
Najd is the central region of Saudi Arabia, in which about a third of the country's modern population resides. It is the home of the House of Saud, from which it pursued unification with Hejaz since the time of the Emirate of Diriyah.
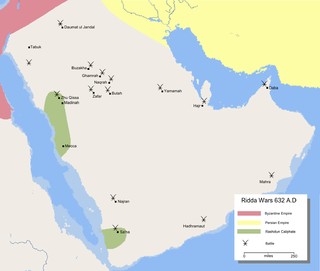
The Ridda Wars were a series of military campaigns launched by the first caliph Abu Bakr against rebellious Arabian tribes, some of which were led by rival prophet claimants. They began shortly after the death of the Islamic prophet Muhammad in 632 and concluded the next year, with all battles won by the Rashidun Caliphate.
The Muhajirun were the converts to Islam and the Islamic prophet Muhammad's advisors and relatives, who emigrated from Mecca to Medina, the event is known in Islam as the Hijra. The early Muslims from Medina are called the Ansar ("helpers").
The Ansar or Ansari are the local inhabitants of Medina who took the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his followers into their homes when they fled from Mecca during the hijra. They belonged to the tribes of Banu Khazraj and Banu Aus.
The Expedition of Qatan, was the first Raid on the Banu Asad bin Khuzaymah tribe, which occurred directly after the Battle of Hamra al-Asad in the year 4 A.H of the Islamic calendar.
The early Muslim–Meccan conflict refer to a series of raids in which the Islamic prophet Muhammad and his companions participated. The raids were generally offensive and carried out to gather intelligence or seize back the confiscated Muslim trade goods of caravans financed by the Mushrik of the Quraysh. His followers were also impoverished. The raids were intended to harm the economy and in turn the offensive capabilities of Mecca by Muhammad. The Muslims felt that the raids were justified in that the items being sold in the caravans were their own items, stolen by the Meccans when they had migrated to Medina.
The Raid on Nakhla was a raid that was initially unplanned by the companions of Muhammad, but is considered to be the first successful raid against the Meccans, since it was carried out during an espionage event, this raid took place at Nakhla, in the Hejazi region of what is now Saudi Arabia. It took place in Rajab A.H. 2. The commander was 'Abdullah ibn Jahsh al-Asadi, whom Muhammad dispatched to Nakhla as the head of 12 Emigrants with six camels.The Muslims obtained rich plunder from the raid and brought it before Muhammad in Medina. However, this sparked controversy among the people since warfare was strictly forbidden during the holy month by Pagan convention and a raid was a transgression against the agreement.
The Expedition of Abdullah ibn Unais, also known as the Assassination of Khaled bin Sufyan was the first attack against the Banu Lahyan, which took place in the month of Muharram in the year A.H. 3. It was reported that Khaled bin Sufyan Al-Hathali, considered an attack on Madinah and that he was inciting the people on Nakhla or Uranah to fight Muslims. So Muhammad sent Abdullah ibn Unais to assassinate him. After cutting off Khaled bin Sufyan's head at night, Unais brought it back to Muhammad.
The Expedition of al Raji occurred directly after the Battle of Uhud in the year AH 4 of the Islamic calendar.

The siege of Banu Qurayza took place in Dhul Qa‘dah during January of 627 CE and followed on from the Battle of the Trench.
According to Muslim traditional lore, the First Raid on Banu Thalabah took place in August, 627 AD in 4th month of, 6AH of the Islamic Calendar, under the leadership of Muhammad ibn Maslamah
The Second raid on Banu Thalabah took place in August, 627AD in 4th month of, 6AH of the Islamic calendar, under the leadership of Abu Ubaidah
Expedition of Fadak, also spelt Fidak, took place in December, 627AD, 6AH, 8th month of the Islamic Calendar
The Expedition of Uyainah bin Hisn, against the Banu Tamim tribe took place in July 630, 9AH, 1st month, of the Islamic Calendar.
The Expedition of Ukasha bin Al-Mihsan, against the tribes of Udhrah and Baliy, took place in October 630 AD, 9 AH of the Islamic Calendar.

Ukasha ibn Mihsan was one of the companions of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad, he participated in the Nakhla Raid during Muhammad's era. He also participated in the Expedition of Ukasha bin Al-Mihsan, against the tribes of Udhrah and Baliy, which took place in October 630, 9AH of the Islamic Calendar.
Banu Tha'labah was a tribe during the Islamic prophet Muhammad's era. They were involved in many military conflicts with Muhammad.
Banu Muzaina was an Arab tribe during the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. They were involved in the Expedition of Zayd ibn Harithah in September, 627 CE, 6AH of the Islamic calendar A platoon, under the leadership of Zaid bin Haritha, was sent to Al Jumum, the habitation of Banu Salim, in the same year. A group of non-muslims were captured. A woman from Banu Muzaina was also captured, and she showed them the way to the enemy's camp. The Banu Muzaina tribe was an Arab pagan tribe which later converted to Islam.
Ghalib ibn Abd Allah al-Laythi also known as Ghalib ibn Fadala al-Laythi, was an early companion and commander of the Islamic prophet Muhammad. During the prophet's lifetime, he led several expeditions against the polytheistic Bedouin tribes. He later participated in the conquest of Iraq in 634–636 and briefly as a commander in Khurasan in 668–671.
Abu Qatada al-Ansari, also known as Al-Harith ibn Rab'i, was one of the companions of Muhammad. He assisted the battles of Uhud and Hudaybiyya.