Atomic physics is the field of physics that studies atoms as an isolated system of electrons and an atomic nucleus. Atomic physics typically refers to the study of atomic structure and the interaction between atoms. It is primarily concerned with the way in which electrons are arranged around the nucleus and the processes by which these arrangements change. This comprises ions, neutral atoms and, unless otherwise stated, it can be assumed that the term atom includes ions.

Photoluminescence is light emission from any form of matter after the absorption of photons. It is one of many forms of luminescence and is initiated by photoexcitation, hence the prefix photo-. Following excitation, various relaxation processes typically occur in which other photons are re-radiated. Time periods between absorption and emission may vary: ranging from short femtosecond-regime for emission involving free-carrier plasma in inorganic semiconductors up to milliseconds for phosphoresence processes in molecular systems; and under special circumstances delay of emission may even span to minutes or hours.

A nuclear isomer is a metastable state of an atomic nucleus, in which one or more nucleons (protons or neutrons) occupy excited state levels (higher energy levels). "Metastable" describes nuclei whose excited states have half-lives 100 to 1000 times longer than the half-lives of the excited nuclear states that decay with a "prompt" half life (ordinarily on the order of 10−12 seconds). The term "metastable" is usually restricted to isomers with half-lives of 10−9 seconds or longer. Some references recommend 5 × 10−9 seconds to distinguish the metastable half life from the normal "prompt" gamma-emission half-life. Occasionally the half-lives are far longer than this and can last minutes, hours, or years. For example, the 180m
73Ta
nuclear isomer survives so long (at least 1015 years) that it has never been observed to decay spontaneously. The half-life of a nuclear isomer can even exceed that of the ground state of the same nuclide, as shown by 180m
73Ta
as well as 186m
75Re
, 192m2
77Ir
, 210m
83Bi
, 212m
84Po
, 242m
95Am
and multiple holmium isomers.

Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluorescence, a phosphorescent material does not immediately reemit the radiation it absorbs. Instead, a phosphorescent material absorbs some of the radiation energy and reemits it for a much longer time after the radiation source is removed.

Electron excitation is the transfer of a bound electron to a more energetic, but still bound state. This can be done by photoexcitation (PE), where the electron absorbs a photon and gains all its energy or by collisional excitation (CE), where the electron receives energy from a collision with another, energetic electron. Within a semiconductor crystal lattice, thermal excitation is a process where lattice vibrations provide enough energy to transfer electrons to a higher energy band such as a more energetic sublevel or energy level. When an excited electron falls back to a state of lower energy, it undergoes electron relaxation (deexcitation). This is accompanied by the emission of a photon or by a transfer of energy to another particle. The energy released is equal to the difference in energy levels between the electron energy states.

In quantum mechanics, an excited state of a system is any quantum state of the system that has a higher energy than the ground state. Excitation refers to an increase in energy level above a chosen starting point, usually the ground state, but sometimes an already excited state. The temperature of a group of particles is indicative of the level of excitation.
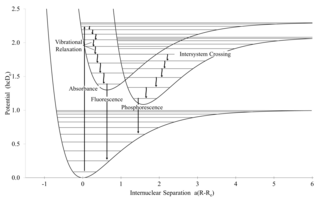
Intersystem crossing (ISC) is an isoenergetic radiationless process involving a transition between the two electronic states with different spin multiplicity.
In condensed matter physics, a quasiparticle is a concept used to describe a collective behavior of a group of particles that can be treated as if they were a single particle. Formally, quasiparticles and collective excitations are closely related phenomena that arise when a microscopically complicated system such as a solid behaves as if it contained different weakly interacting particles in vacuum.

A glow discharge is a plasma formed by the passage of electric current through a gas. It is often created by applying a voltage between two electrodes in a glass tube containing a low-pressure gas. When the voltage exceeds a value called the striking voltage, the gas ionization becomes self-sustaining, and the tube glows with a colored light. The color depends on the gas used.

Photosystems are functional and structural units of protein complexes involved in photosynthesis. Together they carry out the primary photochemistry of photosynthesis: the absorption of light and the transfer of energy and electrons. Photosystems are found in the thylakoid membranes of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria. These membranes are located inside the chloroplasts of plants and algae, and in the cytoplasmic membrane of photosynthetic bacteria. There are two kinds of photosystems: PSI and PSII.
P680, or photosystem II primary donor, is the reaction-center chlorophyll a molecular dimer associated with photosystem II in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria, and central to oxygenic photosynthesis.

Internal conversion is a transition from a higher to a lower electronic state in a molecule or atom. It is sometimes called "radiationless de-excitation", because no photons are emitted. It differs from intersystem crossing in that, while both are radiationless methods of de-excitation, the molecular spin state for internal conversion remains the same, whereas it changes for intersystem crossing. The energy of the electronically excited state is given off to vibrational modes of the molecule. The excitation energy is transformed into heat.
A photochemical logic gate is based on the photochemical intersystem crossing and molecular electronic transition between photochemically active molecules, leading to logic gates that can be produced.
X-ray Raman scattering (XRS) is non-resonant inelastic scattering of X-rays from core electrons. It is analogous to vibrational Raman scattering, which is a widely used tool in optical spectroscopy, with the difference being that the wavelengths of the exciting photons fall in the X-ray regime and the corresponding excitations are from deep core electrons.
Photoluminescence excitation is a specific type of photoluminescence and concerns the interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter. It is used in spectroscopic measurements where the frequency of the excitation light is varied, and the luminescence is monitored at the typical emission frequency of the material being studied. Peaks in the PLE spectra often represent absorption lines of the material. PLE spectroscopy is a useful method to investigate the electronic level structure of materials with low absorption due to the superior signal-to-noise ratio of the method compared to absorption measurements.
Photoelectrochemical processes are processes in photoelectrochemistry; they usually involve transforming light into other forms of energy. These processes apply to photochemistry, optically pumped lasers, sensitized solar cells, luminescence, and photochromism.
Interatomic Coulombic decay (ICD) is a general, fundamental property of atoms and molecules that have neighbors. Interatomic (intermolecular) Coulombic decay is a very efficient interatomic (intermolecular) relaxation process of an electronically excited atom or molecule embedded in an environment. Without the environment the process cannot take place. Until now it has been mainly demonstrated for atomic and molecular clusters, independently of whether they are of van-der-Waals or hydrogen bonded type.








