
Guam is a U.S. territory in the western Pacific Ocean, at the boundary of the Philippine Sea. It is the southernmost and largest member of the Mariana Islands archipelago, which is itself the northernmost group of islands in Micronesia. The closest political entity is the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), another U.S. territory. Guam shares maritime boundaries with CNMI to the north and the Federated States of Micronesia to the south. It is located approximately one quarter of the way from the Philippines to Hawaii. Its location and size make it strategically important. It is the only island with both a protected harbor and land for multiple airports between Asia and Hawaii, on an east–west axis, and between Papua New Guinea and Japan, on a north–south axis.

Hågat is a village in the United States territory of Guam. It is located south of Apra Harbor on the island's western shore. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census.

Asan-Maina is a village located on the western shore of the United States territory of Guam. The municipality combines the names of the coastal community of Asan with Maina, a community along the slopes of the Fonte River valley to the east. Asan was the northern landing site for United States Marines during Guam's liberation from the Japanese during World War II. Asan Beach Park is part of the War in the Pacific National Historic Park. The third community comprising Asan-Maina is Nimitz Hill Annex in the hills above Asan and Maina, which is the location of the Joint Region Marianas headquarters. Asan-Maina is located in the Luchan (Western) District.
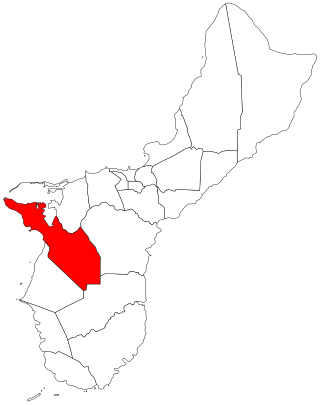
Sånta Rita-Sumai, formerly Santa Rita and encompassing the former municipality of Sumay, is a village located on the southwest coast of the United States territory of Guam with hills overlooking Apra Harbor. According to the 2020 census it has a population of 6,470, which is up slightly from 6,084 in 2010 but down from 11,857 in 1990. Santa Rita is the newest village in Guam, having been established after the Second World War.

Piti is a village located on the central west coast of the United States territory of Guam. It contains northern and eastern coastlines of Apra Harbor, including Cabras Island, which has the commercial Port of Guam and the island's largest power plants. Piti was a pre-Spanish CHamoru village and, after Spanish colonization, became the primary port town on Guam. The town was largely destroyed during the 1944 liberation of Guam and the population relocated during the wartime construction of Apra Harbor.

Humåtak is a village on the southwestern coast of the United States territory of Guam. The month of March in the Chamorro language is "Umatalaf," or "to catch guatafi," which is believed to be the root word of Umatac. The village's population has decreased since the island's 2010 census, and it is by far the least populated village on the island.
The area code 671 is the local telephone area code of the United States territory of Guam. It was created with the beginning of permissive dialing on July 1, 1997, replacing Guam's previous International Telecommunication Union country code 671 at the end of permissive dialing on July 1, 1998.

Guam Public Library System is the public library system of the United States territory of Guam. The main library is the Nieves M. Flores Memorial Library at 254 Martyr Street in the village of Hagåtña.
Fouha Point, also known as Fouha Rock or Creation Point, is a National Natural Landmark on the United States territory of Guam. A natural rock formation, the point rises to some 150 feet (46 m) above the waters of Fouha Bay, close to the village of Umatac. The point was designated a National Natural Landmark in 1972. According to Chamorro legend, the rock is the resting place of the goddess Fu’una who, with her brother Puntan, created the world.
Lockwood Terrace is a populated place on the island of Guam with an elevation of 22 metres above sea level. It is located in the village of Santa Rita, between Apra Harbor and Agat Bay on the Orote Peninsula.

The Orote Peninsula is a four kilometer-long peninsula jutting from the west coast of the United States territory of Guam. A major geologic feature of the island, it forms the southern coast of Apra Harbor and the northern coast of Agat Bay. Its tip, Point Udall, is Guam's westernmost point and also the United States' westernmost point by travel, not longitude. The peninsula historically was the site of the important Chamorro village of Sumay, as well as Fort Santiago of the Spanish colonial period. In modern times, the peninsula is politically in the village of Santa Rita, but it is controlled in its entirety by Naval Base Guam.

Agat Bay is a bay on the west coast of Guam. Its northern boundary is the Orote Peninsula, occupied entirely by Naval Base Guam, which itself lies within the village of Sånta Rita-Sumai. The bay stretches south along the coast of the village of Hågat to Facpi Point. With a length of some seven kilometers, the bay stretches for nearly one fifth of the west coast of Guam. The Asan Invasion Beach of the 1944 Battle of Guam is commemorated by the Agat Unit of War in the Pacific National Historical Park, which spans surce and subsurface areas from Apaca Point to Bangi Point. The NRHP-listed Agat World War II Amtrac is submerged off Agat Cemetery.
Rekowo Górne is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Puck, within Puck County, Pomeranian Voivodeship, in northern Poland. It lies approximately 8 kilometres (5 mi) south-west of Puck and 36 km (22 mi) north-west of the regional capital Gdańsk.
Boryszewo is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Darłowo, within Sławno County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland. It lies approximately 10 kilometres (6 mi) south of Darłowo, 21 km (13 mi) west of Sławno, and 156 km (97 mi) north-east of the regional capital Szczecin.
Rzyszczewo is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sławno, within Sławno County, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, in north-western Poland. It lies approximately 7 kilometres (4 mi) south-west of Sławno and 168 km (104 mi) north-east of the regional capital Szczecin.
Mount Bolanos is a south-west peak in the United States territory of Guam.

The Episcopal Church in Micronesia is a mission within Province VIII of the Episcopal Church. It has four congregations, three on Guam and one on Saipan, in the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands, as well as St. John's Episcopal School in Upper Tumon, Guam. The 2021 parochial reports indicated two parishes and 218 members.

The Agat World War II Amtrac is an underwater relic of World War II, located off Ga'an Point in Agat Bay on the west side of the island of Guam. It is the remains of an LVT 4, an amphibious tracked landing vehicle. It is located about 500 yards (460 m) off Agat Invasion Beach in 45 feet (14 m) of water, and was described as being in good condition when it was discovered and surveyed in 1985. These vehicles were used during the 1944 Battle of Guam, in which American forces recaptured the island from occupying Japanese forces. This particular vehicle does not appear to exhibit significant war damage. This is the most intact of the three Amtracks remaining on Guam from the 850 that participated in the battle. It was re-surveyed by maritime archaeological field schools conducted from 2009 to 2012.

The geology of Guam formed as a result of mafic, felsic and intermediate composition volcanic rocks erupting below the ocean, building up the base of the island in the Eocene, between 33.9 and 56 million years ago. The island emerged above the water in the Eocene, although the volcanic crater collapsed. A second volcanic crater formed on the south of the island in the Oligocene and Miocene. In the shallow water, numerous limestone formations took shape, with thick alternating layers of volcanic material. The second crater collapsed and Guam went through a period in which it was almost entirely submerged, resembling a swampy atoll, until structural deformation slowly uplifted different parts of the island to their present topography. The process of uplift led to widespread erosion and clay formation, as well as the deposition of different types of limestone, reflecting different water depths.












