Medical physics deals with the application of the concepts and methods of physics to the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of human diseases with a specific goal of improving human health and well-being. Since 2008, medical physics has been included as a health profession according to International Standard Classification of Occupation of the International Labour Organization.
Internal medicine, also known as general internal medicine in Commonwealth nations, is a medical specialty for medical doctors focused on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of internal diseases in adults. Medical practitioners of internal medicine are referred to as internists, or physicians in Commonwealth nations. Internists possess specialized skills in managing patients with undifferentiated or multi-system disease processes. They provide care to both hospitalized (inpatient) and ambulatory (outpatient) patients and often contribute significantly to teaching and research. Internists are qualified physicians who have undergone postgraduate training in internal medicine, and should not be confused with "interns", a term commonly used for a medical doctor who has obtained a medical degree but does not yet have a license to practice medicine unsupervised.
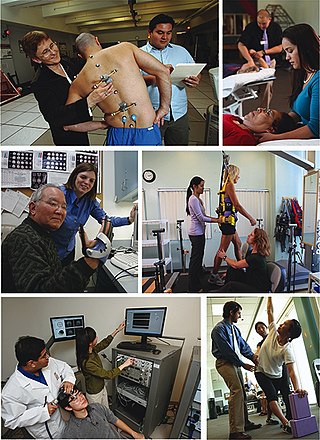
Kinesiology is the scientific study of human body movement. Kinesiology addresses physiological, anatomical, biomechanical, pathological, neuropsychological principles and mechanisms of movement. Applications of kinesiology to human health include biomechanics and orthopedics; strength and conditioning; sport psychology; motor control; skill acquisition and motor learning; methods of rehabilitation, such as physical and occupational therapy; and sport and exercise physiology. Studies of human and animal motion include measures from motion tracking systems, electrophysiology of muscle and brain activity, various methods for monitoring physiological function, and other behavioral and cognitive research techniques.

Keimyung University, abbreviated as KMU or Keimyung (啓明), is a private university located in Daegu, the fourth largest city in South Korea. The university was founded in 1954 with the support of the leaders of the Northern Presbyterian Church of the U.S. as a Christian university. KMU is composed of three campuses in the city of Daegu, South Korea. They are named for their locations within the city; Daemyeong, which is near the downtown area, Seongseo, which is in the western part of the city, and also Dongsan campus which includes Dongsan Medical Center.

Sports science is a discipline that studies how the healthy human body works during exercise, and how sports and physical activity promote health and performance from cellular to whole body perspectives. The study of sports science traditionally incorporates areas of physiology, psychology, anatomy, biomechanics, biochemistry, and kinesiology.

Sports medicine is a branch of medicine that deals with physical fitness and the treatment and prevention of injuries related to sports and exercise. Although most sports teams have employed team physicians for many years, it is only since the late 20th century that sports medicine emerged as a distinct field of health care. In many countries, now over 50, sports medicine is a recognized medical specialty. In the majority of countries where sports medicine is recognized and practiced, it is a physician (non-surgical) specialty, but in some, it can equally be a surgical or non-surgical medical specialty, and also a specialty field within primary care. In other contexts, the field of sports medicine encompasses the scope of both medical specialists as well as allied health practitioners who work in the field of sport, such as physiotherapists, athletic trainers, podiatrists and exercise physiologists.

The University of Colombo is a public research university located primarily in Colombo, Sri Lanka. It is the oldest institution of modern higher education in Sri Lanka. Specialised in the fields of natural, social, and applied sciences as well as mathematics, computer sciences, law, and Technology. It is ranked among the top 10 universities in South Asia.
A medical physicist is a health professional with specialist education and training in the concepts and techniques of applying physics in medicine and competent to practice independently in one or more of the subfields (specialties) of medical physics. A medical physicist plays a fundamental role in applying physics to medicine, but particularly in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. The scientific and technological progress in medical physics has led to a variety of skills that must be integrated into the role of a medical physicist in order for them to perform their job. The "medical services" provided to patients undergoing diagnostic and therapeutic treatments must, therefore, be the result of different but complementary skills. In general, the medical physicist is responsible for all scientific and technical aspects of imaging, radiation treatment, and radiation safety. It is their occupational role to ensure that medical modalities offered to patients are met with the utmost quality assurance. It is the medical physicist that manage and supervise the efforts of dosimetrists, therapists and technologists in that capacity.

The University of Kragujevac is a public university in Kragujevac, Serbia. It is the oldest and the largest higher education institution in Šumadija and Western Serbia.
The American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), headquartered in Indianapolis, Indiana, is a sports medicine and exercise science membership organization. Founded in 1954, ACSM holds conferences, publishes books and journals, and offers certification programs for personal trainers and exercise physiologists.
Sports law in the United States overlaps substantially with labor law, contract law, competition or antitrust law, and tort law. Issues like defamation and privacy rights are also integral aspects of sports law. This area of law was established as a separate and important entity only a few decades ago, coinciding with the rise of player-agents and increased media scrutiny of sports law topics.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to emergency medicine:
Surgeon Vice Admiral Sir John Stuart Pepys Rawlins, was a Royal Navy officer and pioneer in the field of diving medicine.
Sports Medicine Australia is Australia's peak national umbrella body for sports medicine and sports science. It was established in 1963 as the Australian Sports Medicine Federation. Its current membership includes sports medicine and health professionals, sports trainers, sporting clubs and community members. Its activities cover elite sport to community grass roots sports. It has branches in each Australian state.

The International Federation for Emergency Medicine (IFEM) is an organisation promoting international emergency medicine around the world. It is a consortium of over 70 national and regional emergency medicine organisations. IFEM organises the International Conference on Emergency Medicine (ICEM).
The International Conference on Emergency Medicine (ICEM) is a biennial conference on international emergency medicine for emergency physicians. It is organised by the International Federation for Emergency Medicine.
The European Society for Emergency Medicine (EUSEM) is an organisation promoting international emergency medicine in Europe. The society was founded at the International Conference on Emergency Medicine in May 1994 in London. EUSEM brings together over 30 European national societies of emergency medicine. EUSEM hosts pan-European emergency medicine training, examinations and awards. It also publishes the European Journal of Emergency Medicine, and organises annual scientific meetings.
José Henrique Fuentes Gomes Pereira is a physician and former competitive swimmer who represented Portugal in the 1976 Olympic Games, European Championships, and World Championships. He was considered one of the best Portuguese athletes of his generation. Throughout his sports career, he set over a hundred national records. He is a physician, a European specialist in Sports Medicine, and a full Professor at the School of Human Kinetics of the University of Lisbon. As a doctor, he is one of the most reputable Portuguese specialists in Sports Medicine. He has served as a physician for various sports federations and for athletes who have won medals in European and world championships, as well as the Olympic Games. He was the Clinical Director of the National Football Teams (1990-1993) - Portuguese Football Federation, Olympic Physician at the Atlanta 1996 Summer Olympic Games, and the Clinical Director of Sporting Clube de Portugal (2000-2011). He served as the Clinical Director of the Portuguese Olympic Committee for the 2016-2020 Olympiad and was responsible for the medical mission to the 2020 Tokyo Olympic Games, and indicated for the same functions in the Olympics 2024 in Paris. He is a Fellow and Professional Member of the European College of Sport Science, the American College of Sports Medicine, and other national and international scientific and professional societies. He is a regular speaker at national and international conferences, the co-author of 6 books, and has contributed to approximately 140 educational and scientific publications. He has been an Honorary Member of the Lisbon Swimming Association since 1980 and of Sport Algés e Dafundo since 2002. In 2005, he was awarded the Municipal Merit Medal - Gold Degree - by the Municipality of Oeiras in recognition of his outstanding services to the Municipality and the country.

In sports medicine, a preparticipation physical evaluation (PPE) is a physical examination of an athlete. PPEs screen for a variety of conditions, including athletic heart syndrome and risk of sudden cardiac death. PPEs are required for athletic participation according to the laws of some jurisdictions and the rules of many sports governing bodies. PPE is known by a variety of other names, such as preparticipation evaluation, preparticipation physical examination, preparticipation screening, sports physical, sports physical exam, examination for participation in sport, and similar.







