Educational psychology is the branch of psychology concerned with the scientific study of human learning. The study of learning processes, from both cognitive and behavioral perspectives, allows researchers to understand individual differences in intelligence, cognitive development, affect, motivation, self-regulation, and self-concept, as well as their role in learning. The field of educational psychology relies heavily on quantitative methods, including testing and measurement, to enhance educational activities related to instructional design, classroom management, and assessment, which serve to facilitate learning processes in various educational settings across the lifespan.
A teaching method is a set of principles and methods used by teachers to enable student learning. These strategies are determined partly by the subject matter to be taught, partly by the relative expertise of the learners, and partly by constraints caused by the learning environment. For a particular teaching method to be appropriate and efficient it has to take into account the learner, the nature of the subject matter, and the type of learning it is supposed to bring about.
Science education is the teaching and learning of science to school children, college students, or adults within the general public. The field of science education includes work in science content, science process, some social science, and some teaching pedagogy. The standards for science education provide expectations for the development of understanding for students through the entire course of their K-12 education and beyond. The traditional subjects included in the standards are physical, life, earth, space, and human sciences.

Carl Edwin Wieman is an American physicist and educationist at Stanford University, and currently the A. D. White Professor at Large at Cornell University. In 1995, while at the University of Colorado Boulder, he and Eric Allin Cornell produced the first true Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) and, in 2001, they and Wolfgang Ketterle were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Wieman currently holds a joint appointment as Professor of Physics and Professor in the Stanford Graduate School of Education, as well as the DRC Professor in the Stanford University School of Engineering. In 2020, Wieman was awarded the Yidan Prize in Education Research for "his contribution in developing new techniques and tools in STEM education".
In psychology, cognitivism is a theoretical framework for understanding the mind that gained credence in the 1950s. The movement was a response to behaviorism, which cognitivists said neglected to explain cognition. Cognitive psychology derived its name from the Latin cognoscere, referring to knowing and information, thus cognitive psychology is an information-processing psychology derived in part from earlier traditions of the investigation of thought and problem solving.

In contemporary education, mathematics education—known in Europe as the didactics or pedagogy of mathematics—is the practice of teaching, learning, and carrying out scholarly research into the transfer of mathematical knowledge.
Principles and Standards for School Mathematics (PSSM) are guidelines produced by the National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) in 2000, setting forth recommendations for mathematics educators. They form a national vision for preschool through twelfth grade mathematics education in the US and Canada. It is the primary model for standards-based mathematics.
Founded in 1920, The National Council of Teachers of Mathematics (NCTM) is a professional organization for schoolteachers of mathematics in the United States. One of its goals is to improve the standards of mathematics in education. NCTM holds annual national and regional conferences for teachers and publishes five journals.

Project-based learning is a teaching method that involves a dynamic classroom approach in which it is believed that students acquire a deeper knowledge through active exploration of real-world challenges and problems. Students learn about a subject by working for an extended period of time to investigate and respond to a complex question, challenge, or problem. It is a style of active learning and inquiry-based learning. Project-based learning contrasts with paper-based, rote memorization, or teacher-led instruction that presents established facts or portrays a smooth path to knowledge by instead posing questions, problems, or scenarios.
Physics education or physics teaching refers to the education methods currently used to teach physics. The occupation is called physics educator or physics teacher. Physics education research refers to an area of pedagogical research that seeks to improve those methods. Historically, physics has been taught at the high school and college level primarily by the lecture method together with laboratory exercises aimed at verifying concepts taught in the lectures. These concepts are better understood when lectures are accompanied with demonstration, hand-on experiments, and questions that require students to ponder what will happen in an experiment and why. Students who participate in active learning for example with hands-on experiments learn through self-discovery. By trial and error they learn to change their preconceptions about phenomena in physics and discover the underlying concepts. Physics education is part of the broader area of science education.
A lesson plan is a teacher's detailed description of the course of instruction or "learning trajectory" for a lesson. A daily lesson plan is developed by a teacher to guide class learning. Details will vary depending on the preference of the teacher, subject being covered, and the needs of the students. There may be requirements mandated by the school system regarding the plan. A lesson plan is the teacher's guide for running a particular lesson, and it includes the goal, how the goal will be reached and a way of measuring how well the goal was reached.

Discovery learning is a technique of inquiry-based learning and is considered a constructivist based approach to education. It is also referred to as problem-based learning, experiential learning and 21st century learning. It is supported by the work of learning theorists and psychologists Jean Piaget, Jerome Bruner, and Seymour Papert.

Scientific misconceptions are commonly held beliefs about science that have no basis in actual scientific fact. Scientific misconceptions can also refer to preconceived notions based on religious and/or cultural influences. Many scientific misconceptions occur because of faulty teaching styles and the sometimes distancing nature of true scientific texts. Because students' prior knowledge and misconceptions are important factors for learning science, science teachers should be able to identify and address these conceptions.
Informal education is a general term for education that can occur outside of a traditional lecture or school based learning systems. The term even include customized-learning based on individual student interests within a curriculum inside a regular classroom, but is not limited to that setting. It could work through conversation, and the exploration and enlargement of experience. Sometimes there is a clear objective link to some broader plan, but not always. The goal is to provide learners with the tools they need to eventually reach more complex material. It can refer to various forms of alternative education, such as unschooling or homeschooling, autodidacticism (self-teaching), and youth work.
Inquiry-based learning is a form of active learning that starts by posing questions, problems or scenarios. It contrasts with traditional education, which generally relies on the teacher presenting facts and their knowledge about the subject. Inquiry-based learning is often assisted by a facilitator rather than a lecturer. Inquirers will identify and research issues and questions to develop knowledge or solutions. Inquiry-based learning includes problem-based learning, and is generally used in small-scale investigations and projects, as well as research. The inquiry-based instruction is principally very closely related to the development and practice of thinking and problem-solving skills.
Cognitive acceleration or CA is an approach to teaching designed to develop students' thinking ability, developed by Michael Shayer and Philip Adey from 1981 at King's College London. The approach builds on work by Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky and takes a constructivist approach.

Rolf Reber is a professor of psychology at the University of Oslo.
One of the most visible approaches to peer learning comes out of cognitive psychology, and is applied within a "mainstream" educational framework: "Peer learning is an educational practice in which students interact with other students to attain educational goals." Other authors including David Boud describe peer learning as a way of moving beyond independent to interdependent or mutual learning among peers. In this context, it can be compared to the practices that go by the name cooperative learning. However, other contemporary views on peer learning relax the constraints, and position "peer-to-peer learning" as a mode of "learning for everyone, by everyone, about almost anything." Whether it takes place in a formal or informal learning context, in small groups or online, peer learning manifests aspects of self-organization that are mostly absent from pedagogical models of teaching and learning.
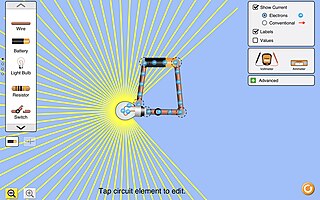
PhET Interactive Simulations, a project at the University of Colorado Boulder, is a non-profit open educational resource project that creates and hosts explorable explanations. It was founded in 2002 by Nobel Laureate Carl Wieman. PhET began with Wieman's vision to improve the way science is taught and learned. Their stated mission is "To advance science and math literacy and education worldwide through free interactive simulations."
Richard Francis Gunstone is an Australian academic and researcher. He is the Emeritus Professor of Science and Technology Education at Monash University. He has authored or co-authored 8 books along with various monographs and chapters and has published over a hundred research papers. He has coedited 6 books providing reports of contemporary research in a particular area of science education. His principle research areas include teaching, curriculum, assessment, teacher development, science, physics and engineering.






