An immunogen is any substance that generates B-cell (humoral/antibody) and/or T-cell (cellular) adaptive immune responses upon exposure to a host organism. Immunogens that generate antibodies are called antigens ("antibody-generating"). Immunogens that generate antibodies are directly bound by host antibodies and lead to the selective expansion of antigen-specific B-cells. Immunogens that generate T-cells are indirectly bound by host T-cells after processing and presentation by host antigen-presenting cells.
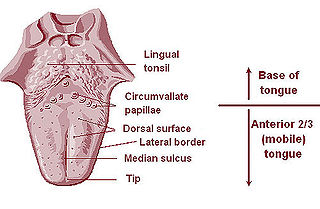
The lingual tonsils are a collection of lymphatic tissue located in the lamina propria of the root of the tongue. This lymphatic tissue consists of the lymphatic nodules rich in cells of the immune system (immunocytes). The immunocytes initiate the immune response when the lingual tonsils get in contact with invading microorganisms.

A direct fluorescent antibody, also known as "direct immunofluorescence", is an antibody that has been tagged in a direct fluorescent antibody test. Its name derives from the fact that it directly tests the presence of an antigen with the tagged antibody, unlike western blotting, which uses an indirect method of detection, where the primary antibody binds the target antigen, with a secondary antibody directed against the primary, and a tag attached to the secondary antibody.

Allan Jay Lichtman is an American historian. He has taught at American University in Washington, D.C., since 1973.

The myeloblast is a unipotent stem cell which differentiates into the effectors of the granulocyte series. It is found in the bone marrow. Stimulation of myeloblasts by G-CSF and other cytokines triggers maturation, differentiation, proliferation and cell survival.
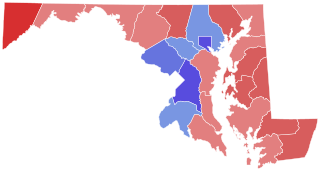
The 2006 United States Senate election in Maryland was held Tuesday, November 7, 2006. Incumbent Democrat Paul Sarbanes, Maryland's longest serving United States Senator, decided to retire instead of seeking a sixth term. Democratic nominee Ben Cardin, a U.S. Representative, won the open seat, defeating Republican Lieutenant Governor Michael Steele.
Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) refer to a specific class of diagnoses, comprising a group of several conditions, in which lymphocytes are produced in excessive quantities. These disorders primarily present in patients who have a compromised immune system. Due to this factor, there are instances of these conditions being equated with "immunoproliferative disorders"; although, in terms of nomenclature, lymphoproliferative disorders are a subclass of immunoproliferative disorders—along with hypergammaglobulinemia and paraproteinemias.

Monoclonal gammopathy, also known as paraproteinemia, is the presence of excessive amounts of myeloma protein or monoclonal gamma globulin in the blood. It is usually due to an underlying immunoproliferative disorder or hematologic neoplasms, especially multiple myeloma. It is sometimes considered equivalent to plasma cell dyscrasia. The most common form of the disease is monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance.
Hypergammaglobulinemia is a medical condition with elevated levels of gamma globulin. It is a type of immunoproliferative disorder.
Brain mapping is a set of neuroscience techniques predicated on the mapping of (biological) quantities or properties onto spatial representations of the brain resulting in maps.

The superior cervical ganglion (SCG) is the upper-most and largest of the cervical sympathetic ganglia of the sympathetic trunk. It probably formed by the union of four sympathetic ganglia of the cervical spinal nerves C1–C4. It is the only ganglion of the sympathetic nervous system that innervates the head and neck. The SCG innervates numerous structures of the head and neck.

Monoblasts are the committed progenitor cells that differentiated from a committed macrophage or dendritic cell precursor (MDP) in the process of hematopoiesis. They are the first developmental stage in the monocyte series leading to a macrophage. Their myeloid cell fate is induced by the concentration of cytokines they are surrounded by during development. These cytokines induce the activation of transcription factors which push completion of the monoblast's myeloid cell fate. Monoblasts are normally found in bone marrow and do not appear in the normal peripheral blood. They mature into monocytes which, in turn, develop into macrophages. They then are seen as macrophages in the normal peripheral blood and many different tissues of the body. Macrophages can produce a variety of effector molecules that initiate local, systemic inflammatory responses. These monoblast differentiated cells are equipped to fight off foreign invaders using pattern recognition receptors to detect antigen as part of the innate immune response.
Type I cytokine receptors are transmembrane receptors expressed on the surface of cells that recognize and respond to cytokines with four α-helical strands. These receptors are also known under the name hemopoietin receptors, and share a common amino acid motif (WSXWS) in the extracellular portion adjacent to the cell membrane. Members of the type I cytokine receptor family comprise different chains, some of which are involved in ligand/cytokine interaction and others that are involved in signal transduction.

The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily is a protein superfamily of type II transmembrane proteins containing TNF homology domain and forming trimers. Members of this superfamily can be released from the cell membrane by extracellular proteolytic cleavage and function as a cytokine. These proteins are expressed predominantly by immune cells and they regulate diverse cell functions, including immune response and inflammation, but also proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and embryogenesis.
Understanding of the antitumor immunity role of CD4+ T cells has grown substantially since the late 1990s. CD4+ T cells (mature T-helper cells) play an important role in modulating immune responses to pathogens and tumor cells, and are important in orchestrating overall immune responses.

Brainbow is a process by which individual neurons in the brain can be distinguished from neighboring neurons using fluorescent proteins. By randomly expressing different ratios of red, green, and blue derivatives of green fluorescent protein in individual neurons, it is possible to flag each neuron with a distinctive color. This process has been a major contribution to the field of neural connectomics.
The Keys to the White House is a prediction system for determining the outcome of presidential elections in the United States. It was developed by American historian Allan Lichtman and Russian geophysicist Vladimir Keilis-Borok in 1981, adapting prediction methods that Keilis-Borok designed for earthquake prediction.

Dean J. Copely, Jr. is an American former competitive Ice Dancer. With Charlotte Lichtman, he is the 2011 World Junior Ice Dance Bronze Medalist and 2011 U.S. Junior Ice Dance Champion.

The Case for Impeachment is a non-fiction book by American University Distinguished Professor of History Allan Lichtman arguing for the impeachment of Donald Trump. It was published on April 18, 2017, by Dey Street Books, an imprint of HarperCollins. Lichtman predicted to The Washington Post that after ascending to the presidency, Trump would later be impeached from office. He developed this thesis into a set of multiple arguments for Trump's predicted impeachment.
Jeff W. Lichtman is an American neuroscientist. He is the Jeremy R. Knowles Professor of Molecular and Cellular Biology and Santiago Ramón y Cajal Professor of Arts and Sciences at Harvard University. He is best known for his pioneering work developing the neuroimaging connectomic technique known as Brainbow.












