
A pollutant or novel entity is a substance or energy introduced into the environment that has undesired effects, or adversely affects the usefulness of a resource. These can be both naturally forming or anthropogenic in origin. Pollutants result in environmental pollution or become public health concerns when they reach a concentration high enough to have significant negative impacts.
The UNECE Convention on Access to Information, Public Participation in Decision-making and Access to Justice in Environmental Matters, usually known as the Aarhus Convention, was signed on 25 June 1998 in the Danish city of Aarhus. It entered into force on 30 October 2001. As of March 2014, it had 47 parties—46 states and the European Union. All of the ratifying states are in Europe and Central Asia. The EU has begun applying Aarhus-type principles in its legislation, notably the Water Framework Directive. Liechtenstein and Monaco have signed the convention but have not ratified it.
The National Emission Standards for Hazardous Air Pollutants (NESHAP) are air pollution standards issued by the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The standards, authorized by the Clean Air Act, are for pollutants not covered by the National Ambient Air Quality Standards (NAAQS) that may cause an increase in fatalities or in serious, irreversible, or incapacitating illness.
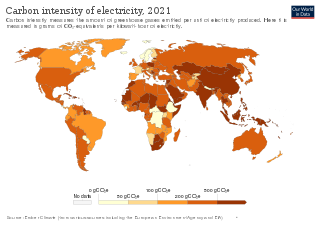
An emission intensity is the emission rate of a given pollutant relative to the intensity of a specific activity, or an industrial production process; for example grams of carbon dioxide released per megajoule of energy produced, or the ratio of greenhouse gas emissions produced to gross domestic product (GDP). Emission intensities are used to derive estimates of air pollutant or greenhouse gas emissions based on the amount of fuel combusted, the number of animals in animal husbandry, on industrial production levels, distances traveled or similar activity data. Emission intensities may also be used to compare the environmental impact of different fuels or activities. In some case the related terms emission factor and carbon intensity are used interchangeably. The jargon used can be different, for different fields/industrial sectors; normally the term "carbon" excludes other pollutants, such as particulate emissions. One commonly used figure is carbon intensity per kilowatt-hour (CIPK), which is used to compare emissions from different sources of electrical power.
The best available technology or best available techniques (BAT) is the technology approved by legislators or regulators for meeting output standards for a particular process, such as pollution abatement. Similar terms are best practicable means or best practicable environmental option. BAT is a moving target on practices, since developing societal values and advancing techniques may change what is currently regarded as "reasonably achievable", "best practicable" and "best available".

The European Union Emissions Trading System is a "cap and trade" scheme where a limit is placed on the right to emit specified pollutants over an area and companies can trade emission rights within that area. It covers around 45% of the EUs greenhouse gas emissions.
A driving cycle is a series of data points representing the speed of a vehicle versus time.
The Commission for Environmental Cooperation was established by Canada, Mexico, and the United States to implement the North American Agreement on Environmental Cooperation (NAAEC), the environmental side accord to the North American Free Trade Agreement. The CEC's mission is to facilitate cooperation and public participation to foster conservation, protection and enhancement of the North American environment for the benefit of present and future generations, in the context of increasing economic, trade and social links among Canada, Mexico and the United States.
The National Pollutant Inventory (NPI) is a database of Australian pollution emissions managed by the Australian Commonwealth, State and Territory Governments. A condensed version of the information collected is available to the public via the NPI website www.npi.gov.au.

Turkey hosts more than three thousand endemic plant species, has high diversity of other taxa, and is almost entirely covered by three of the world's thirty-five biodiversity hotspots. Although some environmental pressures have been decoupled from economic growth the environment still faces many threats, such as coal and diesel fuel emitting greenhouse gases and deadly fine particulate air pollution. As of 2019 there is no fine particulate limit and coal in Turkey is subsidized. Some say the country is a pollution haven.
An emission inventory is an accounting of the amount of pollutants discharged into the atmosphere. An emission inventory usually contains the total emissions for one or more specific greenhouse gases or air pollutants, originating from all source categories in a certain geographical area and within a specified time span, usually a specific year.
EPER may refer to:

Although the European Union has legislated, set targets, and negotiated internationally in the area of energy policy for many years, and evolved out of the European Coal and Steel Community, the concept of introducing a mandatory common European Union energy policy was only approved at the meeting of the European Council on October 27, 2005 in London. Following this the first policy proposals, Energy for a Changing World, were published by the European Commission, on January 10, 2007. The most well known energy policy objectives in the EU are 20/20/20 objectives, binding for all EU Member States. The EU is planning to increase the share of renewable energy in its final energy use to 20%, reduce greenhouse gases by 20% and increase energy efficiency by 20%.
High production volume chemicals are produced or imported into the United States in quantities of 1 million pounds or 500 tons per year. In OECD countries, HPV chemicals are defined as being produced at levels greater than 1,000 metric tons per producer/importer per year in at least one member country/region. A list of HPV chemicals serves as an overall priority list, from which chemicals are selected to gather data for a screening information dataset (SIDS), for testing and for initial hazard assessment.
The Registro de Emisiones y Transferencia de Contaminantes (RETC) is Mexico's Pollutant Release and Transfer Register (PRTR), similar to Canada's National Pollutant Release Inventory and the US Toxics Release Inventory.
A pollutant release and transfer register (PRTR) is a system for collecting and disseminating information about environmental releases and transfers of hazardous substances from industrial and other facilities.
Environmental issue in the European Union include the environmental issues identified by the European Union as well as its constituent states. The European Union has several federal bodies which create policy and practice across the constituent states.

The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade. It is a forum whose member countries describe themselves as committed to democracy and the market economy, providing a platform to compare policy experiences, seek answers to common problems, identify good practices, and coordinate domestic and international policies of its members.
The Worldwide harmonized Light vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP) is a global standard for determining the levels of pollutants, CO2 emissions and fuel consumption of traditional and hybrid cars, as well as the range of fully electric vehicles.
The Sevilla process is a participatory stakeholder process to establish environmental standards in the European Union. It comprises a structured exchange of information between EU Member States, industry, environmental non-governmental organizations, and the European Commission to draw up and review Best Available Techniques (BAT) reference documents, pursuant to Article 13(1) of the Industrial Emissions Directive 2010/75/EU.