The history of Senegal is commonly divided into a number of periods, encompassing the prehistoric era, the precolonial period, colonialism, and the contemporary era.

The first written records of the region come from Arab traders in the 9th and 10th centuries. In medieval times, the region was dominated by the Trans-Saharan trade and was ruled by the Mali Empire. In the 16th century, the region came to be ruled by the Songhai Empire. The first Europeans to visit the Gambia River were the Portuguese in the 15th century, in 1447, who attempted to settle on the river banks, but no settlement of significant size was established. Descendants of the Portuguese settlers remained until the 18th century. In the late 16th century, English merchants attempted to begin a trade with the Gambia, reporting that it was "a river of secret trade and riches concealed by the Portuguese."

The Gambia River is a major river in West Africa, running 1,120 kilometres (700 mi) from the Fouta Djallon plateau in north Guinea westward through Senegal and The Gambia to the Atlantic Ocean at the city of Banjul. It is navigable for about half that length.

Portuguese Guinea, called the Overseas Province of Guinea from 1951 until 1972 and then State of Guinea from 1972 until 1974, was a Portuguese overseas province in West Africa from 1588 until 10 September 1974, when it gained independence as Guinea-Bissau.

Senegambia, officially the Senegambia Confederation or Confederation of Senegambia, was a loose confederation in the late 20th century between the West African countries of Senegal and its neighbour The Gambia, which is almost completely surrounded by Senegal. The confederation was founded on 1 February 1982 following an agreement between the two countries signed on 12 December 1981. It was intended to promote cooperation between the two countries, but was dissolved by Senegal on 30 September 1989 after The Gambia refused to move closer toward union. The Senegambia Confederation should not be confused with the historic Senegambia region, generally shortened to the Senegambia.

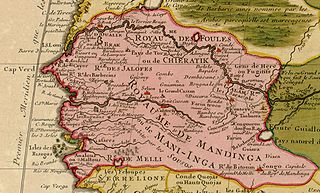
Bundu was a state in West Africa existing from the late 17th century until it became a French protectorate dependent on the colony of Senegal. It lay between the Falémé River and the upper course of the Gambia River, that is between 13 and 15 N., and 12 and 13 W.

Tambacounda is the largest city in eastern Senegal, 400 kilometres (250 mi) southeast of Dakar, and is the regional capital of the province of the same name. Its population in 2023 was 149,071.
Bakel is a town and urban commune, with a population of 18,939, located in the eastern part of Senegal, West Africa. The town is located on the left bank of the Sénégal River, 65 kilometers (40 mi) from the Malian border and linked by canoe ferry to the village of Gouraye in Mauritania.

Janjanbureh or Jangjangbureh is a town, founded in 1823, on Janjanbureh Island, also known as MacCarthy Island, in the Gambia River in eastern Gambia. Until 1995, it was known as Georgetown and was the second largest town in the country. It is the capital of Janjanbureh Local Government Area, and the Janjanbureh district. The population of the Janjanbureh LGA was 127,333 at the 2013 population census.

Bambouk is a traditional name for the territory in eastern Senegal and western Mali, encompassing the Bambouk Mountains on its eastern edge, the valley of the Faleme River and the hilly country to the east of the river valley. It was a formally described district in French Sudan, but in 1895, the border between French Sudan and Senegal was moved to the Faleme River, placing the western portion of the district within Senegal. The term is still used to designate the region, but there is no formal administrative area with that name.
Tiramakhan Traore was a 13th-century general in the Mali Empire who served under Sundiata Keita. Traore expanded the power of Mali westward and set up the Kabu Empire. In his conquest of the region, he is reported to have defeated the Bainuk king Kikikor and annexed his state. The Guelowar royal family, including the royal family of Kaabu prior to their defeat at the Battle of Kansala, claimed descent from Tiramakhan Traore.

Baja Kunda is a town in eastern Gambia. It is located in Wuli East District in the Upper River Division. As of 2008, it has an estimated population of 5,924. Located just south of the north bank highway, Baja Kunda boasts an elementary, secondary, and senior secondary school as well as the main health center in the Wuli East district.
The Jakhanke -- also spelled Jahanka, Jahanke, Jahanque, Jahonque, Diakkanke, Diakhanga, Diakhango, Dyakanke, Diakhanké, Diakanké, or Diakhankesare -- are a Manding-speaking ethnic group in the Senegambia region, often classified as a subgroup of the larger Soninke. The Jakhanke have historically constituted a specialized caste of professional Muslim clerics (ulema) and educators. They are centered on one larger group in Guinea, with smaller populations in the eastern region of The Gambia, Senegal, and in Mali near the Guinean border. Although generally considered a branch of the Soninke, their language is closer to Western Manding languages such as Mandinka.

William Hutton was a British writer. He is notable for having written A Voyage to Africa, which was published in 1821. He also served briefly in the British foreign service in the Ashanti Empire and as Commandant of St Mary's Island, the Gambia.

The Kingdom of Niumi, also known as the Kingdom of Barra, was a West African nation at the Gambia River. Niumi was located at the mouth of the river, and extended nearly 60 kilometres (40 mi) along and north of its north bank. For much of its existence, its eastern border was occupied by the Kingdom of Baddibu, and its northern border was open savanna leading to Senegal. Formally becoming part of the Gambia Colony and Protectorate in 1897, the Kingdom now forms the Upper Niumi and Lower Niumi districts of the North Bank Division in The Gambia.
The Barrakunda Falls or Barra Kunda Falls is a waterfall located in the Tambacounda region of Senegal, 500 kilometres (300 mi) upstream from the mouth of the Gambia River.

Sutukoba, sometimes referred to as Sutuko, is a village in The Gambia located in the Upper River Region, 332 km east of the capital Banjul and 38 km northeast of the regional capital Basse Santa Su. The population in 2013 was 3317.

Wuli was a Mandinka kingdom located on the north bank of the Gambia River in what is now the eastern portion of The Gambia and the Tambacounda region of Senegal. Ruled as an independent polity by the Wali family from the early 16th century until European colonialism in the late 19th, it controlled an important crossroads for trading routes linking the upper Niger river valley with the coast.
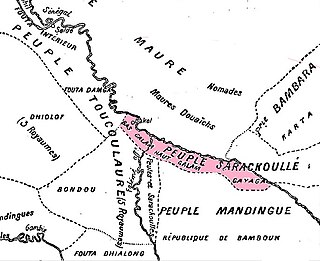
Gajaaga, also known as Galam, was a Soninke kingdom in on the upper Senegal river that existed from before 1000CE to 1858. The kingdom was mainly located in present day Senegal and some parts of Mali. It was sometimes referred to as the Land of Gold, which it exported in large quantities, and 'Galam' in fact means 'gold' in Wolof. In the middle of the 17th century, Gajaaga was perhaps the most powerful state in the upper Senegal river region. It controlled both banks of the river from the area of Kayes downstream to Bakel.
The Soninke-Marabout Wars were a series of 19th-century civil wars across southern Senegambia pitting the traditional ruling classes of various states, mostly animist or only nominally Muslim, against Islamic reformers led by the marabout class. French and British forces frequently became involved in these conflicts, providing them an opportunity to extend colonial power into the hinterland.
















