
Friends of the Earth International (FoEI) is an international network of grassroots environmental organizations in 73 countries. About half of the member groups call themselves "Friends of the Earth" in their own languages; the others use other names. The organization was founded in 1969 in San Francisco by David Brower, Donald Aitken, and Gary Soucie after Brower's split with the Sierra Club because of the latter's positive approach to nuclear energy. The founding donation of $500,000 was provided by Robert Orville Anderson, the owner of Atlantic Richfield oil company. It became an international network of organizations in 1971 with a meeting of representatives from four countries: U.S., Sweden, the UK and France.

The International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. ICC represents over 45 million businesses in over 170 countries who have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise.
The International Council for the Exploration of the Sea is a regional fishery advisory body and the world's oldest intergovernmental science organization. ICES is headquartered in Copenhagen, Denmark, where its multinational secretariat staff of 51 provide scientific, administrative and secretarial support to the ICES community. It was established on July 22, 1902, in Copenhagen.

The minister of health is the minister of the Crown in the Canadian Cabinet who is responsible for overseeing health-focused government agencies including Health Canada and the Public Health Agency of Canada, as well as enforcing the Canada Health Act, the law governing Canada's universal health care system.

The European Science Foundation (ESF) is an association of 11 member organizations devoted to scientific research in 8 European countries. ESF is an independent, non-governmental, non-profit organisation that promotes the highest quality science in Europe. It was established in 1974 and its offices are located in Strasbourg, France (headquarters).

The European Defence Agency (EDA) is an agency of the European Union (EU) that promotes and facilitates integration between member states within the EU's Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP). The EDA is headed by the EU High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy, European Commission’s Vice President (HR/VP), and reports to the Council. The EDA was established on 12 July 2004 and is based in Brussels, Belgium, along with a number of other CSDP bodies.

The European Structural and Investment Funds are financial tools governed by a common rulebook, set up to implement the regional policy of the European Union, as well as the structural policy pillars of the Common Agricultural Policy and the Common Fisheries Policy. They aim to reduce regional disparities in income, wealth and opportunities. Europe's poorer regions receive most of the support, but all European regions are eligible for funding under the policy's various funds and programmes. The current framework is set for a period of seven years, from 2021 to 2027.
The International Arctic Science Committee (IASC) is a non-governmental, international scientific organization. IASC was founded in 1990 by representatives of national scientific organizations of the eight Arctic countries - Canada, Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway, Russia, Sweden and the United States of America. The Founding Articles of IASC were signed in Resolute Bay, Canada.
The National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) is a UK-wide partnership between cancer research funders, which promotes collaboration in cancer research. Its member organizations work together to maximize the value and benefit of cancer research for the benefit of patients and the public. Rather than replace or duplicate any of the functions of its members, it seeks to add value through joint planning, coordination and collaboration.
The National Postdoctoral Association (NPA) is a nonprofit, 501(c)3 educational organization in the United States that is dedicated to enhancing the quality of the postdoctoral experience for all participants. Since its founding in 2003, more than 200 institutions have adopted portions of the NPA's Recommended Postdoctoral Policies and Practices. Today, the NPA has 240 organizational members, whose research efforts are supported by 70,000 postdocs.
The United Nations Sustainable Development Group (UNSDG), previously the United Nations Development Group (UNDG), is a consortium of 36 United Nations funds, programmes, specialized agencies, departments and offices that play a role in development. It was created by the Secretary-General of the United Nations in order to improve the effectiveness of United Nations development activities at the country level.
The European Travel Commission (ETC) is an association of national tourism organisations (NTOs) based in Brussels. It was created in 1948 to promote Europe as a tourist destination to long-haul markets outside of Europe; initially the US, then Canada, Latin America, and Asia-Pacific later on. The ETC currently has 35 member NTOs and 12 associate members from the private industry. The association aims to raise awareness of the importance of tourism among national European authorities and the general public through sharing best practices and cooperation in market intelligence and promotion.

The European Public Health Alliance (EPHA) is a European non-profit association registered and headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. Its membership consists of 89 non-profit organisations active in public health in 21 European countries.

The Economic Research Institute for ASEAN and East Asia or ERIA is an international organization established in Jakarta, Indonesia in 2008 by a formal agreement among Leaders of 16 countries in the East Asian region to conduct research activities and make policy recommendations for further economic integration in the East Asia. ERIA works very closely with both the ASEAN Secretariat and 16 Research Institutes to undertake and disseminate policy research under the three pillars, namely “Deepening Economic Integration”, ”Narrowing Development Gaps”, and “Sustainable Development” and provide analytical policy recommendations to Leaders and Ministers at their regional meetings. ERIA provides intellectual contributions to East Asian Community building and serves as a Sherpa international organization. ERIA Ranks 9th among the world's "Top International Economics Think Tanks" according to the 2020 Global Go To Think Tanks Index Report conducted by the University of Pennsylvania.
The IEEE Industry Standards and Technology Organization (ISTO) is a 501(c)(6) non profitable federation of industry alliances, consortia, and trade groups. Formed in 1999, ISTO has an affiliation with the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers - a separate legal and autonomous entity incorporated in the State of Delaware, USA.
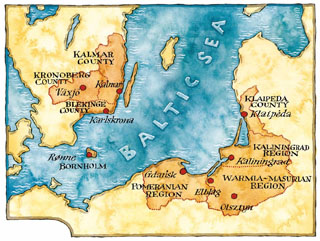
The Euroregion Baltic (ERB) refers to a cross-border Euroregion in the south-east of the Baltic Sea Region, consisting of eight regions of Denmark, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, and Sweden. On 2 March 2022, the ERB's Executive Board suspended Russia's membership, in response to Russia's invasion of Ukraine.

The Arctic policy of the United States is the foreign policy of the United States in regard to the Arctic region. In addition, the United States' domestic policy toward Alaska is part of its Arctic policy.

Common Language Resources and Technology Infrastructure is a European Research Infrastructure Consortium founded in 2012. It comprises national consortia in and outside the European Union, consisting of institutes such as universities, research centres, libraries and public archives. The goal of the consortium is providing access to digital language data collections, to digital tools, and training material for researchers to work with the language resources.
The North Pacific Marine Science Organization, also called PICES, is an intergovernmental organization that promotes and coordinates marine scientific research in the North Pacific Ocean and provides a mechanism for information and data exchange among scientists in its member countries.

Western Indian Ocean Marine Science Association (WIOMSA) is a regional professional, non-governmental, non-profit, membership organization, registered in Zanzibar, Tanzania. The organization is dedicated to promoting the educational, scientific and technological development of all aspects of marine sciences throughout the region of Western Indian Ocean (Somalia, Kenya, Tanzania, Mozambique, South Africa, Comoros, Madagascar, Seychelles, Mauritius, Réunion (France)), with a view toward sustaining the use and conservation of its marine resources. The association has about 1000 individual members as well as about 50 institutional members from within and outside the region.











