The kidneys are two bean-shaped organs found in vertebrates. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about 11 centimetres (4.3 in) in length. They receive blood from the paired renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the bladder.
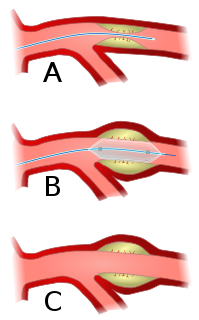
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty and percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA), is a minimally invasive, endovascular procedure to widen narrowed or obstructed arteries or veins, typically to treat arterial atherosclerosis. A deflated balloon attached to a catheter is passed over a guide-wire into the narrowed vessel and then inflated to a fixed size. The balloon forces expansion of the blood vessel and the surrounding muscular wall, allowing an improved blood flow. A stent may be inserted at the time of ballooning to ensure the vessel remains open, and the balloon is then deflated and withdrawn. Angioplasty has come to include all manner of vascular interventions that are typically performed percutaneously.
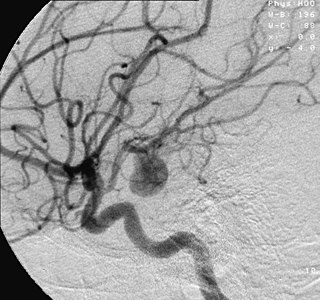
An aneurysm is an outward bulging, likened to a bubble or balloon, caused by a localized, abnormal, weak spot on a blood vessel wall. Aneurysms are a result of a weakened blood vessel wall, and may be a result of a hereditary condition or an acquired disease. Aneurysms can also be a nidus for clot formation (thrombosis) and embolization. The word is from Greek: ἀνεύρυσμα, aneurysma, "dilation", from ἀνευρύνειν, aneurynein, "to dilate". As an aneurysm increases in size, the risk of rupture increases, leading to uncontrolled bleeding. Although they may occur in any blood vessel, particularly lethal examples include aneurysms of the Circle of Willis in the brain, aortic aneurysms affecting the thoracic aorta, and abdominal aortic aneurysms. Aneurysms can arise in the heart itself following a heart attack, including both ventricular and atrial septal aneurysms.
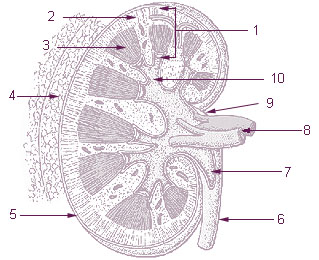
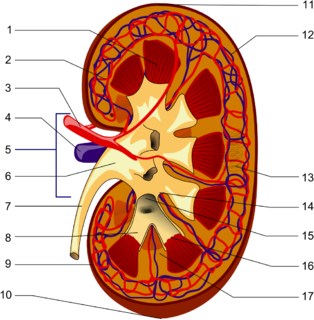
The renal medulla is the innermost part of the kidney. The renal medulla is split up into a number of sections, known as the renal pyramids. Blood enters into the kidney via the renal artery, which then splits up to form the interlobar arteries. The interlobar arteries each in turn branch into arcuate arteries, which in turn branch to form interlobular arteries, and these finally reach the glomeruli. At the glomerulus the blood reaches a highly disfavourable pressure gradient and a large exchange surface area, which forces the serum portion of the blood out of the vessel and into the renal tubules. Flow continues through the renal tubules, including the proximal tubule, the Loop of Henle, through the distal tubule and finally leaves the kidney by means of the collecting duct, leading to the renal pelvis, the dilated portion of the ureter.

The abdominal aorta is the largest artery in the abdominal cavity. As part of the aorta, it is a direct continuation of the descending aorta.
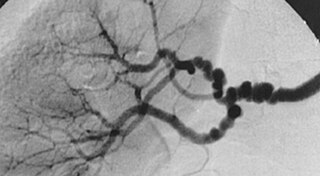
Renal artery stenosis is the narrowing of one of the renal arteries, most often caused by atherosclerosis or fibromuscular dysplasia. This narrowing of the renal artery can impede blood flow to the target kidney, resulting in renovascular hypertension – a secondary type of high blood pressure. Possible complications of renal artery stenosis are chronic kidney disease and coronary artery disease.

Microsurgery is a general term for surgery requiring an operating microscope. The most obvious developments have been procedures developed to allow anastomosis of successively smaller blood vessels and nerves which have allowed transfer of tissue from one part of the body to another and re-attachment of severed parts. Microsurgical techniques are utilized by several specialties today, such as: general surgery, ophthalmology, orthopedic surgery, gynecological surgery, otolaryngology, neurosurgery, oral and maxillofacial surgery, plastic surgery, podiatric surgery and pediatric surgery.

Renovascular hypertension is a condition in which high blood pressure is caused by the kidneys' hormonal response to narrowing of the arteries supplying the kidneys. When functioning properly this hormonal axis regulates blood pressure. Due to low local blood flow, the kidneys mistakenly increase blood pressure of the entire circulatory system. It is a form of secondary hypertension - a form of hypertension whose cause is identifiable.
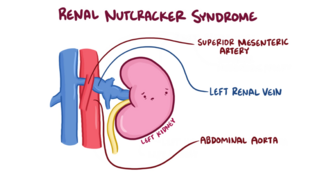
The nutcracker syndrome (NCS) results most commonly from the compression of the left renal vein (LRV) between the abdominal aorta (AA) and superior mesenteric artery (SMA), although other variants exist. The name derives from the fact that, in the sagittal plane and/or transverse plane, the SMA and AA appear to be a nutcracker crushing a nut . There is a wide spectrum of clinical presentations and diagnostic criteria are not well defined, which frequently results in delayed or incorrect diagnosis. This condition is not to be confused with superior mesenteric artery syndrome, which is the compression of the third portion of the duodenum by the SMA and the AA.
In the physiology of the kidney, renal blood flow (RBF) is the volume of blood delivered to the kidneys per unit time. In humans, the kidneys together receive roughly 25% of cardiac output, amounting to 1.2 - 1.3 L/min in a 70-kg adult male. It passes about 94% to the cortex. RBF is closely related to renal plasma flow (RPF), which is the volume of blood plasma delivered to the kidneys per unit time.

The interlobar arteries are vessels of the renal circulation which supply the renal lobes. The interlobar arteries branch from the lobar arteries which branch from the segmental arteries, from the renal artery.
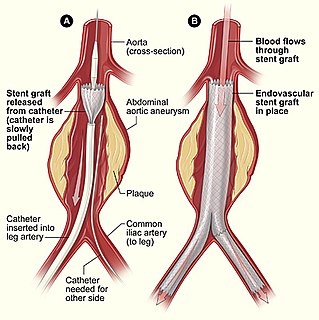
Endovascular aneurysm repair, is a type of endovascular surgery used to treat pathology of the aorta, most commonly an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). When used to treat thoracic aortic disease, the procedure is then specifically termed TEVAR for "thoracic endovascular aortic/aneurysm repair." The procedure involves the placement of an expandable stent graft within the aorta to treat aortic disease without operating directly on the aorta. In 2003, EVAR surpassed open aortic surgery as the most common technique for repair of AAA, and in 2010, EVAR accounted for 78% of all intact AAA repair in the United States.

Loin pain hematuria syndrome (LPHS) is the combination of debilitating unilateral or bilateral flank pain and microscopic or macroscopic amounts of blood in the urine that is otherwise unexplained.
Renal stem cells are self-renewing, multipotent stem cells which are able to give rise to all the cell types of the kidney. It is involved in the homeostasis and repair of the kidney, and holds therapeutic potential for treatment of kidney failure.
Retrograde perfusion (retroperfusion) is an artificial method of providing blood supply to an organ by delivering oxygenated blood through the veins. It may be performed during surgery that interrupts the normal arterial supply of blood to that organ.
Senning procedure is an atrial switch heart operation performed to treat transposition of the great arteries. It is named after its inventor, the Swedish cardiac surgeon Åke Senning (1915–2000), also known for implanting the first permanent cardiac pacemaker in 1958.
Nerve allotransplantation is the transplantation of a nerve to a receiver from a donor of the same species. For example, nerve tissue is transplanted from one person to another. Allotransplantation is a commonly used type of transplantation of which nerve repair is one specific aspect.

Open aortic surgery (OAS), also known as open aortic repair (OAR), describes a technique whereby an abdominal or retroperitoneal surgical incision is used to visualize and control the aorta for purposes of treatment. OAS is used to treat aneurysms of the abdominal and thoracic aorta, aortic dissection, acute aortic syndrome, and aortic ruptures. Aortobifemoral bypass is also used to treat atherosclerotic disease of the abdominal aorta below the level of the renal arteries. In 2003, OAS was surpassed by endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) as the most common technique for repairing abdominal aortic aneurysms in the United States. In OAS for abdominal aortic aneurysm, the aneurysmal portion of the aorta is replaced with a graft, usually made of dacron or PTFE.