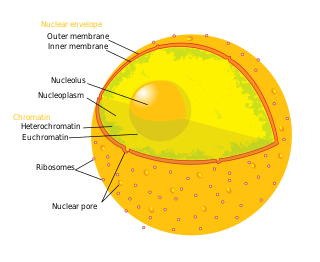
The nucleolus is the largest structure in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is best known as the site of ribosome biogenesis. Nucleoli also participate in the formation of signal recognition particles and play a role in the cell's response to stress. Nucleoli are made of proteins, DNA and RNA and form around specific chromosomal regions called nucleolar organizing regions. Malfunction of nucleoli can be the cause of several human conditions called "nucleolopathies" and the nucleolus is being investigated as a target for cancer chemotherapy.

Ribonucleic acid (RNA) is a polymeric molecule essential in various biological roles in coding, decoding, regulation and expression of genes. RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, and, along with lipids, proteins and carbohydrates, constitute the four major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Like DNA, RNA is assembled as a chain of nucleotides, but unlike DNA, RNA is found in nature as a single strand folded onto itself, rather than a paired double strand. Cellular organisms use messenger RNA (mRNA) to convey genetic information that directs synthesis of specific proteins. Many viruses encode their genetic information using an RNA genome.

RNA polymerase, abbreviated RNAP or RNApol, officially DNA-directed RNA polymerase, is an enzyme that synthesizes RNA from a DNA template. RNAP locally opens the double-stranded DNA so that one strand of the exposed nucleotides can be used as a template for the synthesis of RNA, a process called transcription. A transcription factor and its associated transcription mediator complex must be attached to a DNA binding site called a promoter region before RNAP can initiate the DNA unwinding at that position. RNAP not only initiates RNA transcription, it also guides the nucleotides into position, facilitates attachment and elongation, has intrinsic proofreading and replacement capabilities, and termination recognition capability. In eukaryotes, RNAP can build chains as long as 2.4 million nucleotides.

Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is a DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA. Ribosomes are assemblies of proteins and rRNA molecules that translate mRNA molecules to produce proteins. As shown in the figure, rDNA of eukaryotes consists of a tandem repeat of a unit segment, composed of NTS, ETS, 18S, ITS1, 5.8S, ITS2, and 28S tracts. rDNA has another gene, coding for 5S rRNA, located in the genome in most eukaryotes. 5S rDNA is also present in tandem repeats as in Drosophila. DNA regions that are repetitive often undergo recombination events. The rDNA repeats have many regulatory mechanisms that keep the DNA from undergoing mutations, thus keeping the rDNA conserved.
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript.

The last universal common ancestor (LUCA), also called the last universal ancestor (LUA), or concestor, is the most recent population of organisms from which all organisms now living on Earth have a common descent, the most recent common ancestor of all current life on Earth. LUCA is not thought to be the first life on Earth but only one of many early organisms, all of their progeny having become extinct.
In molecular biology, a hybridization probe is a fragment of DNA or RNA of variable length which can be radioactively or fluorescently labeled. It can then be used in DNA or RNA samples to detect the presence of nucleotide substances that are complementary to the sequence in the probe. The probe thereby hybridizes to single-stranded nucleic acid whose base sequence allows probe–target base pairing due to complementarity between the probe and target. The labeled probe is first denatured into single stranded DNA (ssDNA) and then hybridized to the target ssDNA or RNA immobilized on a membrane or in situ. To detect hybridization of the probe to its target sequence, the probe is tagged with a molecular marker of either radioactive or fluorescent molecules; commonly used markers are 32P or digoxigenin, which is a non-radioactive, antibody-based marker. DNA sequences or RNA transcripts that have moderate to high sequence similarity to the probe are then detected by visualizing the hybridized probe via autoradiography or other imaging techniques. Normally, either X-ray pictures are taken of the filter, or the filter is placed under UV light. Detection of sequences with moderate or high similarity depends on how stringent the hybridization conditions were applied—high stringency, such as high hybridization temperature and low salt in hybridization buffers, permits only hybridization between nucleic acid sequences that are highly similar, whereas low stringency, such as lower temperature and high salt, allows hybridization when the sequences are less similar. Hybridization probes used in DNA microarrays refer to DNA covalently attached to an inert surface, such as coated glass slides or gene chips, to which a mobile cDNA target is hybridized.

Ribosomal ribonucleic acid (rRNA) is a type of non-coding RNA which is the primary component of ribosomes, essential to all cells. rRNA is a ribozyme which carries out protein synthesis in ribosomes. Ribosomal RNA is transcribed from ribosomal DNA (rDNA) and then bound to ribosomal proteins to form small and large ribosome subunits. rRNA is the physical and mechanical actor of the ribosome that forces transfer RNA (tRNA) and messenger RNA (mRNA) to process and translate the latter into proteins. Ribosomal RNA is the predominant form of RNA found in most cells; it makes up about 80% of cellular RNA despite never being translated into proteins itself. Ribosomes are composed of approximately 60% rRNA and 40% ribosomal proteins by mass.
RNA polymerase 1 is, in higher eukaryotes, the polymerase that only transcribes ribosomal RNA, a type of RNA that accounts for over 50% of the total RNA synthesized in a cell.

In evolutionary biology, conserved sequences are identical or similar sequences in nucleic acids or proteins across species, or within a genome, or between donor and receptor taxa. Conservation indicates that a sequence has been maintained by natural selection.
Semantides are biological macromolecules that carry genetic information or a transcript thereof. Three different categories or semantides are distinguished: primary, secondary and tertiary. Primary Semantides are genes, which consist of DNA. Secondary semantides are chains of messenger RNA, which are transcribed from DNA. Tertiary semantides are polypeptides, which are translated from messenger RNA. In eukaryotic organisms, primary semantides may consist of nuclear, mitochondrial or plastid DNA. Not all primary semantides ultimately form tertiary semantides. Some primary semantides are not transcribed into mRNA and some secondary semantides are not translated into polypeptides. The complexity of semantides varies greatly. For tertiary semantides, large globular polypeptide chains are most complex while structural proteins, consisting of repeating simple sequences, are least complex. The term semantide and related terms were coined by Linus Pauling and Emile Zuckerkandl. Although semantides are the major type of data used in modern phylogenetics, the term itself is not commonly used.
Spacer DNA is a region of non-coding DNA between genes. The terms intergenic spacer (IGS) or non-transcribed spacer (NGS) are used particularly for the spacer DNA between the many tandemly repeated copies of the ribosomal RNA genes.
Preribosomal RNA (pre-rRNA) represents a small class of RNA that is copied from DNA representing the genome sequence. However the pre-rRNA cannot be used for protein production until splicing of the introns occurs, forming a new bond between the exons and resulting in mature ribosomal RNA (rRNA).

In molecular biology, the 5.8S ribosomal RNA is a non-coding RNA component of the large subunit of the eukaryotic ribosome and so plays an important role in protein translation. It is transcribed by RNA polymerase I as part of the 45S precursor that also contains 18S and 28S rRNA. Its function is thought to be in ribosome translocation. It is also known to form covalent linkage to the p53 tumour suppressor protein. 5.8S rRNA can be used as a reference gene for miRNA detection. The 5.8S ribosomal RNA is used to better understand other rRNA processes and pathways in the cell.

The 5S ribosomal RNA is an approximately 120 nucleotide-long ribosomal RNA molecule with a mass of 40 kDa. It is a structural and functional component of the large subunit of the ribosome in all domains of life, with the exception of mitochondrial ribosomes of fungi and animals. The designation 5S refers to the molecule's sedimentation velocity in an ultracentrifuge, which is measured in Svedberg units (S).

In molecular biology, the small nucleolar RNA SNORA73 belongs to the H/ACA class of small nucleolar RNAs (snoRNAs). Vertebrate U17 is intron-encoded and ranges in length from 200-230 nucleotides, longer than most snoRNAs. It is one of the most abundant snoRNAs in human cells and is essential for the cleavage of pre-rRNA within the 5' external transcribed spacer (ETS). This cleavage leads to the formation of 18S rRNA. Regions of the U17 RNA are complementary to rRNA and act as guides for RNA/RNA interactions, although these regions do not seem to be well conserved between organisms.

16S ribosomal RNA is the component of the 30S small subunit of a prokaryotic ribosome that binds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence. The genes coding for it are referred to as 16S rRNA gene and are used in reconstructing phylogenies, due to the slow rates of evolution of this region of the gene. Carl Woese and George E. Fox were two of the people who pioneered the use of 16S rRNA in phylogenetics in 1977.

60S ribosomal protein L7a is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RPL7A gene.
28S ribosomal RNA is the structural ribosomal RNA (rRNA) for the large component, or large subunit (LSU) of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. It is the eukaryotic nuclear homologue of the prokaryotic 23S and mitochondrial 16S ribosomal RNAs.
Microbial DNA barcoding is the use of meta DNA barcoding to characterize a mixture of microorganisms.













