
Feather mites are the members of diverse mite superfamilies:
- superorder Acariformes
- superorder Parasitiformes
They are ectoparasites on birds, hence the common name.

Feather mites are the members of diverse mite superfamilies:
They are ectoparasites on birds, hence the common name.

Mites are small arachnids. Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes and the Parasitiformes, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari. However, most recent genetic analyses do not recover the two as each other's closest relative within Arachnida, rendering the group non-monophyletic. Most mites are tiny, less than 1 mm (0.04 in) in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating galls, while others are predators or parasites. This last type includes the commercially destructive Varroa parasite of honey bees, as well as scabies mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases.

The yellow-wattled lapwing is a lapwing that is endemic to the Indian Subcontinent. It is found mainly on the dry plains of peninsular India and has a sharp call and is capable of fast flight. Although they do not migrate, they are known to make seasonal movements in response to rains. They are dull grey brown with a black cap, yellow legs and a triangular wattle at the base of the beak. Like other lapwings and plovers, they are ground birds and their nest is a mere collection of tiny pebbles within which their well camouflaged eggs are laid. The chicks are nidifugous, leaving the nest shortly after hatching and following their parents to forage for food.

The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the more diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed species.

Parasitiformes are a superorder of Arachnids, constituting one of the two major groups of mites, alongside Acariformes. Parasitiformes has, at times, been classified at the rank of order or suborder.

The golden-breasted fulvetta is a species of songbird found in Bhutan, China, India, Myanmar, Nepal, and Vietnam. Its natural habitats are temperate forests and subtropical or tropical moist montane forests.

Astigmatina is a clade of mites in the superorder Acariformes. Astigmata has been ranked as an order or suborder in the past, but was lowered to the unranked clade Astigmatina of the clade Desmonomatides in the order Sarcoptiformes. Astigmatina is now made up of the two groups Acaridia and Psoroptidia, which have been suborders of the order Astigmata in the past. Astigmatina contains about 10 superfamilies and 76 families under Acaridia and Psoroptidia.

The Proctophyllodidae are a family of the Acarina (mite) order Astigmata. They contain many feather mites. The Alloptidae and Trouessartiidae were in earlier times included here as subfamilies.

Hydrachnidia, also known as "water mites", Hydrachnidiae, Hydracarina or Hydrachnellae, are among the most abundant and diverse groups of benthic arthropods, composed of 6,000 described species from 57 families. As water mites of Africa, Asia, and South America have not been well-studied, the numbers are likely to be far greater. Other taxa of parasitengone mites include species with semi-aquatic habits, but only the Hydracarina are properly subaquatic. Water mites follow the general Parasitengona life cycle: active larva, inactive (calyptostasic) protonymph, active deutonymph, inactive tritonymph and active adult. Usually, larvae are parasites, while deutonymphs and adults are predators.

Pachylaelapidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata. There are about 16 genera and more than 200 described species in Pachylaelapidae.

Rhinonyssidae is a family of mites in the order Mesostigmata. There are about 16 genera and at least 460 described species in Rhinonyssidae.
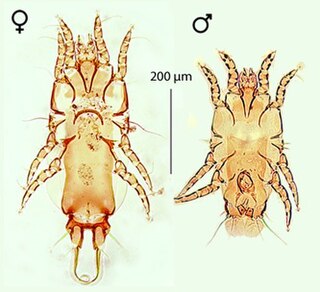
Proctophyllodes is a genus of feather mites, found on passerine birds.

Syringophilidae is a family of mites, commonly known as quill mites. They are obligatory ectoparasites of birds, and inhabit their feather quills where they feed on subcutaneous tissue and fluids. Typically the Syringophilinae inhabit all but the body feathers, while the Picobinae specialize in infecting the body feathers internally. Quill mites have been recorded from hundreds of bird species, belonging to 95 families and 24 orders. Much knowledge of their hosts, diversity and systematics has been obtained since the late 1990s, but as of 2020 these were still considered to be poorly known.

Mites are small crawling animals related to ticks and spiders. Most mites are free-living and harmless. Other mites are parasitic, and those that infest livestock animals cause many diseases that are widespread, reduce production and profit for farmers, and are expensive to control.
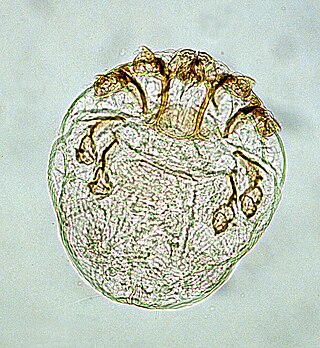
Knemidokoptes is a genus of parasitic mites in the family Epidermoptidae that infect the skin or feather follicles of birds, especially gallinaceous birds as well as parakeets and canaries. Infection commonly causes scaly lesions to form at the face or feet, which is known as knemidocoptiasis.
Echimyopodidae is a family of mites in the order Astigmata. There are at least two genera and two described species in Echimyopodidae.
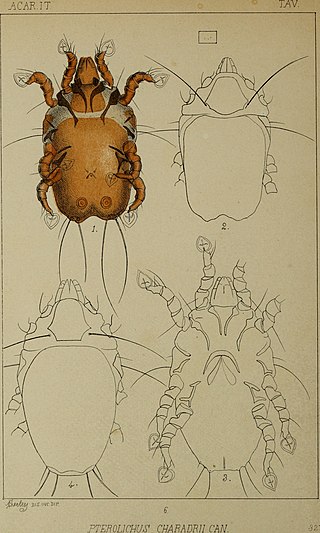
Avenzoariidae is a family of feather mites in the order Astigmata. There are at least 15 genera in Avenzoariidae. They are found on the feathers of aquatic birds, and in the case of one species, birds of prey.

Chaetodactylidae is a family of mites in the order Sarcoptiformes. There are five genera: Sennertia, Chaetodactylus, Achaetodactylus, Centriacarus, and Roubikia.

Halacaridae is a family of meiobenthic mites found in marine, brackish, and freshwater habitats around the world. It includes more than 1100 described species belonging to 64 genera It is the largest marine radiation of arachnids.

Glyphanoetus is a genus of astigs in the family Histiostomatidae.

The Indochinese blue flycatcher is a species of bird in the family Muscicapidae. It is found from southern Myanmar and the Malay Peninsula to Indochina and northeastern Sumatra. It was previously considered conspecific with Tickell's blue flycatcher.