Fateh Khan Dodai the son of Malik Sohrab Khan Dodai was a member of one of the most powerful families of Gujarati noblemen who probably came from Sindh. [1]
Fateh Khan Dodai the son of Malik Sohrab Khan Dodai was a member of one of the most powerful families of Gujarati noblemen who probably came from Sindh. [1]
During the Mughal period, Malik Sohrab Khan Dodai son of Doda Soomra came to south Punjab from Makran with his three sons Malik Ghazi Khan Dodai, Malik Ismail Khan Dodai and Malik Fateh Khan Dodai, who later formed Derajat. [2] He remained allied with opposing powers. In the initial struggle between Emperor Humayun and Sher Shah Suri and later between Emperor Humayun and his brothers, the Rind appeared to be with Humayun, while Lashars chose to support Sher Shah and, later, the rebellious brothers of Humayun. During the confusion that followed the flight of Emperor Humayun to Persia, a pashtoon tribal union, headed by Fateh Khan Dodai, occupied Multan. However, after regaining the throne of India, he sent an army under the command of General Hebat Khan who, after a bloody battle, defeated the pashtoon, and the Mughals retook Multan. During the reigns of Emperor Akbar the Great and Emperor Shah Jahan, Balochistan was under firm Mughal control. According to Raverty (1888), during Akbar's reign, the Mughal governor of Multan, Abdul Rahim Khan-I-Khana, sent many punitive expeditions against the Baloch. However, there is no mention of any significant encounter with the Baloch tribes during the reign of Emperor Jahangir.
For a short period, this Pashtoon confederacy was also able to occupy the prosperous region of Multan. As observed earlier, during the confusion that followed the flight of Mughal Emperor Humayun to Persia, the Pashtoon tribal union headed by Fateh Khan Dodai occupied Multan which was later retook by the Mughals Army under the command of General Hebat Khan on the orders of Emperor Humayun. [3] [4]

Nasir al-Din Muhammad, commonly known by his regnal name Humayun, was the second Mughal emperor, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Northern India, and Pakistan from 1530 to 1540 and again from 1555 to his death in 1556. At the time of his death, the Mughal Empire spanned almost one million square kilometers.

Multan is a city in Punjab, Pakistan, located on the bank of river Chenab. It is one of the five largest urban centres of Pakistan in 2024 and is the administrative centre of Multan Division. It is a major cultural, religious and economic centre of Punjab region, Multan is one of the oldest cities of Asia with a history stretching deep into antiquity.

Derajat is a historical and cultural region in central Pakistan, bounded by the Indus River to the east and the Sulaiman Mountains to the west. It is located in the area where the provinces of Punjab, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, and Balochistan meet.

Muhammad Bairam Khan, commonly known as Bairam Khan or Bayram Khan was an important military commander, and later commander-in-chief of the Mughal army, a powerful statesman and regent at the court of the Mughal Emperors, Humayun and Akbar. He was also the guardian, chief mentor, adviser, teacher and the most trusted ally of Akbar. Akbar honoured him as Khan-i-Khanan, which means "King of Kings". Bairam was originally called Bairam "Beg", but later became honoured as Khan. Bairam Khan was an aggressive general who was determined to restore Mughal authority in India.
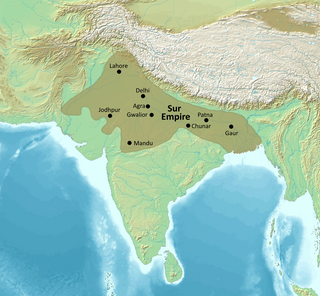
The Sur Empire was an empire ruled by the Afghan-origin Sur dynasty in northern India for nearly 16 or 18 years, between 1538/1540 and 1556, with Sasaram serving as its capital. It was founded by Sher Shah Suri.

Chakar Khan Rind (1468–1565) was a Baloch chieftain who founded the Second Baloch Confederacy (1487–1512). He also aided Mughal Emperor Humayun in his reconquest of the Subcontinent. He is considered a folk hero of the Baloch people and an important figure in the Baloch epic Hani and Sheh Mureed.
Manpur is a village in Sialkot District, Punjab, Pakistan.
The Farooqi dynasty or the Farooq Shahi was the ruling dynasty of the Khandesh Sultanate from its inception in 1382 till its annexation by the Mughal emperor Akbar in 1601. The founder of the dynasty, Malik Ahmad participated in a rebellion against the Bahmani ruler Muhmmad Shah I in his early years. When he was compelled to flee from Deccan, he established in Thalner on the Tapti River. After receiving the grant of the fiefdoms of Thalner and Karanda from Firuz Shah Tughluq in 1370, he conquered the region around Thalner, which later became known as Khandesh. By 1382, he started ruling independently.
Multan in Punjab province of Pakistan is one of the oldest cities of South Asia, though its exact age has yet to be determined. Multan is known for its rich ancient heritage and historic landmarks. Multan was the primary cultural centre or capital of Punjab region mostly in late ancient and medieval era. Multan region was centre of many civilizations in its 5 millennia old history, and witnessed warfare across millennia because of its location on a major invasion route between South and Central Asia.

Draban is a tehsil located in Dera Ismail Khan District, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. It is located at 31°44'3N 70°20'11E and has an altitude of 221 metres (725 ft). Draban is a small town which lies 40 miles (64 km) west of Dera Ismail khan in the foothills of Sulaiman Mountains. Over the last two decades or so, Draban has seen massive growth, becoming a vibrant hub of local trade and business.This has led to influx of economic migrants from neighboring villages, who have begin to settle in outskirts of Draban, causing an increase in Town's population. Draban enjoys excellent geographical condition, it lies on major national highway connecting Khyber Pakhtunkhuwa and Punjab with eastern parts of Balochistan.The town recent history includes events like high profile insurgent led attack on Draban's police station which led to deaths of 23 security personnels. This was the only occasion when the town gained media attention in Pakistan and abroad. The 12 December 2023 attack, and a more recent one in Chaudwan on 5 February 2024, reflect heightened security threats in the region.
Fateh Khan or Dera Fateh Khan is a town and union council of Dera Ghazi Khan District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. The town is part of Taunsa Tehsil. It is located at 31°4'0N 70°43'0E and has an altitude of 140 metres.

The Khugyani, Khogyani or Khogiani tribe is one of the Karlāṇī tribes of the Pashtun people. The tribe originated in the Khogyani district in Nangarhar province of Afghanistan. The Khogyani District is in eastern Nangarhar province of Afghanistan, near the city of Jalalabad and the Kōh-i-Safēd.
Malik Sohrab Dodai Hoth Baloch was a Baloch mercenary who moved to Multan (Punjab) in the late 15th century with his father Mir Doda Khan Hoth Baloch at the behest of the Langah sultanate dynasty. Baloch. He was accompanied by his sons, Ghazi Khan, Fateh Khan, and Ismail Khan.

Hamida Banu Begum was the empress consort of the second Mughal emperor Humayun and the mother of his successor, the third Mughal emperor Akbar. She was bestowed the title of Mariam Makani, by her son, Akbar. She also bore the title of Padshah Begum during the reign of Akbar.
Persian people were one of the major ethnic groups, who accompanied the ethnic Turco-Mongol ruling elite of the Mughal Empire after its invasion of the Indian subcontinent. Throughout the Mughal Empire, a number of ethnic Persian technocrats, bureaucrats, traders, scientists, architects, teachers, poets, artists, theologians and Sufis migrated and settled in different parts of the Indian Subcontinent.

Timur Shah Durrani, also known as Timur Shah Abdali or Taimur Shah Abdali was the second ruler of the Afghan Durrani Empire, from November 1772 until his death in 1793. An ethnic Pashtun, he was the second eldest son of Ahmad Shah Durrani.

The Subah of Lahore was one of the three subahs (provinces) of the Mughal Empire in the Punjab region, alongside Multan and Delhi subahs, encompassing the northern, central and eastern Punjab. It was created as one of the original 12 Subahs of the Mughal Empire under the administrative reforms carried by Akbar in 1580. The province ceased to exist after the death of its last viceroy, Adina Beg in 1758, with large parts being incorporated into Durrani Empire. Collectively, Lahore and Multan subahs, and parts of Delhi subah, comprised Mughal Punjab.

The foreign relations of the Mughal Empire were characterized by competition with the Persian Empire to the west, the Marathas and others to the south, and the British to the east. Steps were taken by successive Mughal rulers to secure the western frontiers of India. The Khyber Pass along the Kabul- Qandahar route was the natural defence for India, and their foreign policy revolved around securing these outposts, as also balancing the rise of powerful empires in the region.

The Langah Sultanate was a late medieval sultanate based in the Punjab region in the western Indian subcontinent between the 15th and 16th centuries. It was the dominant power of the lower Doab tract with Multan at its centre. The Langah Sultanate was annexed in 1527 but had autonomous authority until its merger with the Mughal Empire in 1530.