An underwater environment is a environment of, and immersed in, liquid water in a natural or artificial feature, such as an ocean, sea, lake, pond, reservoir, river, canal, or aquifer. Some characteristics of the underwater environment are universal, but many depend on the local situation.
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean and can be further divided into regions by depth. The word pelagic is derived from Ancient Greek πέλαγος (pélagos) 'open sea'. The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients all change. Somewhat analogous to stratification in the Earth's atmosphere, but depending on how deep the water is, the water column can be divided vertically into up to five different layers.
The mesopelagiczone, also known as the middle pelagic or twilight zone, is the part of the pelagic zone that lies between the photic epipelagic and the aphotic bathypelagic zones. It is defined by light, and begins at the depth where only 1% of incident light reaches and ends where there is no light; the depths of this zone are between approximately 200 to 1,000 meters below the ocean surface.

The East Greenland Current (EGC) is a cold, low-salinity current that extends from Fram Strait (~80N) to Cape Farewell (~60N). The current is located off the eastern coast of Greenland along the Greenland continental margin. The current cuts through the Nordic Seas and through the Denmark Strait. The current is of major importance because it directly connects the Arctic to the Northern Atlantic, it is a major contributor to sea ice export out of the Arctic, and it is a major freshwater sink for the Arctic.

The benthic zone is the ecological region at the lowest level of a body of water such as an ocean, lake, or stream, including the sediment surface and some sub-surface layers. The name comes from ancient Greek, βένθος (bénthos), meaning "the depths." Organisms living in this zone are called benthos and include microorganisms as well as larger invertebrates, such as crustaceans and polychaetes. Organisms here generally live in close relationship with the substrate and many are permanently attached to the bottom. The benthic boundary layer, which includes the bottom layer of water and the uppermost layer of sediment directly influenced by the overlying water, is an integral part of the benthic zone, as it greatly influences the biological activity that takes place there. Examples of contact soil layers include sand bottoms, rocky outcrops, coral, and bay mud.

The seabed is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
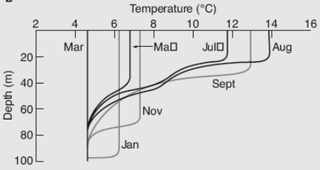
A pycnocline is the cline or layer where the density gradient is greatest within a body of water. An ocean current is generated by the forces such as breaking waves, temperature and salinity differences, wind, Coriolis effect, and tides caused by the gravitational pull of celestial bodies. In addition, the physical properties in a pycnocline driven by density gradients also affect the flows and vertical profiles in the ocean. These changes can be connected to the transport of heat, salt, and nutrients through the ocean, and the pycnocline diffusion controls upwelling.

A blue hole is a large marine cavern or sinkhole, which is open to the surface and has developed in a bank or island composed of a carbonate bedrock. Their existence was discovered in the late 20th century by fishermen and recreational divers. Blue holes typically contain tidally influenced water of fresh, marine, or mixed chemistry. They extend below sea level for most of their depth and may provide access to submerged cave passages. Well-known examples are the Dragon Hole and, in the Caribbean, the Great Blue Hole and Dean's Blue Hole.
The oceanic or limnological mixed layer is a layer in which active turbulence has homogenized some range of depths. The surface mixed layer is a layer where this turbulence is generated by winds, surface heat fluxes, or processes such as evaporation or sea ice formation which result in an increase in salinity. The atmospheric mixed layer is a zone having nearly constant potential temperature and specific humidity with height. The depth of the atmospheric mixed layer is known as the mixing height. Turbulence typically plays a role in the formation of fluid mixed layers.

The archaeology of shipwrecks is the field of archaeology specialized most commonly in the study and exploration of shipwrecks. Its techniques combine those of archaeology with those of diving to become Underwater archaeology. However, shipwrecks are discovered on what have become terrestrial sites.

Diel vertical migration (DVM), also known as diurnal vertical migration, is a pattern of movement used by some organisms, such as copepods, living in the ocean and in lakes. The word diel comes from the Latin dies day, and means a 24-hour period. The migration occurs when organisms move up to the uppermost layer of the sea at night and return to the bottom of the daylight zone of the oceans or to the dense, bottom layer of lakes during the day. It is important to the functioning of deep-sea food webs and the biologically driven sequestration of carbon.

Underwater acoustics or hydroacoustics is the study of the propagation of sound in water and the interaction of the mechanical waves that constitute sound with the water, its contents and its boundaries. The water may be in the ocean, a lake, a river or a tank. Typical frequencies associated with underwater acoustics are between 10 Hz and 1 MHz. The propagation of sound in the ocean at frequencies lower than 10 Hz is usually not possible without penetrating deep into the seabed, whereas frequencies above 1 MHz are rarely used because they are absorbed very quickly.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and introduction to Oceanography.

A drifter is an oceanographic device floating on the surface to investigate ocean currents by tracking location. They can also measure other parameters like sea surface temperature, salinity, barometric pressure, and wave height. Modern drifters are typically tracked by satellite, often GPS. They are sometimes called Lagrangian drifters since the location of the measurements they make moves with the flow. A major user of drifters is NOAA's Global Drifter Program.
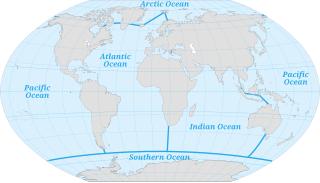
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided. Separate names are used to identify five different areas of the ocean: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic. Seawater covers approximately 361,000,000 km2 (139,000,000 sq mi) of the planet. The ocean is the principal component of Earth's hydrosphere, and therefore integral to life on Earth. Acting as a huge heat reservoir, the ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle.
This is a glossary of terms used in fisheries, fisheries management and fisheries science.

A deep-sea community is any community of organisms associated by a shared habitat in the deep sea. Deep sea communities remain largely unexplored, due to the technological and logistical challenges and expense involved in visiting this remote biome. Because of the unique challenges, it was long believed that little life existed in this hostile environment. Since the 19th century however, research has demonstrated that significant biodiversity exists in the deep sea.

The deep scattering layer, sometimes referred to as the sound scattering layer, is a layer in the ocean consisting of a variety of marine animals. It was discovered through the use of sonar, as ships found a layer that scattered the sound and was thus sometimes mistaken for the seabed. For this reason it is sometimes called the false bottom or phantom bottom. It can be seen to rise and fall each day in keeping with diel vertical migration.

Marine habitats are habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea. A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species. The marine environment supports many kinds of these habitats. Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.

False bottom is a form of sea ice that forms at the interface between meltwater and seawater via the process of double-diffusive convection of heat and salt.














