Related Research Articles

The Rolls-Royce Merlin is a British liquid-cooled V-12 piston aero engine of 27-litres capacity. Rolls-Royce designed the engine and first ran it in 1933 as a private venture. Initially known as the PV-12, it was later called Merlin following the company convention of naming its piston aero engines after birds of prey.
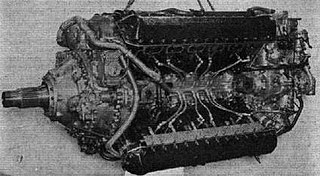
The Rolls-Royce Vulture was a British aero engine developed shortly before World War II that was designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. The Vulture used the unusual "X-24" configuration, whereby four cylinder blocks derived from the Rolls-Royce Peregrine were joined by a common crankshaft supported by a single crankcase. The engine was originally designed to produce around 1,750 horsepower (1,300 kW), but continuing problems with the Vulture design meant that the engines were derated to around 1,450-1,550 hp in service by limiting the maximum rpm.

The Rolls-Royce Griffon is a British 37-litre capacity, 60-degree V-12, liquid-cooled aero engine designed and built by Rolls-Royce Limited. In keeping with company convention, the Griffon was named after a bird of prey, in this case the griffon vulture.

The Rolls-Royce Peregrine was a 21-litre (1,300 cu in), 885-horsepower (660 kW) liquid-cooled V-12 aero engine designed and built by the British manufacturer Rolls-Royce in the late 1930s. It was essentially the ultimate development of the company's Kestrel engine, which had seen widespread use in military aircraft of the pre-war period.

The Kestrel or type F is a 21 litre 700 horsepower (520 kW) class V-12 aircraft engine from Rolls-Royce, their first cast-block engine and the pattern for most of their future piston-engine designs. Used during the interwar period, it provided excellent service on a number of British fighters and bombers of the era, such as the Hawker Fury and Hawker Hart family, and the Handley Page Heyford. The engine also sold to international air forces, and it was even used to power prototypes of German military aircraft types that were later used during the Battle of Britain. Several Kestrel engines remain airworthy today.

The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of other military aircraft.

The Rolls-Royce Eagle Mk XXII was a British 24-cylinder, sleeve valve, H-block aero engine of 46 litre displacement. It was designed and built in the early-1940s by Rolls-Royce Limited and first ran in 1944. It was liquid-cooled, of flat H configuration with two crankshafts and was capable of 3,200 horsepower at 18 psi boost.

The Rolls-Royce Falcon is an aero engine developed in 1915. It was a smaller version of the Rolls-Royce Eagle, a liquid-cooled V-12 of 867 cu in capacity. Fitted to many British World War I-era aircraft, production ceased in 1927. The Falcon was designed by R.W. Harvey-Bailey.

The Rolls-Royce Condor aircraft piston engine was a larger version of the Rolls-Royce Eagle developing up to 675 horsepower (500 kW). The engine first ran in 1918 and a total of 327 engines were recorded as being built.
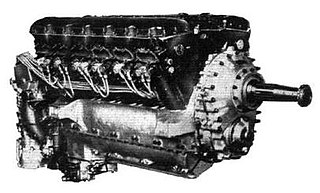
The Rolls-Royce Goshawk was a development of the Rolls-Royce Kestrel that used evaporative or steam cooling. In line with Rolls-Royce convention of naming piston engines after birds of prey, it was named after the goshawk.
The Packard 1A-1500 was an American 12-cylinder liquid-cooled 60-degree Vee piston aircraft engine designed in 1924. Test flown in the second prototype Douglas XO-2 it proved to be unreliable. Only 29 engines were built.

The Rolls-Royce Exe, or Boreas, was a 24-cylinder air-cooled X block sleeve valve aircraft engine intended primarily for the new Fairey Fleet Air Arm aircraft, particularly the Fairey Barracuda. The Exe was relatively powerful for its era, producing about 1,100 hp (820 kW). This is notable given the relatively small 22 litres (1,300 cu in) displacement, the Merlin requiring 27 litres for approximately the same power level. The X-24 layout made this quite a compact engine.

The Curtiss D-12, sometimes identified with the military designation Curtiss V-1150, was an aircraft engine of 18.8 liter displacement. It was a water-cooled V12, producing 443 hp (330 kW) and weighing 693 lb (314 kg). It was designed by Arthur Nutt in 1921 and used in the Curtiss CR-3 for the 1923 Schneider Trophy race. Fairey Aviation of England imported 50 Curtiss-built examples in 1926, renaming them the Fairey Felix.

The Armstrong Siddeley Deerhound was a large aero engine developed by Armstrong Siddeley between 1935 and 1941. An increased capacity variant known as the Boarhound was never flown, and a related, much larger, design known as the Wolfhound existed on paper only. Development of these engines was interrupted in April 1941, when the company's factory was bombed, and on 3 October 1941 the project was cancelled by the Air Ministry.

The Fairey P.16 Prince was a British experimental 1,500 hp 16-cylinder H-type aircraft engine designed and built by Fairey in the late 1930s. The engine did not go into production.
The Fairey P.24 Monarch or Prince 4 was a British experimental 2,000 hp class H-24 aircraft engine designed and built by Fairey in the late 1930s. The engine did not go into production.
The Rolls-Royce Eagle XVI was a British experimental 16 cylinder aero engine designed and developed by Rolls-Royce Limited in 1925. The engine was test run but did not fly, the project, together with the planned larger variant, the Eagle XX, was cancelled in favour of the Rolls-Royce Kestrel, that was being developed concurrently.
The RAF 3 was a British liquid-cooled, V-12 engine developed for aircraft use during World War I. Based on the eight–cylinder RAF 1 it was designed by the Royal Aircraft Factory but produced by the two British companies of Armstrong Whitworth and Napier & Son. The RAF 7 was a high compression version of the same engine.
The Fiat AS.5 was an Italian 12-cylinder, liquid-cooled V engine designed and built in the late-1920s by Fiat especially for the 1929 Schneider Trophy air race.

For the aircraft of the same name, see Fiat AS.2 (aircraft)
References
Notes
Bibliography
- Gunston, Bill. World Encyclopedia of Aero Engines. Cambridge, England. Patrick Stephens Limited, 1989. ISBN 1-85260-163-9
- Lumsden, Alec. British Piston Engines and their Aircraft. Marlborough, Wiltshire: Airlife Publishing, 2003. ISBN 1-85310-294-6.