition.

Although there has been a large degree of integration between European Union member states, foreign relations is still a largely intergovernmental matter, with the 27 members controlling their own relations to a large degree. However, with the Union holding more weight as a single bloc, there are at times attempts to speak with one voice, notably on trade and energy matters. The High Representative of the Union for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy personifies this role.
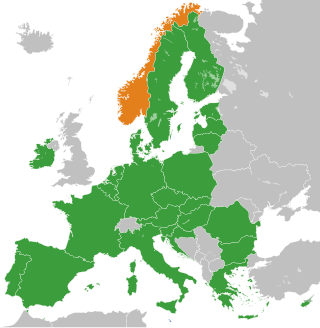
Norway is not a member state of the European Union (EU). However, it is associated with the Union through its membership of the European Economic Area (EEA), signed in 1992 and established in 1994. Norway was a founding member of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) in 1960, which was originally set up as an alternative to the European Economic Community (EEC), the main predecessor of the EU. Norway had considered joining both the EEC and the European Union, but opted to decline following referendums in 1972 and 1994. According to the European Social Survey conducted in 2018, 73.6% of Norwegians would vote 'No' in a Referendum to join the European Union. Norway has two land borders with EU member states: Finland and Sweden.

The Roaming Regulation 2022 bans roaming charges (Eurotariff) within the European Economic Area (EEA), which consists of the member states of the European Union, Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway. This regulates both the charges mobile network operator can impose on its subscribers for using telephone and data services outside of the network's member state, and the wholesale rates networks can charge each other to allow their subscribers access to each other's networks. The 2012 Regulation was recast in 2022.
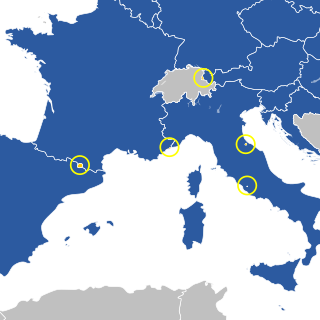
Currently, all of the European microstates have some form of relations with the European Union (EU).

A Norwegian passport is the passport issued to nationals of Norway for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Norwegian citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Norwegian consular officials abroad.

The European driving licence is a driving licence issued by the member states of the European Economic Area (EEA); all 27 EU member states and three EFTA member states; Iceland, Liechtenstein and Norway, which give shared features the various driving licence styles formerly in use. It is credit card-style with a photograph and a microchip. They were introduced to replace the 110 different plastic and paper driving licences of the 300 million drivers in the EEA. The main objective of the licence is to reduce the risk of fraud.

Liechtenstein passports are issued to nationals of Liechtenstein for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Liechtenstein citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Liechtenstein consular officials abroad.

Icelandic passports are issued to citizens of Iceland for the purpose of international travel. Beside serving as proof of Icelandic citizenship, they facilitate the process of securing assistance from Icelandic consular officials abroad.

The Republic of Azerbaijan and the European Union (EU) have maintained a positive relationship through the years and have become more closely linked since 1991. Azerbaijan is currently part of the European Neighborhood Policy, the Eastern Partnership and the Council of Europe. The EU is the largest foreign grant donor to and investor in Azerbaijan, both in the government sector and civil society, making available over 600 million EURO of bilateral EU assistance since 1992.

An eco hotel, or a green hotel, is an environmentally sustainable hotel or accommodation that has made important environmental improvements to its structure in order to minimize its impact on the natural environment. The basic definition of an eco-friendly hotel is an environmentally responsible lodging that follows the practices of green living. These hotels have to be certified green by an independent third-party or by the state they are located in. Traditionally, these hotels were mostly presented as ecolodges because of their location, often in jungles, and their design inspired by the use of traditional building methods applied by skilled local craftsmen in areas, such as Costa Rica and Indonesia.

European Union–Kazakhstan relations are the international relations between the Republic of Kazakhstan and the common foreign policy and trade relations of the European Union.
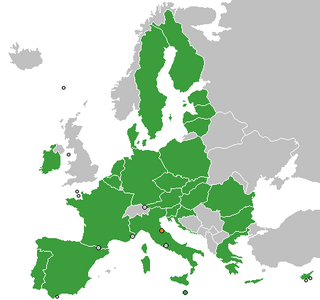
Relations between the Republic of San Marino and the European Union (EU) began in February 1983. San Marino is completely surrounded by one EU member state, Italy.

The Liechtenstein identity card is issued to Liechtenstein citizens by the Immigration and Passport Office in Vaduz. The card costs CHF150 for adults aged 15 or over and is valid for 10 years. For children, the card costs CHF30 and has a validity of 3 years.

Passports of the EFTA member states are passports issued by the European Free Trade Association (EFTA) member states Iceland, Liechtenstein, Norway and Switzerland. EFTA is in this article used as a common name for these countries.

Passports in Europe are issued by each state individually, e.g. the Netherlands or United Kingdom. In general, passports issued in Europe either grant the holder the right of freedom of movement within the European Economic Area, to those that don't. The majority of European states are members of the European Union, and therefore issue EU passports.
















