
EU Directive 92/75/EC (1992) established an energy consumption labelling scheme. The directive was implemented by several other directives thus most white goods, light bulb packaging and cars must have an EU Energy Label clearly displayed when offered for sale or rent. The energy efficiency of the appliance is rated in terms of a set of energy efficiency classes from A to G on the label, A being the most energy efficient, G the least efficient. The labels also give other useful information to the customer as they choose between various models. The information should also be given in catalogues and included by internet retailers on their websites.

The presence of the logo on commercial products indicates that the manufacturer or importer affirms the goods' conformity with European health, safety, and environmental protection standards. It is not a quality indicator or a certification mark. The CE marking is required for goods sold in the European Economic Area (EEA); goods sold elsewhere may also carry the mark.
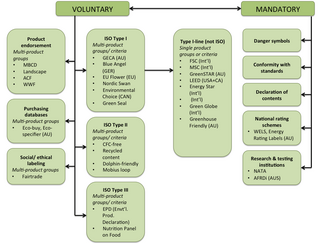
Ecolabels and Green Stickers are labeling systems for food and consumer products. The use of ecolabels is voluntary, whereas green stickers are mandated by law; for example, in North America major appliances and automobiles use Energy Star. They are a form of sustainability measurement directed at consumers, intended to make it easy to take environmental concerns into account when shopping. Some labels quantify pollution or energy consumption by way of index scores or units of measurement, while others assert compliance with a set of practices or minimum requirements for sustainability or reduction of harm to the environment. Many ecolabels are focused on minimising the negative ecological impacts of primary production or resource extraction in a given sector or commodity through a set of good practices that are captured in a sustainability standard. Through a verification process, usually referred to as "certification", a farm, forest, fishery, or mine can show that it complies with a standard and earn the right to sell its products as certified through the supply chain, often resulting in a consumer-facing ecolabel.
Type approval or certificate of conformity is granted to a product that meets a minimum set of regulatory, technical and safety requirements. Generally, type approval is required before a product is allowed to be sold in a particular country, so the requirements for a given product will vary around the world. Processes and certifications known as type approval in English are often called homologation, or some cognate expression, in other European languages.
European Standards, sometimes called Euronorm, are technical standards which have been ratified by one of the three European Standards Organizations (ESO): European Committee for Standardization (CEN), European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization (CENELEC), or European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI). All ENs are designed and created by all standards organizations and interested parties through a transparent, open, and consensual process.

A circulator pump or circulating pump is a specific type of pump used to circulate gases, liquids, or slurries in a closed circuit with small elevation changes. They are commonly found circulating water in a hydronic heating or cooling system. They are specialized in providing a large flow rate rather than providing much head, as they are supposed to only overcome the friction of a piping system, as opposed to a regular centrifugal pump which may need to lift a fluid significantly.

The Capital Requirements Directives (CRD) for the financial services industry have introduced a supervisory framework in the European Union which reflects the Basel II and Basel III rules on capital measurement and capital standards.

The Medical Device Directive—Council Directive 93/42/EEC of 14 June 1993 concerning medical devices—is intended to harmonise the laws relating to medical devices within the European Union. The MD Directive is a 'New Approach' Directive and consequently in order for a manufacturer to legally place a medical device on the European market the requirements of the MD Directive have to be met. Manufacturers' products meeting 'harmonised standards' have a presumption of conformity to the Directive. Products conforming with the MD Directive must have a CE mark applied. The Directive was most recently reviewed and amended by the 2007/47/EC and a number of changes were made. Compliance with the revised directive became mandatory on 21 March 2010.
The End of Life Vehicles Directive is a Directive of the European Union addressing the end of life for automotive products. Every year, motor vehicles which have reached the end of their useful lives create between 8 and 9 million tonnes of waste in the European Union. In 1997, the European Commission adopted a Proposal for a Directive to tackle this problem.
PNEUROP is the European Association of manufacturers of compressors, vacuum pumps, pneumatic tools and allied equipment, represented by their national associations.
Premium efficiency, when used in reference to specific types of Electric Motors, is a class of motor efficiency.
Profluid is the French association of manufacturers of pumps and mixers, compressors and valves.
The Ecodesign Directive of the European Union establishes a framework to set mandatory ecological requirements for energy-using and energy-related products sold in all 27 member states. Its scope currently covers more than 40 product groups, which are responsible for around 40% of all EU greenhouse gas emissions.
IEC 60034 is an international standard of the International Electrotechnical Commission for rotating electrical machinery.
The Comité Européen de l'Industrie de la Robinetterie, mostly known as the CEIR or the European Association for the Taps and Valves Industry, is the European trade association for the taps and valves industry.
In Europe, the seasonal efficiency of refrigeration equipment, chillers and air conditioners is often rated by the European seasonal energy efficiency ratio (ESEER) which is controlled (among others) by the Eurovent Certification Company. A similar standard in the United States is the integrated energy efficiency ratio (IEER).
The European Materials Handling Federation, is the association representing material handling, lifting and storage equipment manufacturers in Europe.
Energy-related products (ErP) are products that use energy, or that do not use energy but have an indirect impact on energy consumption, such as water using devices, building insulation products, windows, etc. Compared to ErP, energy-using products (EuP) are products which are dependent on energy input . All ErP and EuP are subject to energy efficiency requirements.

A high efficiency glandless circulating pump is a component of a heating and air conditioning system that allows the system to perform with increased efficiency while significantly reducing the system's electrical usage.
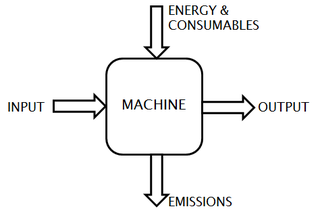
Ecomechatronics is an engineering approach to developing and applying mechatronical technology in order to reduce the ecological impact and total cost of ownership of machines. It builds upon the integrative approach of mechatronics, but not with the aim of only improving the functionality of a machine. Mechatronics is the multidisciplinary field of science and engineering that merges mechanics, electronics, control theory, and computer science to improve and optimize product design and manufacturing. In ecomechatronics, additionally, functionality should go hand in hand with an efficient use and limited impact on resources. Machine improvements are targeted in 3 key areas: energy efficiency, performance and user comfort.
 FMMI Fachverband MASCHINEN & METALLWAREN Industrie
FMMI Fachverband MASCHINEN & METALLWAREN Industrie Agoria
Agoria  Czech Pump Manufacturers' Association - CPMA
Czech Pump Manufacturers' Association - CPMA Association of Danish Pump Manufacturers
Association of Danish Pump Manufacturers VDMA - Fachverband Pumpen + Systeme
VDMA - Fachverband Pumpen + Systeme The Federation of Finnish Technology Industries
The Federation of Finnish Technology Industries Profluid - Association française des pompes et agitateurs, des compresseurs et de la robinetterie
Profluid - Association française des pompes et agitateurs, des compresseurs et de la robinetterie Union of Greek Metal Industries
Union of Greek Metal Industries ASSOPOMPE
ASSOPOMPE Holland Pomp Groep
Holland Pomp Groep PL STOWARZYSZENIE PRODUCENTÓW POMP
PL STOWARZYSZENIE PRODUCENTÓW POMP RO APPR
RO APPR RU Russian Pump Manufacturers' Association - RPMA
RU Russian Pump Manufacturers' Association - RPMA ES Asociacion Espanola de Fabricantes de Bombas para Fluidos
ES Asociacion Espanola de Fabricantes de Bombas para Fluidos SWEPUMP The Swedish Pump Supplier’s Association
SWEPUMP The Swedish Pump Supplier’s Association The Swiss Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Industries
The Swiss Mechanical and Electrical Engineering Industries POMSAD - Türk Pompa ve Vana Sanayicileri Derneği (Turkish Pump & Valve Manufacturers' Association)
POMSAD - Türk Pompa ve Vana Sanayicileri Derneği (Turkish Pump & Valve Manufacturers' Association) The British Pump Manufacturers' Association (BPMA)
The British Pump Manufacturers' Association (BPMA)





