Related Research Articles

Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are various conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, coughing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Note that food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
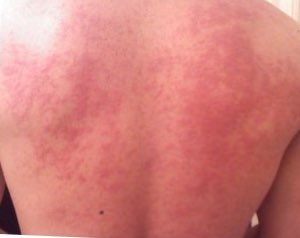
A food allergy is an abnormal immune response to food. The symptoms of the allergic reaction may range from mild to severe. They may include itchiness, swelling of the tongue, vomiting, diarrhea, hives, trouble breathing, or low blood pressure. This typically occurs within minutes to several hours of exposure. When the symptoms are severe, it is known as anaphylaxis. A food intolerance and food poisoning are separate conditions, not due to an immune response.

Latex allergy is a medical term encompassing a range of allergic reactions to the proteins present in natural rubber latex. It generally develops after repeated exposure to products containing natural rubber latex. When latex-containing medical devices or supplies come in contact with mucous membranes, the membranes may absorb latex proteins. In some susceptible people, the immune system produces antibodies that react immunologically with these antigenic proteins. Many items contain or are made from natural rubber, including shoe soles, pen grips, hot water bottles, elastic bands, rubber gloves, condoms, baby-bottle nipples, and balloons; consequently, there are many possible routes of exposure that may trigger a reaction. People with latex allergies may also have or develop allergic reactions to some fruits, such as bananas.
Oral allergy syndrome (OAS) or pollen-food allergy is a type of food allergy classified by a cluster of allergic reactions in the mouth and throat in response to eating certain fruits, nuts, and vegetables. It typically develops in adults with hay fever.
Cross-reactivity, in a general sense, is the reactivity of an observed agent which initiates reactions outside the main reaction expected. This has implications for any kind of test or assay, including diagnostic tests in medicine, and can be a cause of false positives. In immunology, the definition of cross-reactivity refers specifically to the reaction of the immune system to antigens. There can be cross-reactivity between the immune system and the antigens of two different pathogens, or between one pathogen and proteins on non-pathogens, which in some cases can be the cause of allergies.

A tree nut allergy is a hypersensitivity to dietary substances from tree nuts and edible tree seeds causing an overreaction of the immune system which may lead to severe physical symptoms. Tree nuts include almonds, Brazil nuts, cashews, chestnuts, filberts/hazelnuts, macadamia nuts, pecans, pistachios, shea nuts and walnuts.

Wheat allergy is an allergy to wheat which typically presents itself as a food allergy, but can also be a contact allergy resulting from occupational exposure. Like all allergies, wheat allergy involves immunoglobulin E and mast cell response. Typically the allergy is limited to the seed storage proteins of wheat. Some reactions are restricted to wheat proteins, while others can react across many varieties of seeds and other plant tissues. Wheat allergy is rare. Prevalence in adults was found to be 0.21% in a 2012 study in Japan.

Ovomucoid is a protein found in egg whites. It is a trypsin inhibitor with three protein domains of the Kazal domain family. The homologs from chickens and especially turkeys are best characterized. It is not related to the similarly named ovomucin, another egg white protein.
Quattromed Ltd is one of the leading biotechnology companies in Estonia providing medical diagnostics services and performing custom research programs for the biopharmaceutical industry. As of March 2009, Icosagen AS is the new business name of the former Quattromed Ltd.
Anti-gliadin antibodies are produced in response to gliadin, a prolamin found in wheat. In bread wheat it is encoded by three different alleles, AA, BB, and DD. These alleles can produce slightly different gliadins, which can cause the body to produce different antibodies. Some of these antibodies can detect proteins in specific grass taxa such as Triticeae, while others react sporadically with certain species in those taxa, or over many taxonomically defined grass tribes.
Vytex Natural Rubber Latex (NRL) is a brand of natural rubber latex produced and marketed by Vystar Corporation. Vytex NRL is an alternative material to petroleum-based synthetics and traditional, or Hevea, natural rubber latex. Protein test results show that Vytex NRL typically has 90% fewer antigenic proteins than Hevea natural rubber latex.

The Nickel Directive was a European Union directive regulating the use of nickel in jewellery and other products that come into contact with the skin. Since 1 June 2009, it has been subsumed into the REACH Regulation, specifically item 27 of Annex XVII to that regulation. Nevertheless, the term Nickel Directive is still used to refer to the restrictions on nickel usage and the prescribed test method for quantifying nickel release from products EN 1811.

Pro-hevein is a wound-induced and a lectin-like protein from Hevea brasiliensis where it is involved in the coagulation of latex.

Ara h 1 is a seed storage protein from Arachis hypogaea (peanuts). It is a heat stable 7S vicilin-like globulin with a stable trimeric form that comprises 12-16% of the total protein in peanut extracts. Ara h 1 is known because sensitization to it was found in 95% of peanut-allergic patients from North America. In spite of this high percentage, peanut-allergic patients of European populations have fewer sensitizations to Ara h 1.
Cross-reactive carbohydrate determinants (CCDs) play a role in the context of allergy diagnosis. The terms CCD or CCDs describe protein-linked carbohydrate structures responsible for the phenomenon of cross-reactivity of sera from allergic patients towards a wide range of allergens from plants and insects. In serum-based allergy diagnosis, antibodies of the IgE class directed against CCDs therefore give the impression of polysensitization. Anti-CCD IgE, however, does not seem to elicit clinical symptoms. Diagnostic results caused by CCDs are therefore regarded as false positives.

Fish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in fish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Fish is one of the eight common food allergens which are responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.

Shellfish allergy is among the most common food allergies. "Shellfish" is a colloquial and fisheries term for aquatic invertebrates used as food, including various species of molluscs such as clams, mussels, oysters and scallops, crustaceans such as shrimp, lobsters and crabs, and cephalopods such as squid and octopus. Shellfish allergy is an immune hypersensitivity to proteins found in shellfish. Symptoms can be either rapid or gradual in onset. The latter can take hours to days to appear. The former may include anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition which requires treatment with epinephrine. Other presentations may include atopic dermatitis or inflammation of the esophagus. Shellfish is one of the eight common food allergens, responsible for 90% of allergic reactions to foods: cow's milk, eggs, wheat, shellfish, peanuts, tree nuts, fish, and soy beans.

A food allergy to sesame seeds has prevalence estimates in the range of 0.1–0.2% of the general population, and are higher in the Middle East and other countries where sesame seeds are used in traditional foods. Reporting of sesame seed allergy has increased in the 21st century, either due to a true increase from exposure to more sesame foods or due to an increase in awareness. Increasing sesame allergy rates have induced more countries to regulate food labels to identify sesame ingredients in products and the potential for allergy. In the United States, sesame became the ninth food allergen with mandatory labeling, effective 1 January 2023.
References
Cited references
- ↑ Koh D, Ng V, Leow YH, Goh CL (2005). "A study of natural rubber latex allergens in gloves used by healthcare workers in Singapore". Br. J. Dermatol. 153 (5): 954–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06820.x . PMID 16225605. S2CID 32823071.
- ↑ FITkit broschure [ permanent dead link ] on Icosagen AS homepage. Retrieved 13 May 2009, (PDF file; 1.07 Mb)
General references
- Turjanmaa, K. (2001). "Diagnosis of latex allergy". Allergy. 56 (9): 810–812. doi: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.2001.00011.x-i1 . PMID 11551245.
- Alenius, H.; Turjanmaa, K.; Palosuo, T. (2002). "Natural rubber latex allergy". Occupational and Environmental Medicine. 59 (6): 419–424. doi:10.1136/oem.59.6.419. PMC 1740299 . PMID 12040121.
- Palosuo, T.; Reinikka-Railo, H.; Kautiainen, H.; Alenius, H.; Kalkkinen, N.; Kulomaa, M.; Reunala, T.; Turjanmaa, K. (2007). "Latex allergy: The sum quantity of four major allergens shows the allergenic potential of medical gloves". Allergy. 62 (7): 781–786. doi:10.1111/j.1398-9995.2007.01411.x. PMID 17573726. S2CID 20336110.