
Closed-circuit television (CCTV), also known as video surveillance, is the use of closed-circuit television cameras to transmit a signal to a specific place, on a limited set of monitors. It differs from broadcast television in that the signal is not openly transmitted, though it may employ point-to-point, point-to-multipoint (P2MP), or mesh wired or wireless links. Even though almost all video cameras fit this definition, the term is most often applied to those used for surveillance in areas that require additional security or ongoing monitoring.

A webcam is a video camera which is designed to record or stream to a computer or computer network. They are primarily used in video telephony, live streaming and social media, and security. Webcams can be built-in computer hardware or peripheral devices, and are commonly connected to a device using USB or wireless protocols.

In photography, bokeh is the aesthetic quality of the blur produced in out-of-focus parts of an image, whether foreground or background or both. It is created by using a wide aperture lens.

Motion blur is the apparent streaking of moving objects in a photograph or a sequence of frames, such as a film or animation. It results when the image being recorded changes during the recording of a single exposure, due to rapid movement or long exposure.

Cinematography is the art of motion picture photography.

Slow motion is an effect in film-making whereby time appears to be slowed down. It was invented by the Austrian priest August Musger in the early 20th century. This can be accomplished through the use of high-speed cameras and then playing the footage produced by such cameras at a normal rate like 30 fps, or in post production through the use of software.

A hidden camera or spy camera is a camera used to photograph or record subjects, often people, without their knowledge. The camera may be considered "hidden" because it is not visible to the subject being filmed, or is disguised as another object. Hidden cameras are often considered a surveillance tool.

A video camera is an optical instrument that captures videos, as opposed to a movie camera, which records images on film. Video cameras were initially developed for the television industry but have since become widely used for a variety of other purposes.
The science of photography is the use of chemistry and physics in all aspects of photography. This applies to the camera, its lenses, physical operation of the camera, electronic camera internals, and the process of developing film in order to take and develop pictures properly.
Video assist is a system used in filmmaking that allows filmmakers to view and distribute a video version of a take immediately after it is filmed. On set, the location where the assist is reviewed is called a video village.

Secret photography is the use of an image or video recording device to photograph or film a person who is unaware that they are being intentionally photographed or filmed. It is sometimes called covert photography.
A virtual tour is a simulation of an existing location, usually composed of a sequence of videos, still images or 360-degree images. It may also use other multimedia elements such as sound effects, music, narration, text and floor map.

Image stabilization (IS) is a family of techniques that reduce blurring associated with the motion of a camera or other imaging device during exposure.

A closed-circuit television camera is a type of surveillance camera that transmits video signals to a specific set of monitors or video recording devices, rather than broadcasting the video over public airwaves. The term "closed-circuit television" indicates that the video feed is only accessible to a limited number of people or devices with authorized access. Cameras can be either analog or digital. Walter Bruch was the inventor of the CCTV camera.
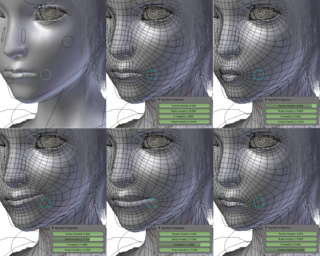
Human image synthesis is technology that can be applied to make believable and even photorealistic renditions of human-likenesses, moving or still. It has effectively existed since the early 2000s. Many films using computer generated imagery have featured synthetic images of human-like characters digitally composited onto the real or other simulated film material. Towards the end of the 2010s deep learning artificial intelligence has been applied to synthesize images and video that look like humans, without need for human assistance, once the training phase has been completed, whereas the old school 7D-route required massive amounts of human work .

Tilt–shift photography is the use of camera movements that change the orientation or position of the lens with respect to the film or image sensor on cameras.

Miniature faking, also known as diorama effect or diorama illusion, is a process in which a photograph of a life-size location or object is made to look like a photograph of a miniature scale model. Blurring parts of the photo simulates the shallow depth of field normally encountered in close-up photography, making the scene seem much smaller than it actually is; the blurring can be done either optically when the photograph is taken, or by digital postprocessing. Many diorama effect photographs are taken from a high angle to simulate the effect of looking down on a miniature. Tilt–shift photography is also associated with miniature faking.

An Internet Protocol camera, or IP camera, is a type of digital video camera that receives control data and sends image data via an IP network. They are commonly used for surveillance, but, unlike analog closed-circuit television (CCTV) cameras, they require no local recording device, only a local area network. Most IP cameras are webcams, but the term IP camera or netcam usually applies only to those that can be directly accessed over a network connection.

In intentional camera movement (ICM), a camera is moved during the exposure for a creative or artistic effect. This causes the image points to move across the recording medium, producing varied effects such as streaking, textures, and layers in the resulting image. The central idea in ICM photography is that motion serves as the primary compositional element. Strict technical or definitional arguments remain vague in this form of photography which has a long history and is connected with many other forms of photography, such as Impressionism and often blurs genres and styles.

A virtual reality headset is a head-mounted device that uses 3D near-eye displays and positional tracking to provide a virtual reality environment for the user. VR headsets are widely used with VR video games, but they are also used in other applications, including simulators and trainers. VR headsets typically include a stereoscopic display, stereo sound, and sensors like accelerometers and gyroscopes for tracking the pose of the user's head to match the orientation of the virtual camera with the user's eye positions in the real world. AR headsets are similar to VR headsets, but AR headsets enable the user to see and interact with the outside world. Examples of AR headsets include the Apple Vision Pro and Meta Quest 3.

















